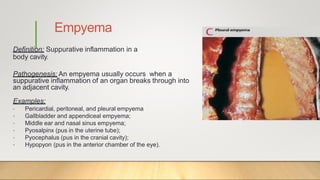
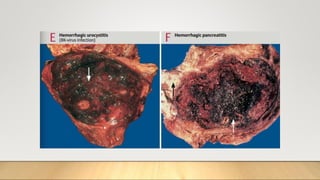
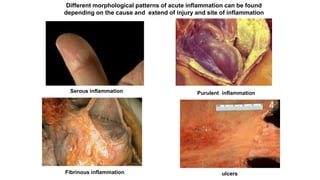
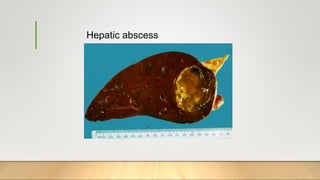
1. The document defines and classifies inflammation as either acute or chronic based on duration and predominant cell types.
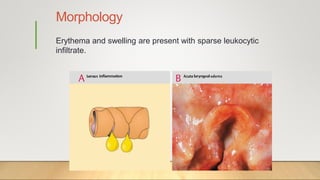
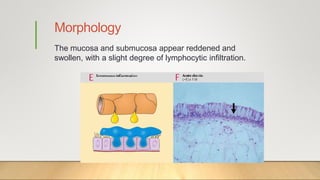
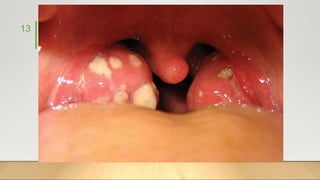
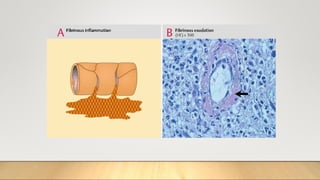
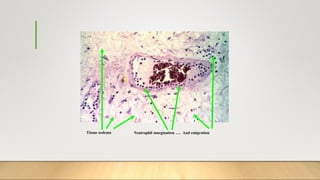
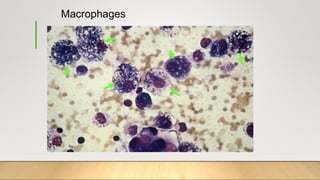
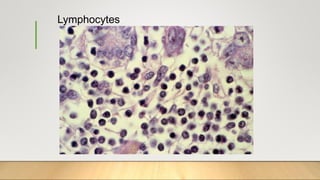
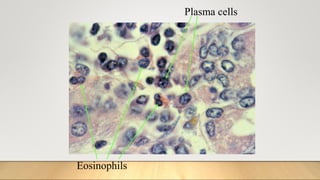
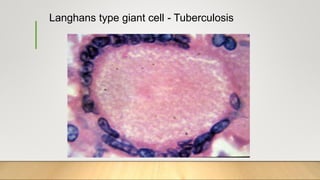
2. Acute inflammation is short-term, involving increased vascular permeability and neutrophil infiltration, while chronic inflammation lasts weeks to years with lymphocytes and macrophages predominant.
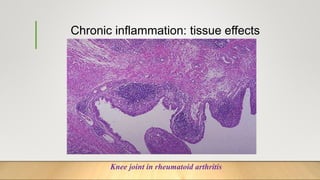
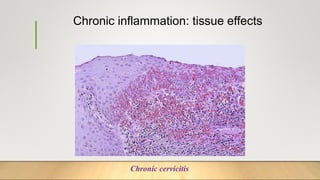
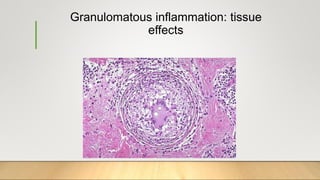
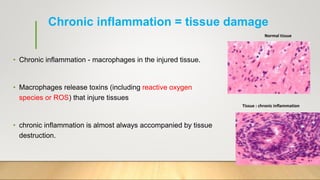
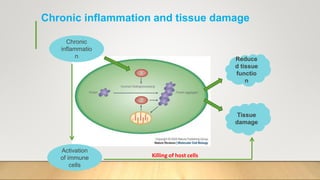
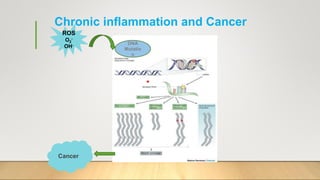
3. Chronic inflammation can lead to tissue damage through macrophage release of reactive oxygen species and is associated with conditions like cancer, fibrosis and impaired tissue function.