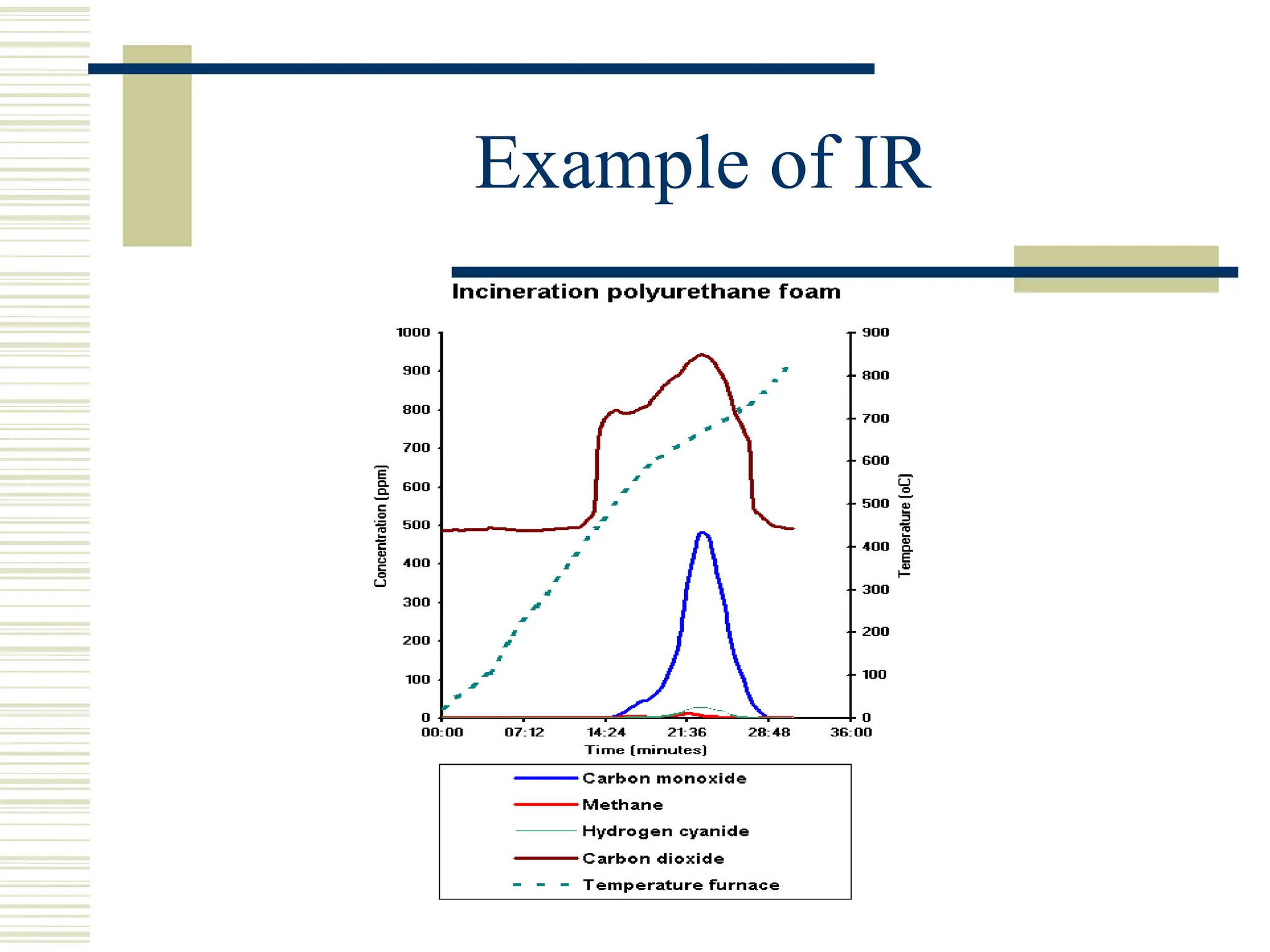
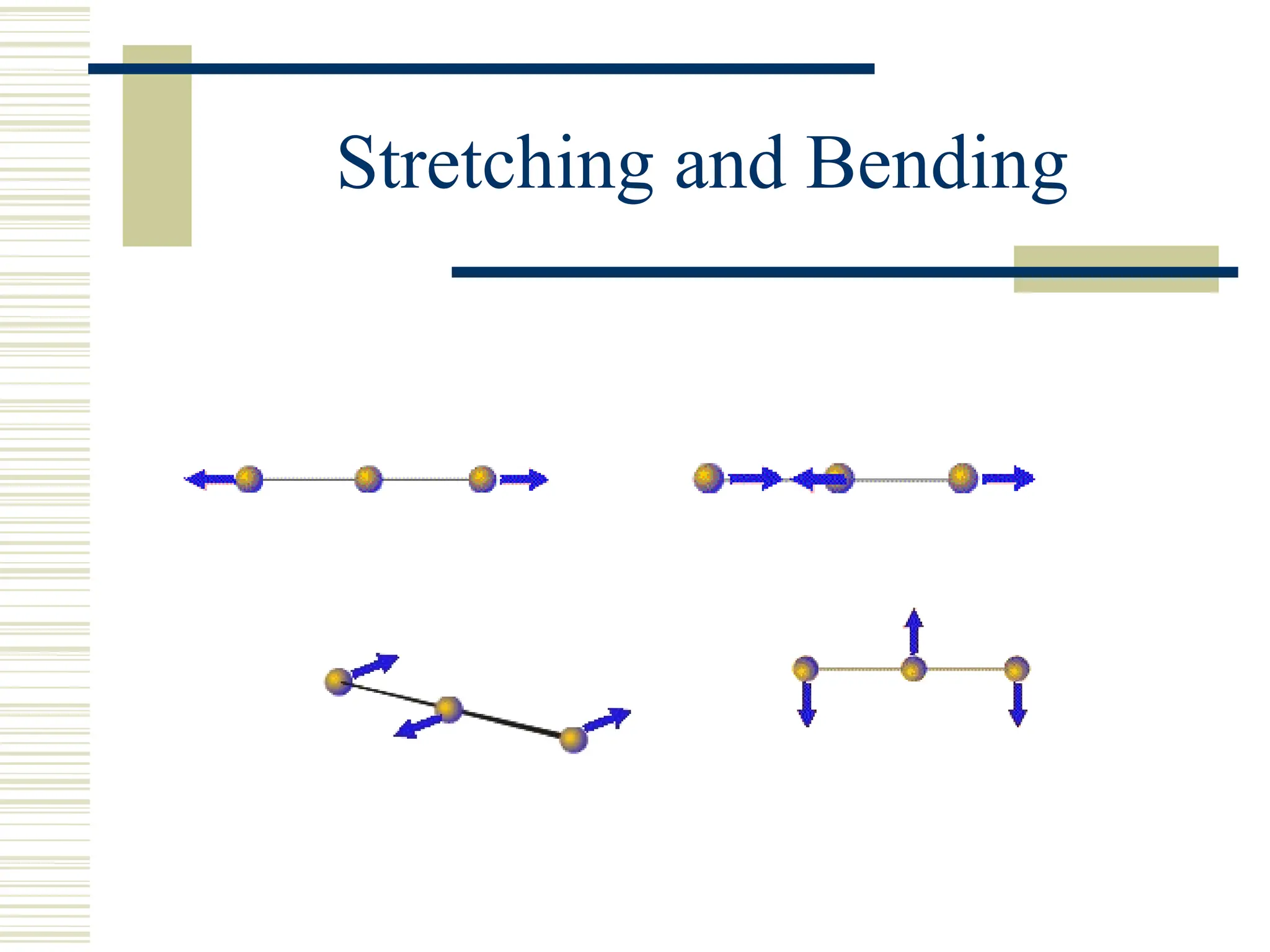
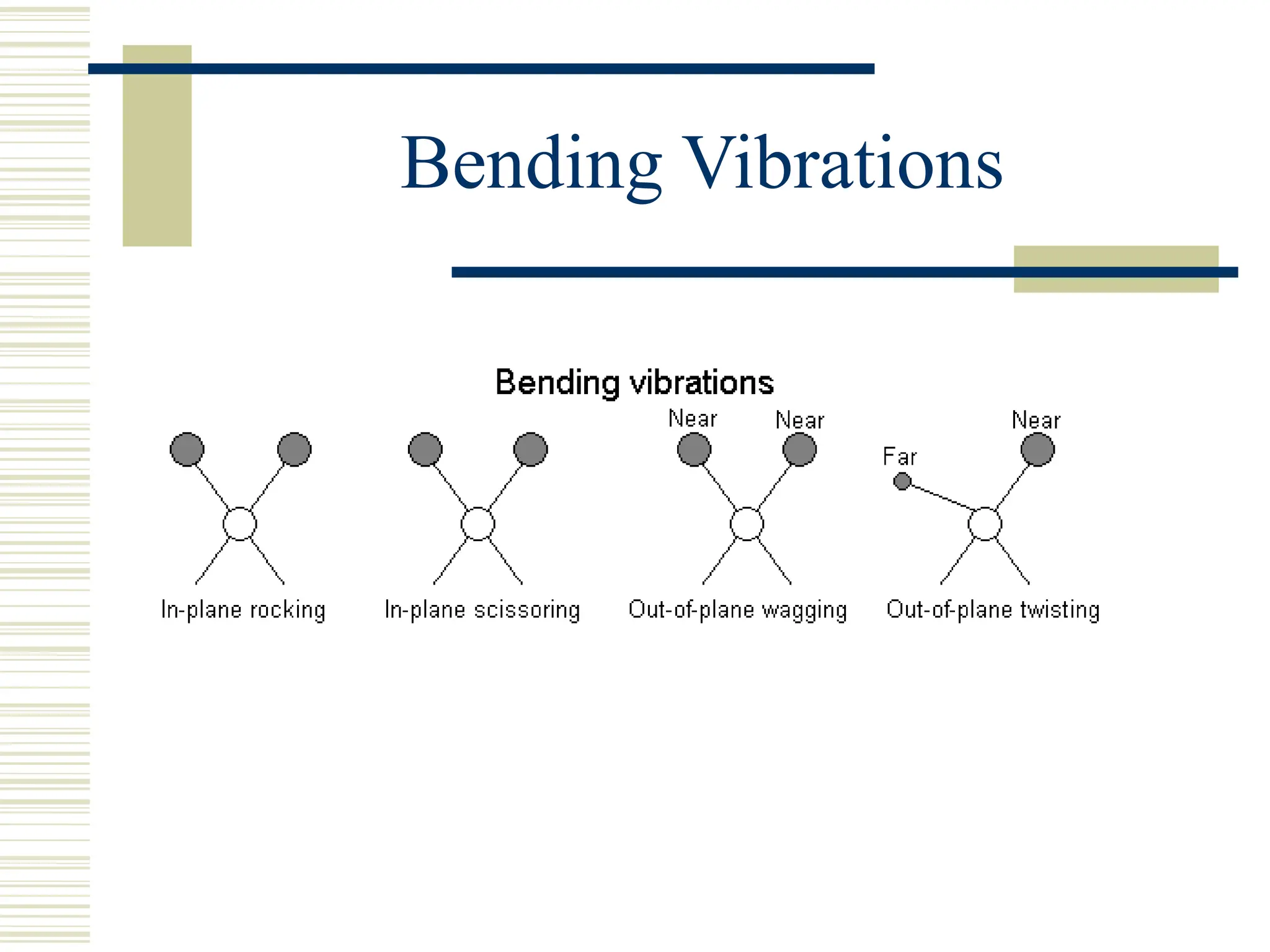
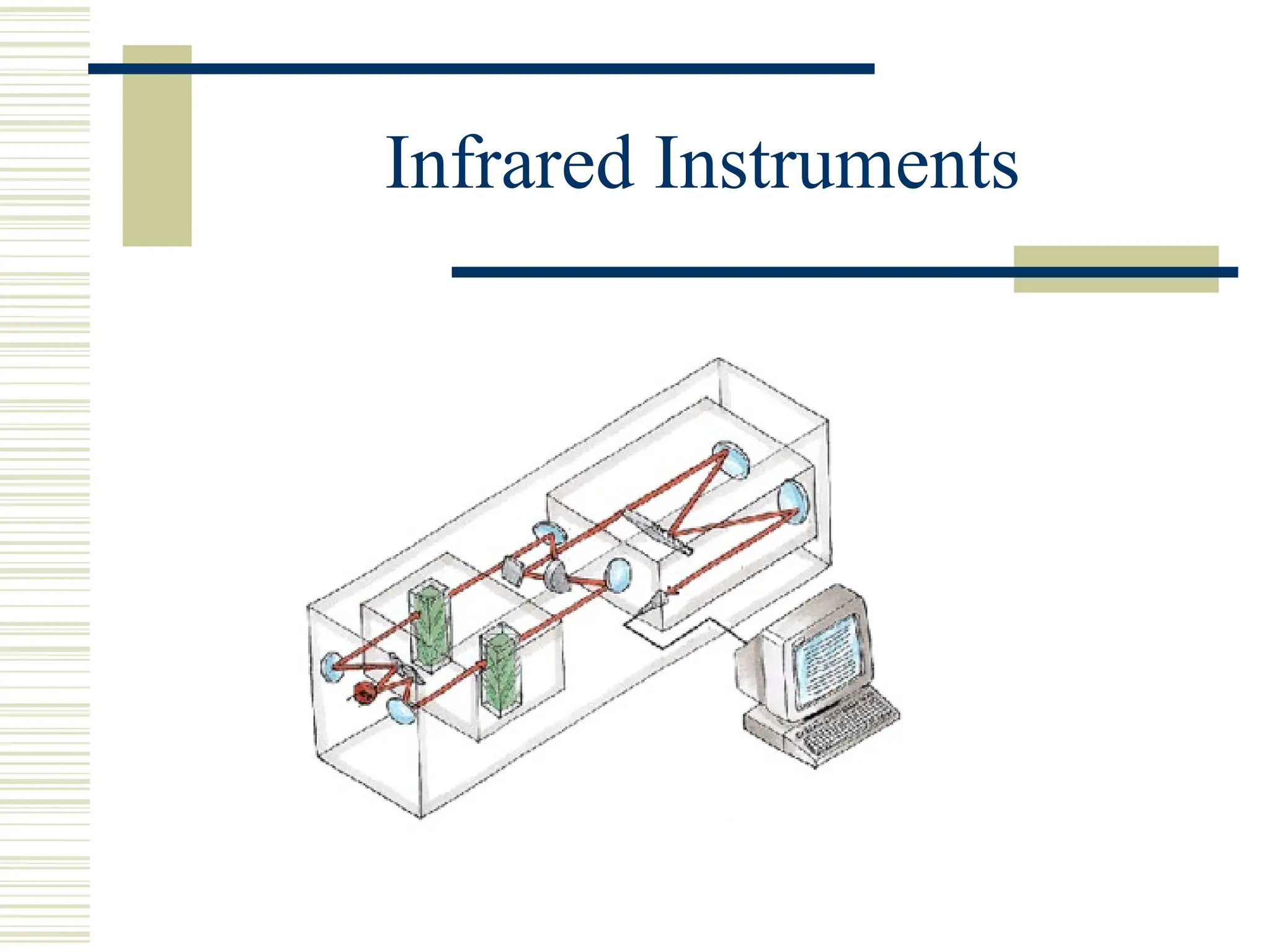
Infrared spectroscopy is the measurement of mid-infrared light absorption by samples, allowing for the identification of organic and organometallic molecules through characteristic absorption bands. Infrared instruments generate spectra that reveal structural data, with applications in chemical analysis, forensic science, and pharmaceutical quality testing. Advantages include low cost and speed, while disadvantages involve sample preparation challenges and limitations in detail compared to other methods.