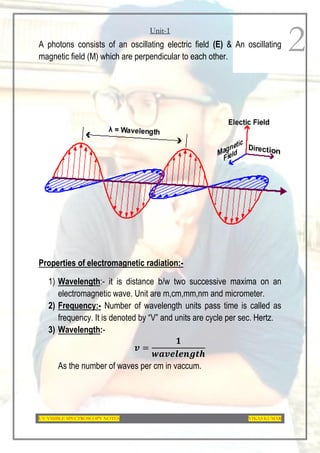
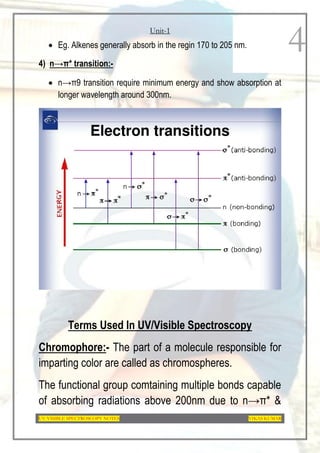
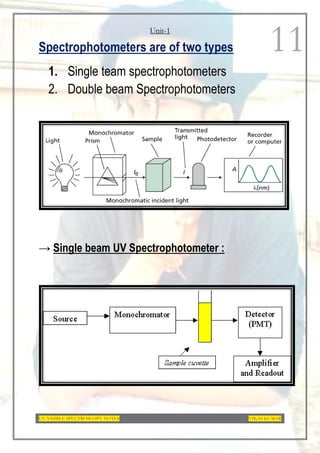
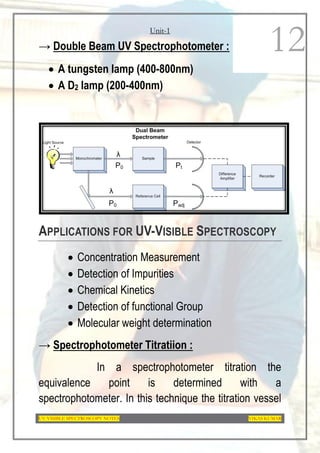
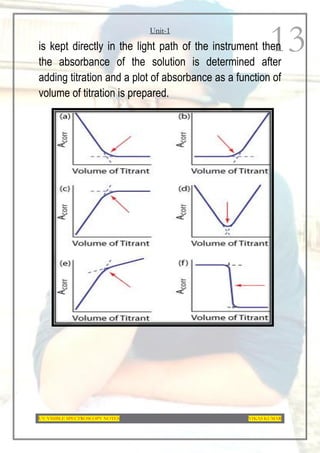
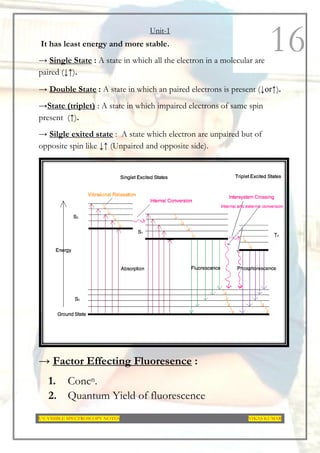
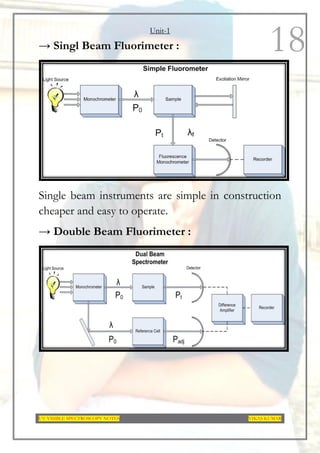
This document provides an overview of UV-Visible spectroscopy. It discusses the basic principles of spectroscopy and absorption spectroscopy. It describes electronic transitions that can occur when electromagnetic radiation interacts with molecules, including σ→σ*, n→σ*, π→π*, and n→π* transitions. Beer's law and Lambert's law are also explained. The key components of a UV-Visible spectrophotometer are outlined. Applications including concentration measurements, detection of impurities and functional groups, and kinetic studies are mentioned. Fluorescence spectroscopy is also briefly discussed.