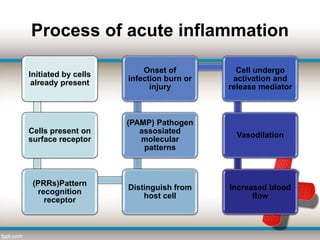
This document provides an overview of inflammation. It defines inflammation and describes the cellular response and mediators involved in acute inflammation. Acute inflammation aims to remove injurious agents, repair tissue damage, and prepare the body for healing. Without inflammation, infections could not be fought off and wounds would never heal. The document outlines the signs of acute (redness, heat, swelling, pain, loss of function) and differences between acute and chronic inflammation. It discusses the cellular events and outcomes of acute inflammation, as well as special types. Chronic inflammation is characterized by mononuclear cell infiltration and tissue destruction or repair over a long period of time.