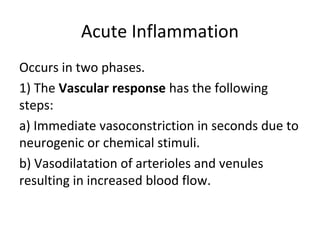
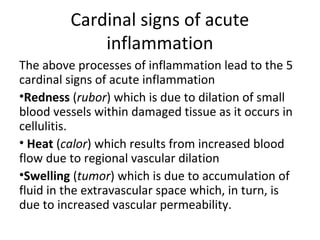
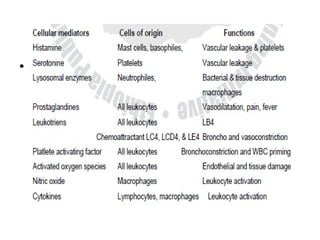
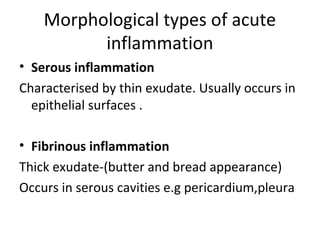
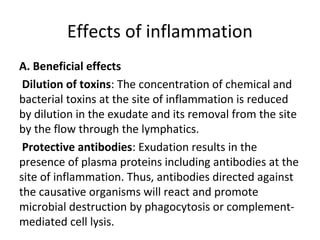
Inflammation is the body's response to injury or infection that helps eliminate the injurious agent and initiate healing. It is classified as either acute or chronic. Acute inflammation occurs rapidly, lasting minutes to days, characterized by increased blood flow, vascular permeability, and white blood cell migration. The cardinal signs are redness, heat, swelling, pain, and loss of function. Chemical mediators released from plasma and cells initiate and sustain acute inflammation and its effects. Outcomes include resolution, fibrosis, abscess, or progression to chronic inflammation.