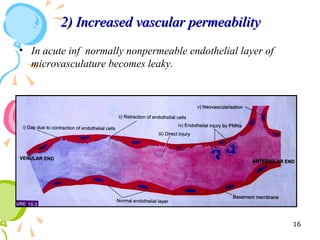
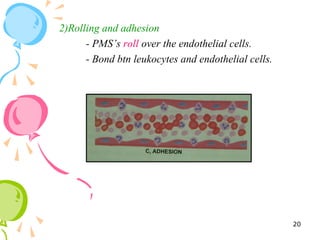
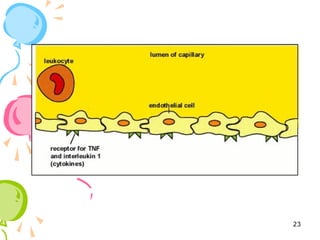
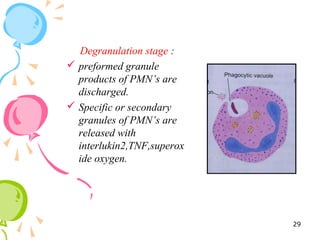
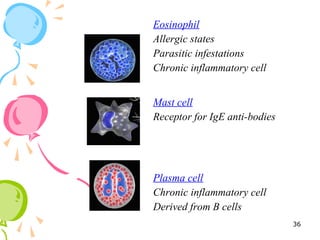
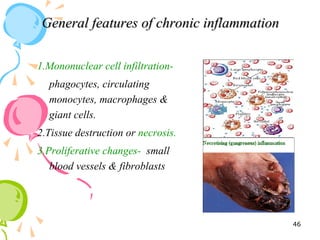
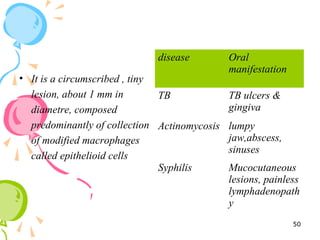
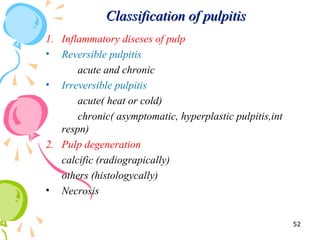
This document defines inflammation and discusses the various types. Inflammation is the body's response to injury or infection and involves increased blood flow, immune cell infiltration, and release of chemical mediators. There are two main types - acute inflammation, which lasts minutes to days and resolves on its own, involving redness, swelling, heat and pain. Chronic inflammation persists longer and involves tissue destruction alongside inflammation. Specific types of chronic inflammation include granulomatous inflammation, which features collections of immune cells called granulomas. The document also discusses inflammation of different oral tissues like the pulp, periodontium and gingiva.