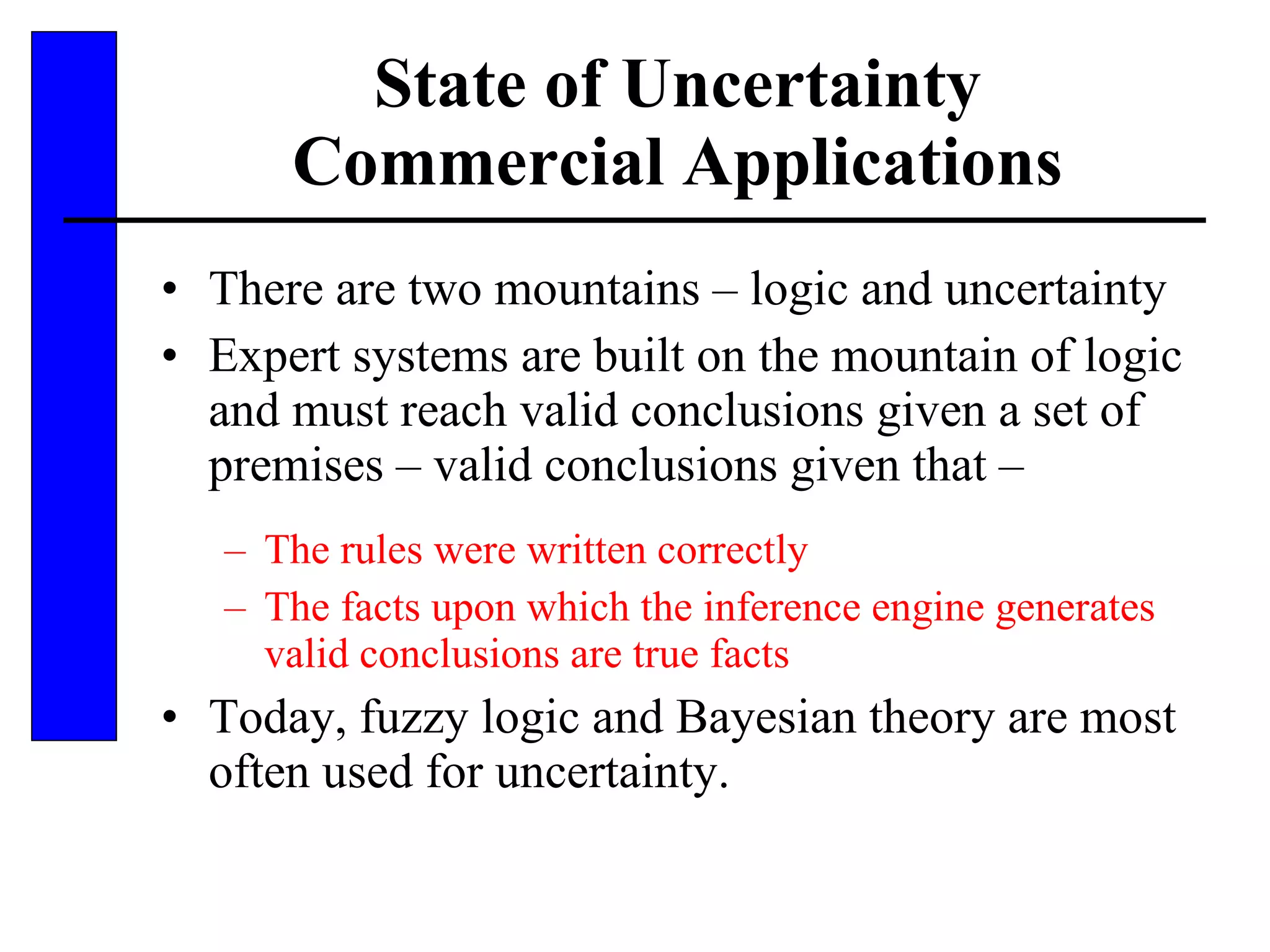
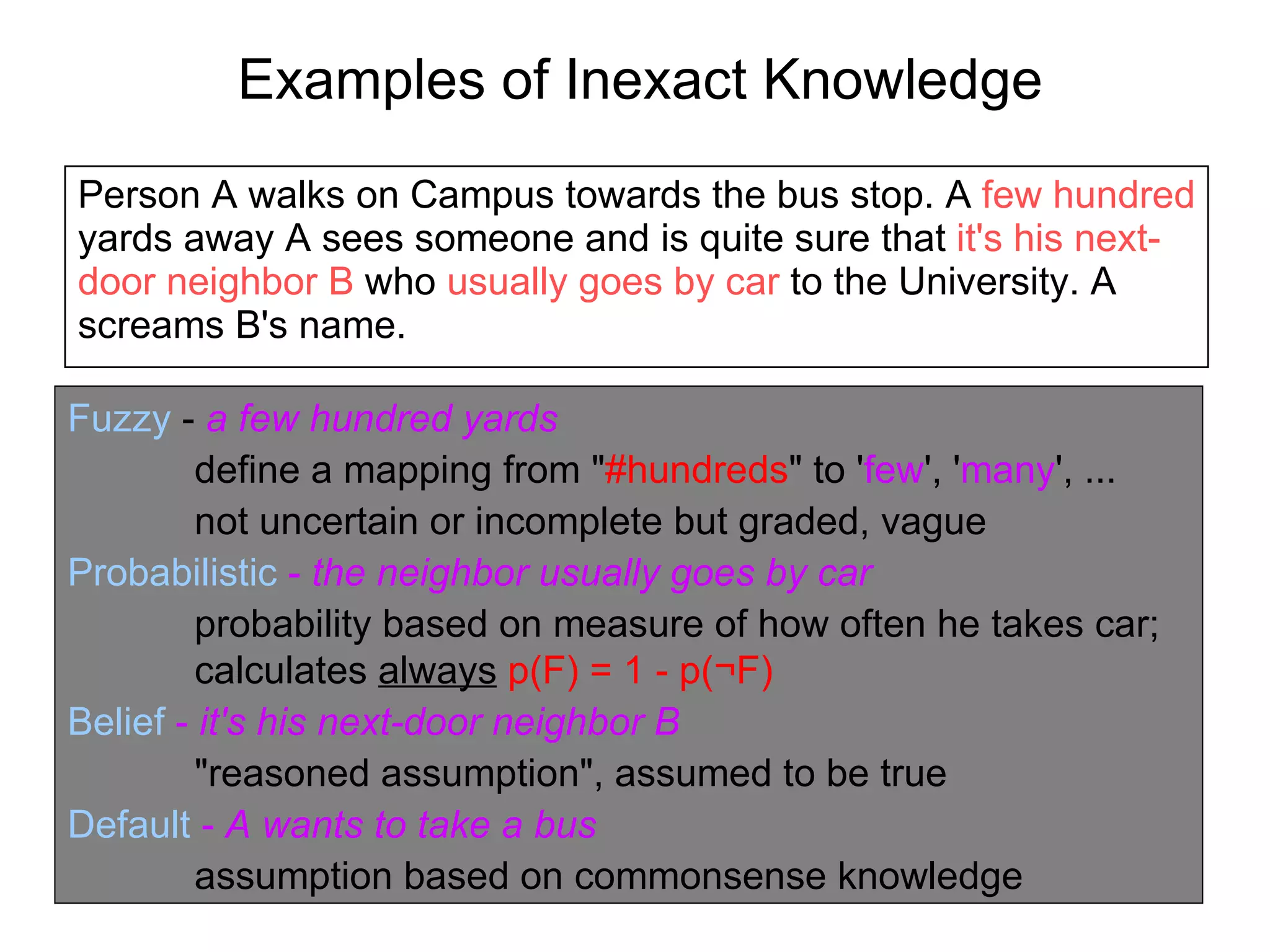
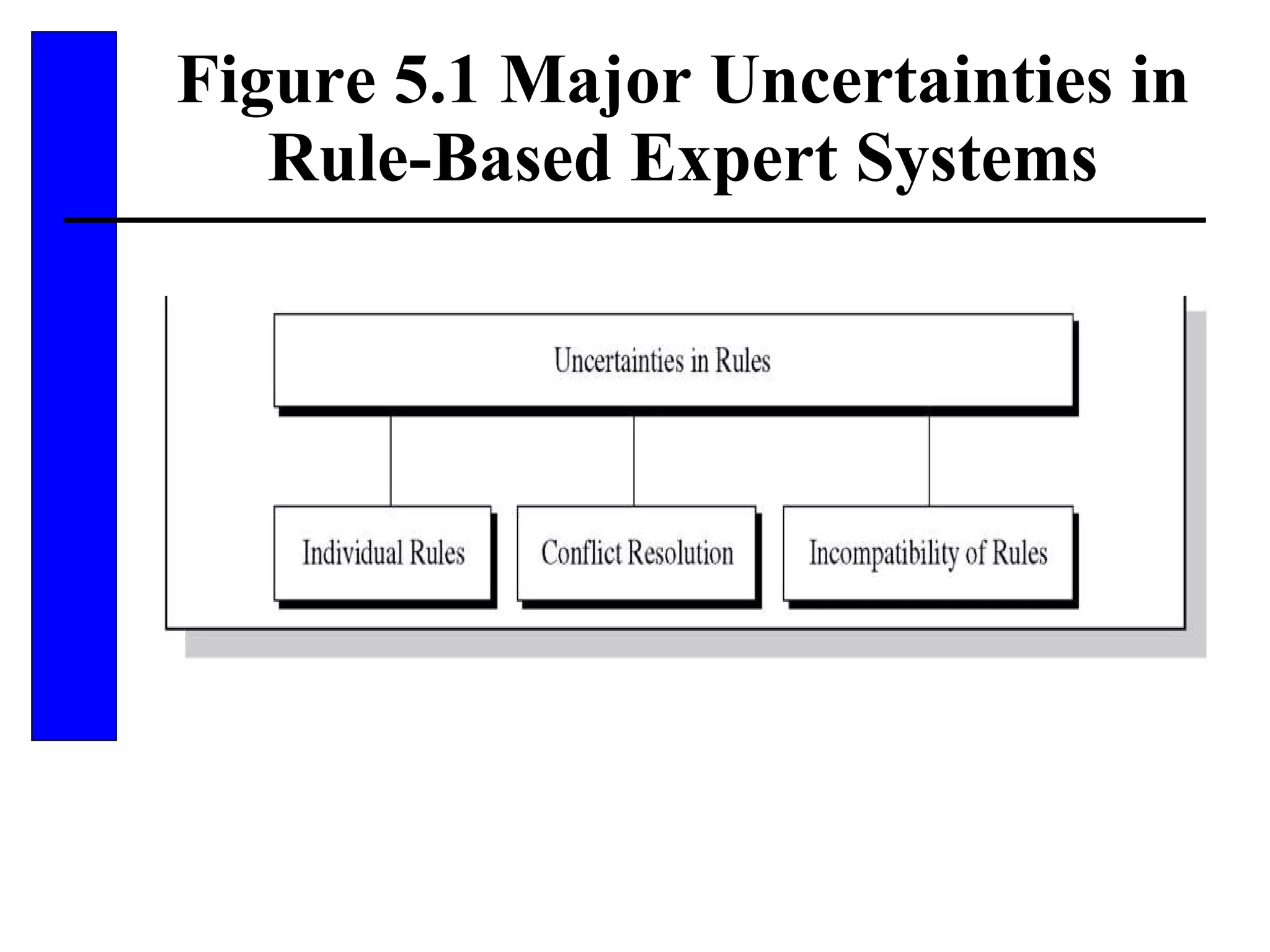
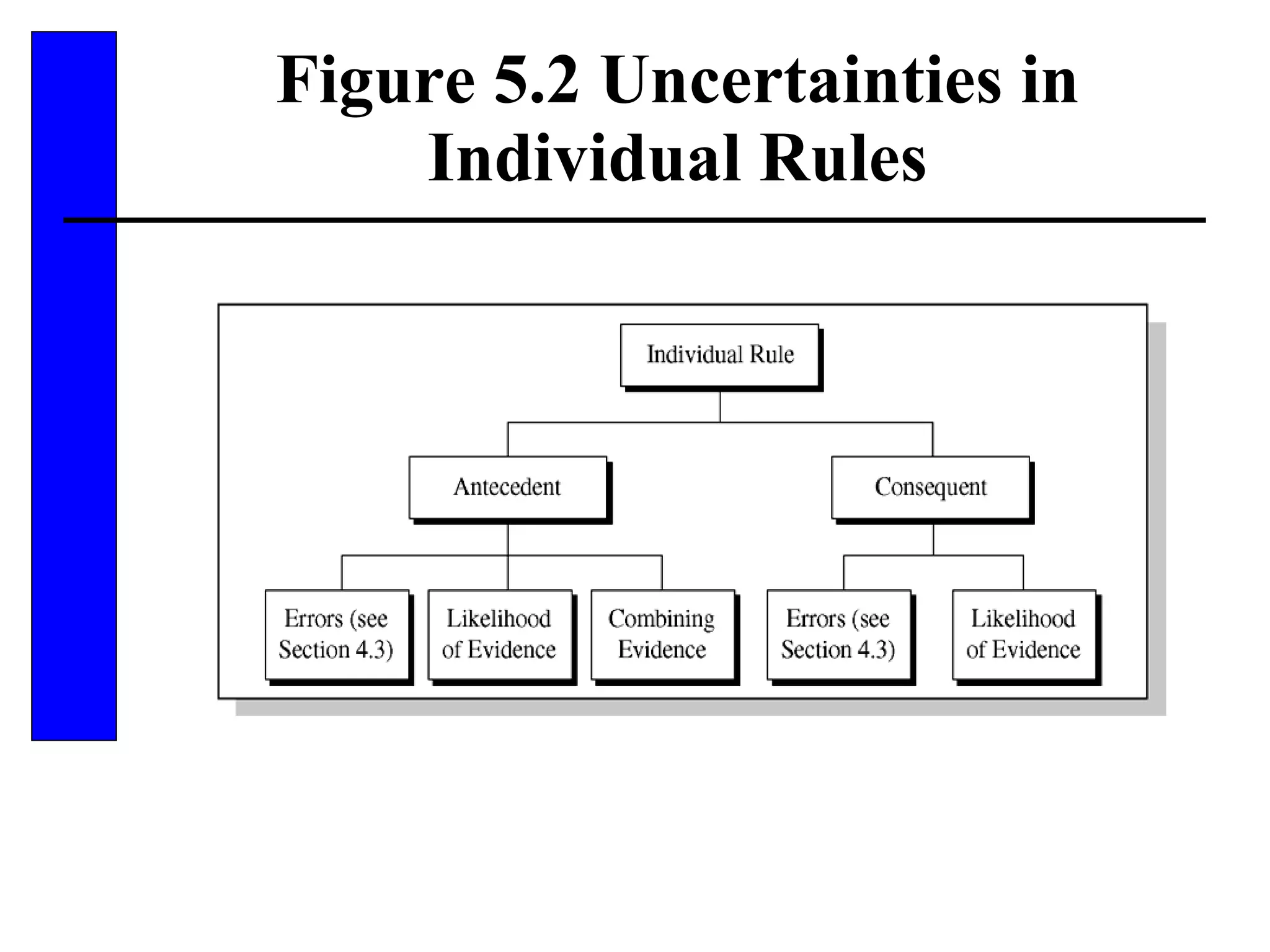
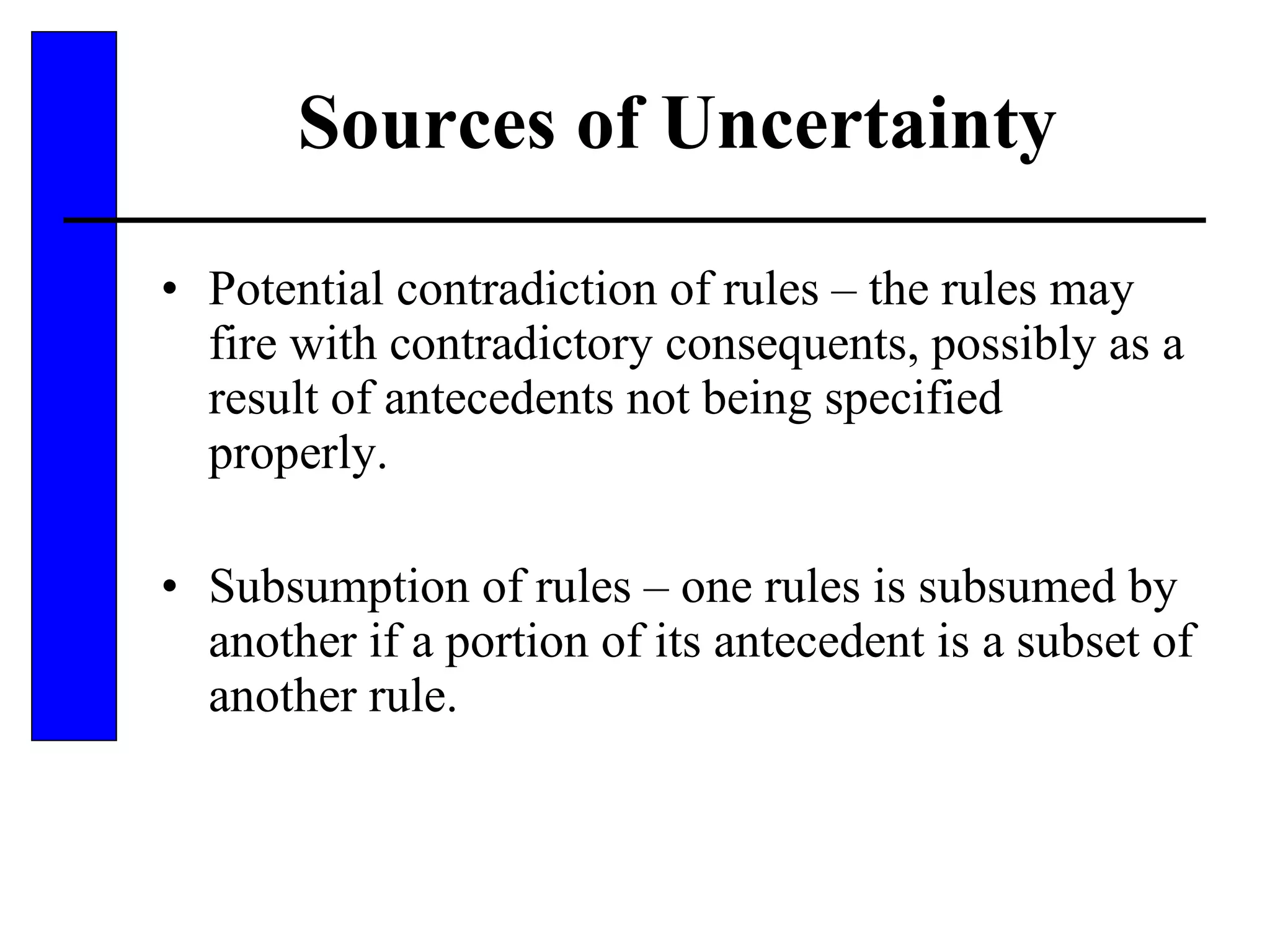
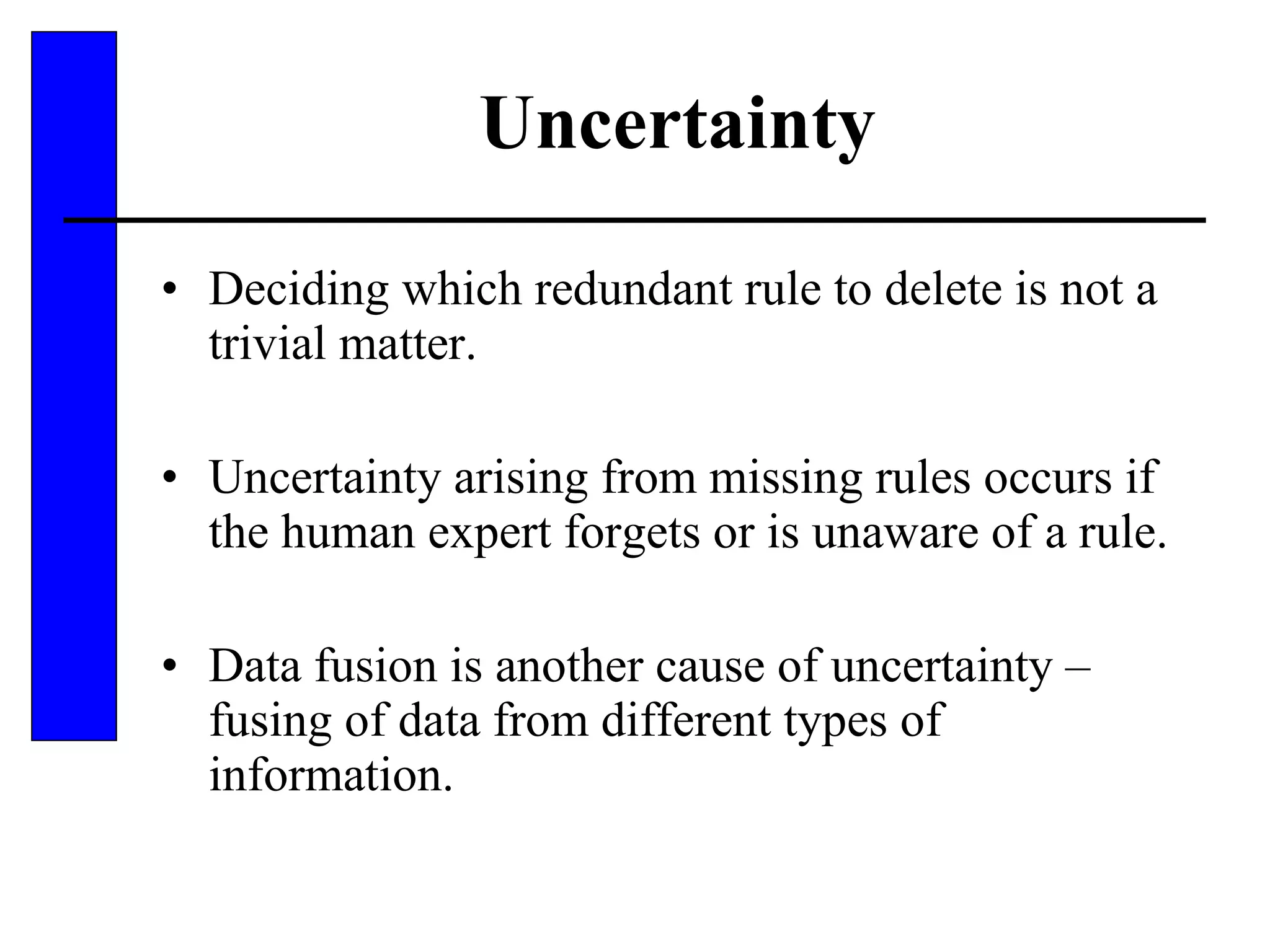
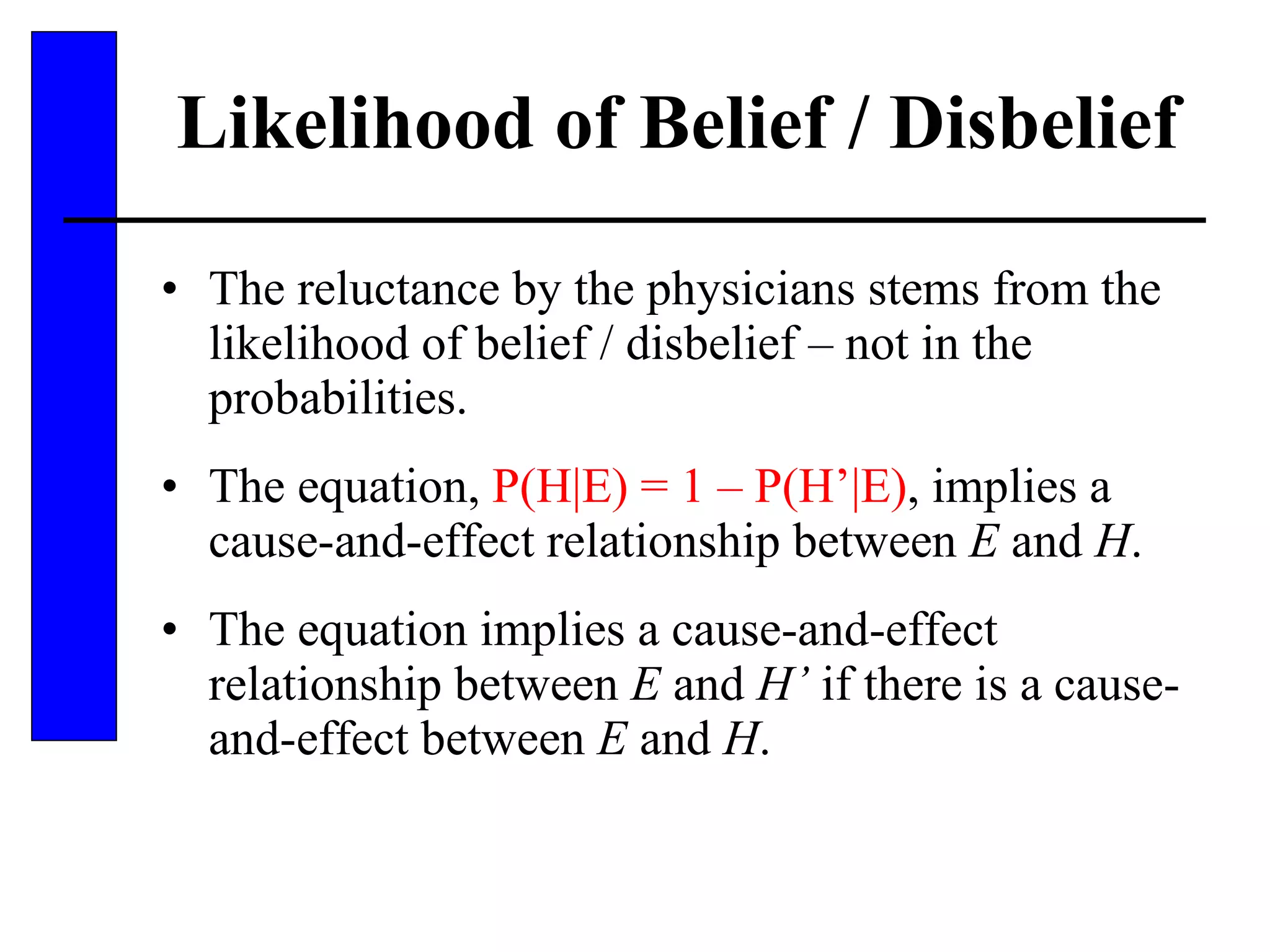
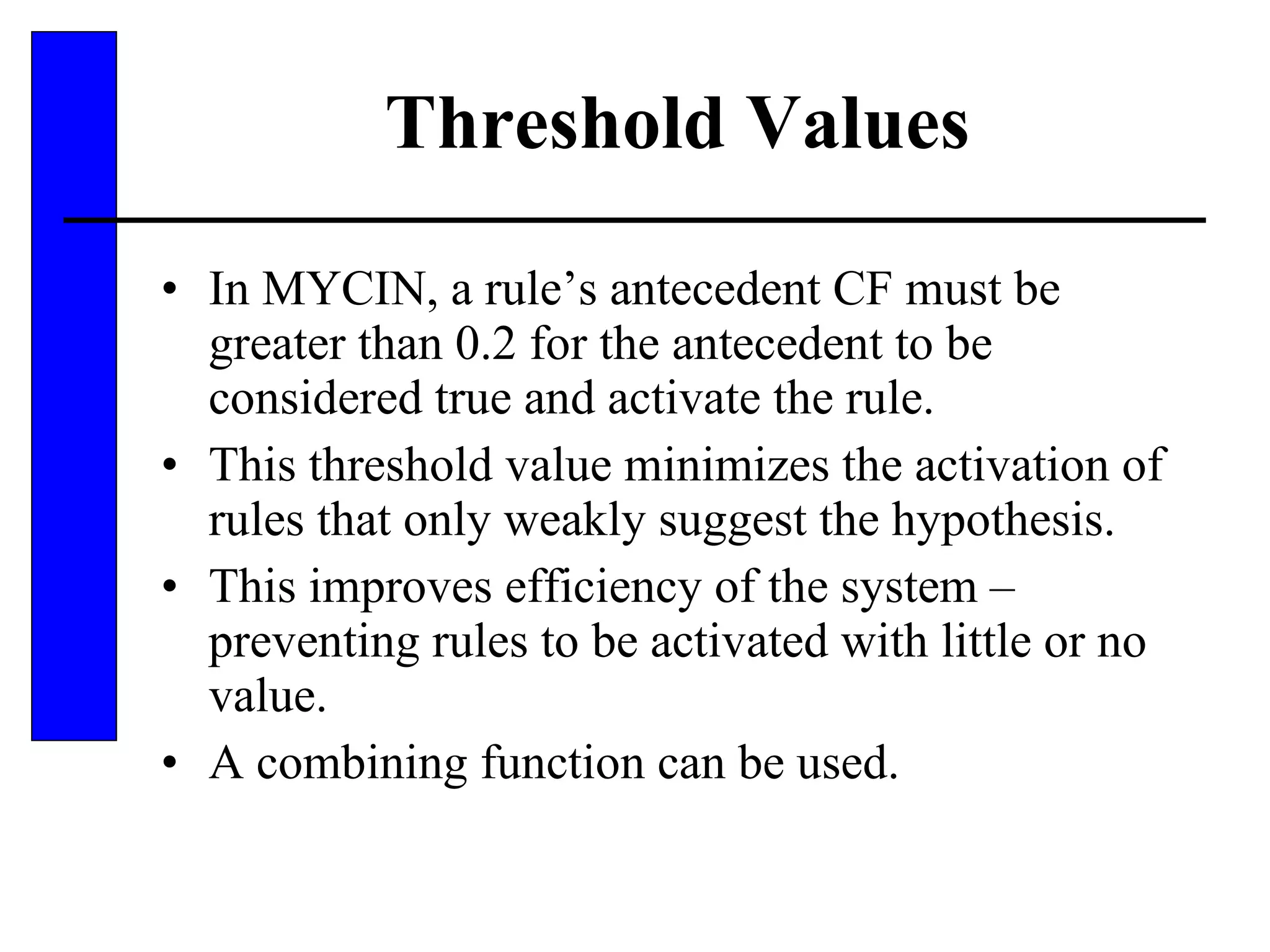
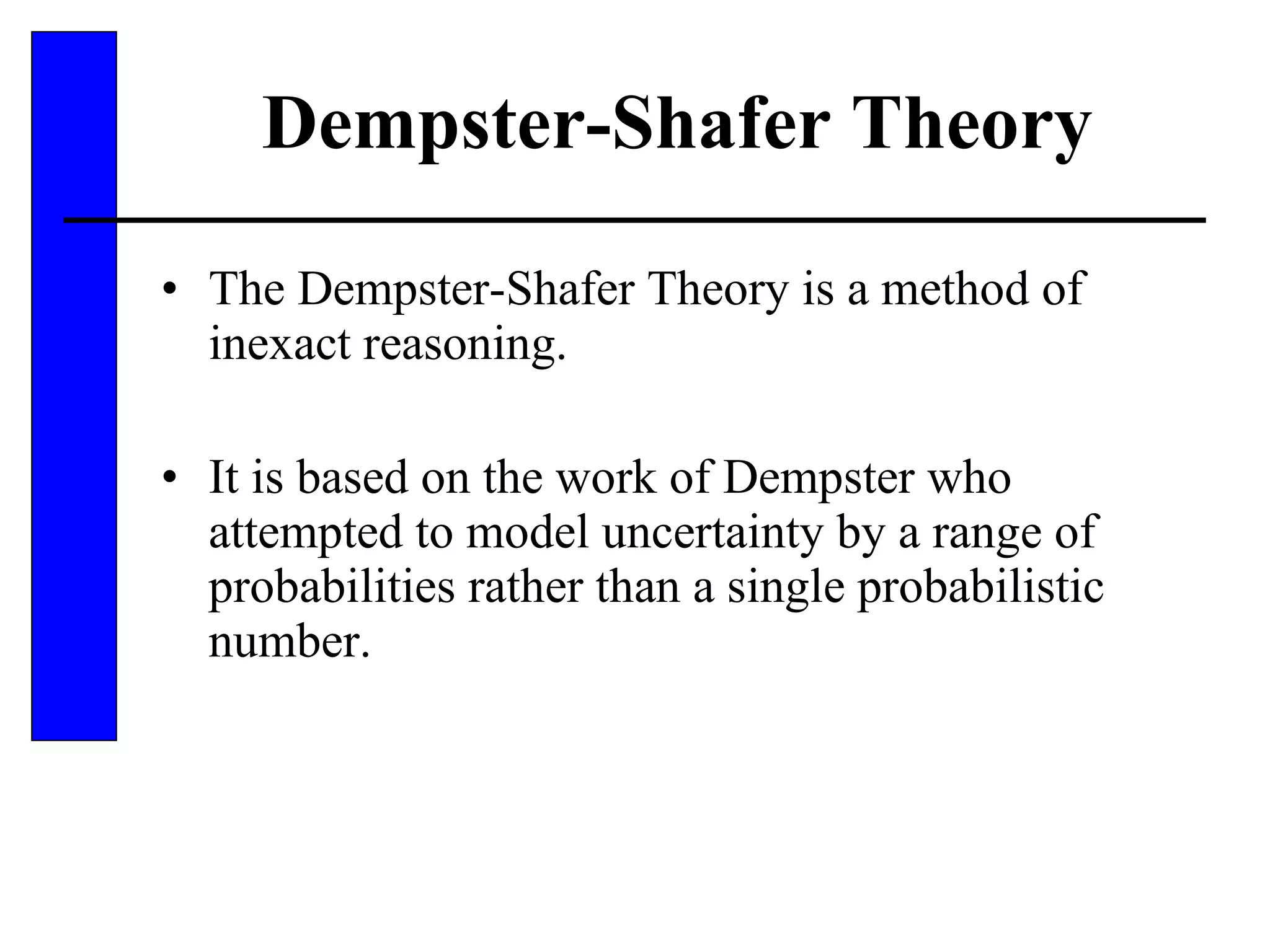
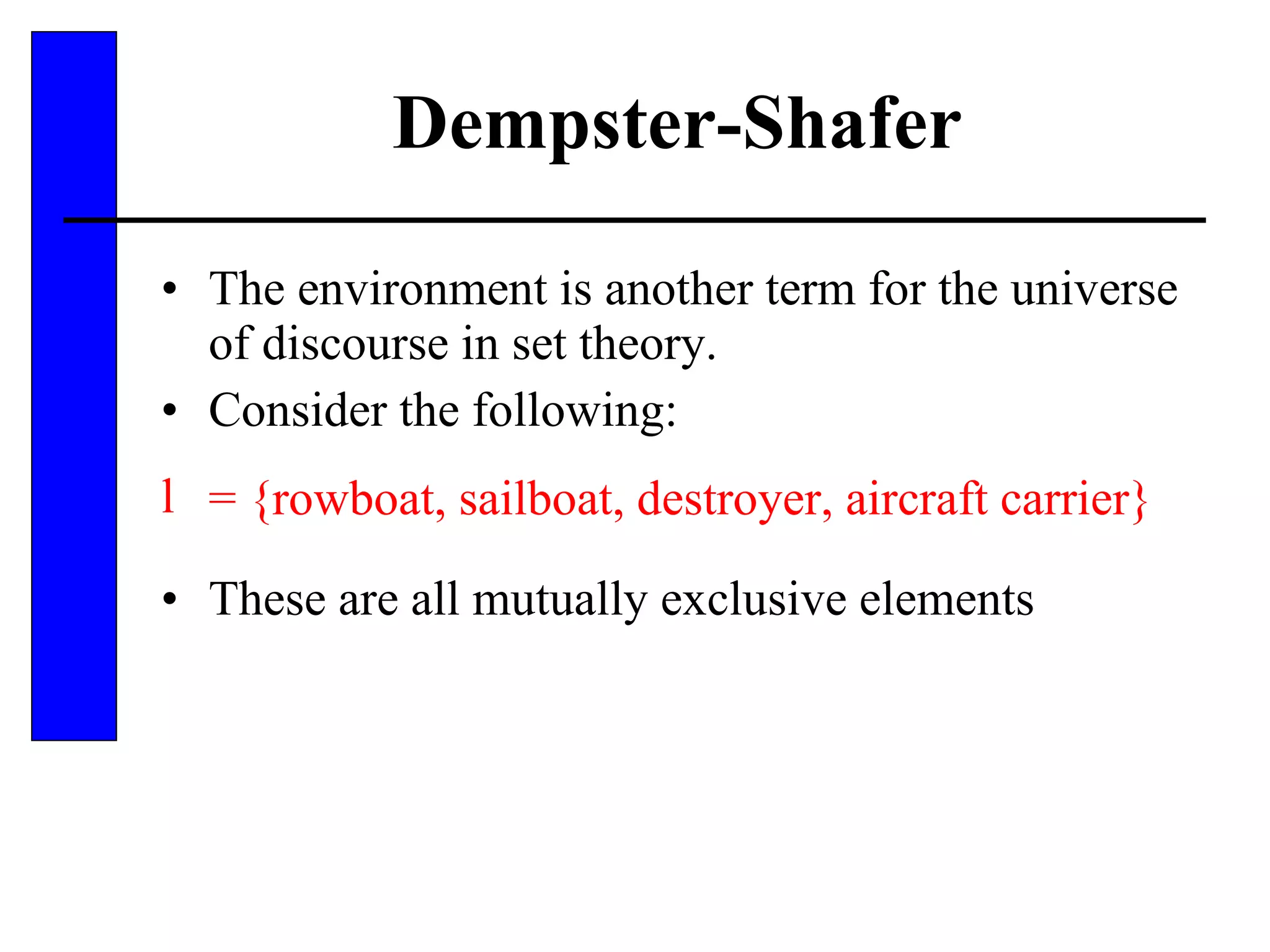
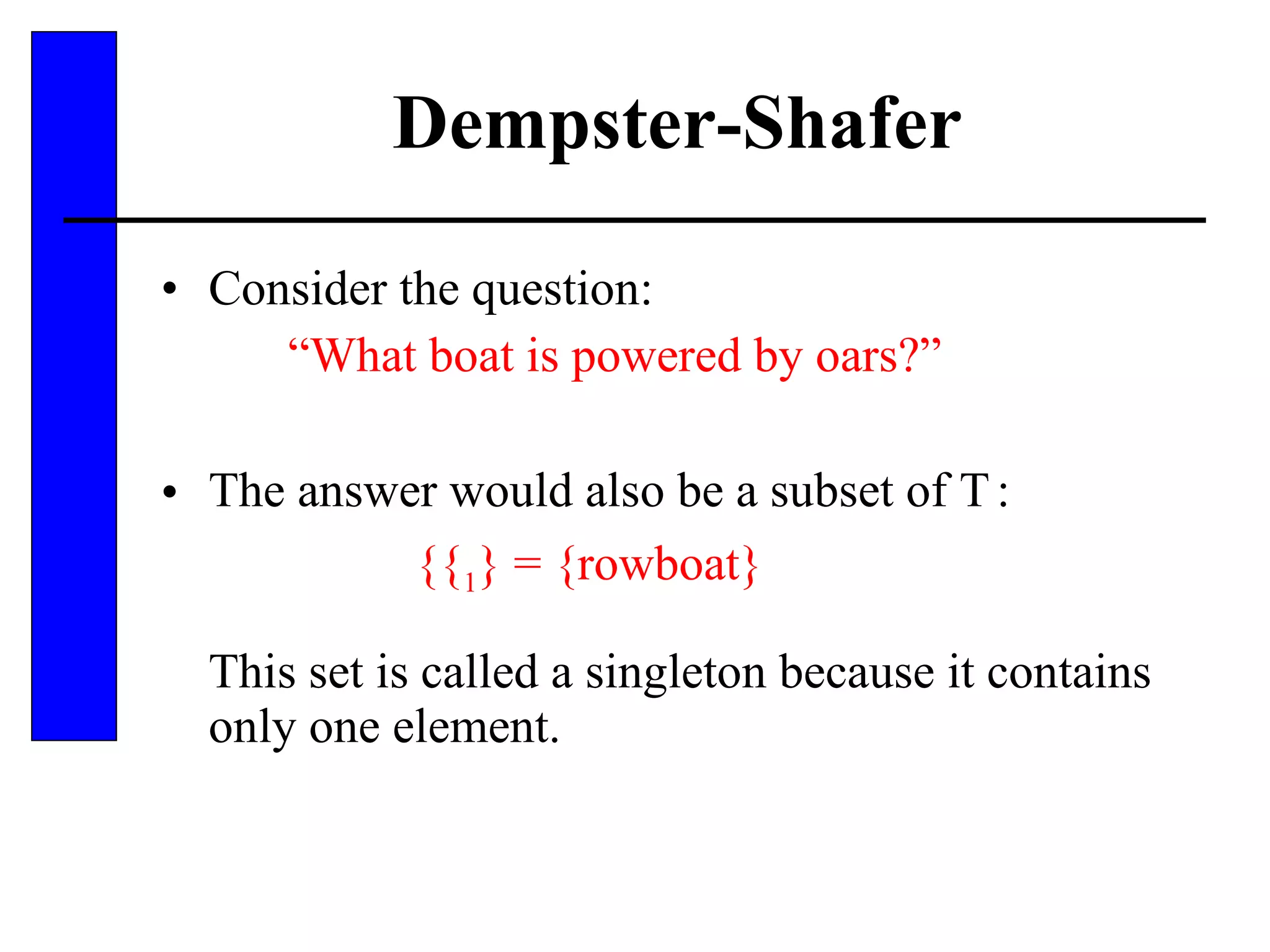
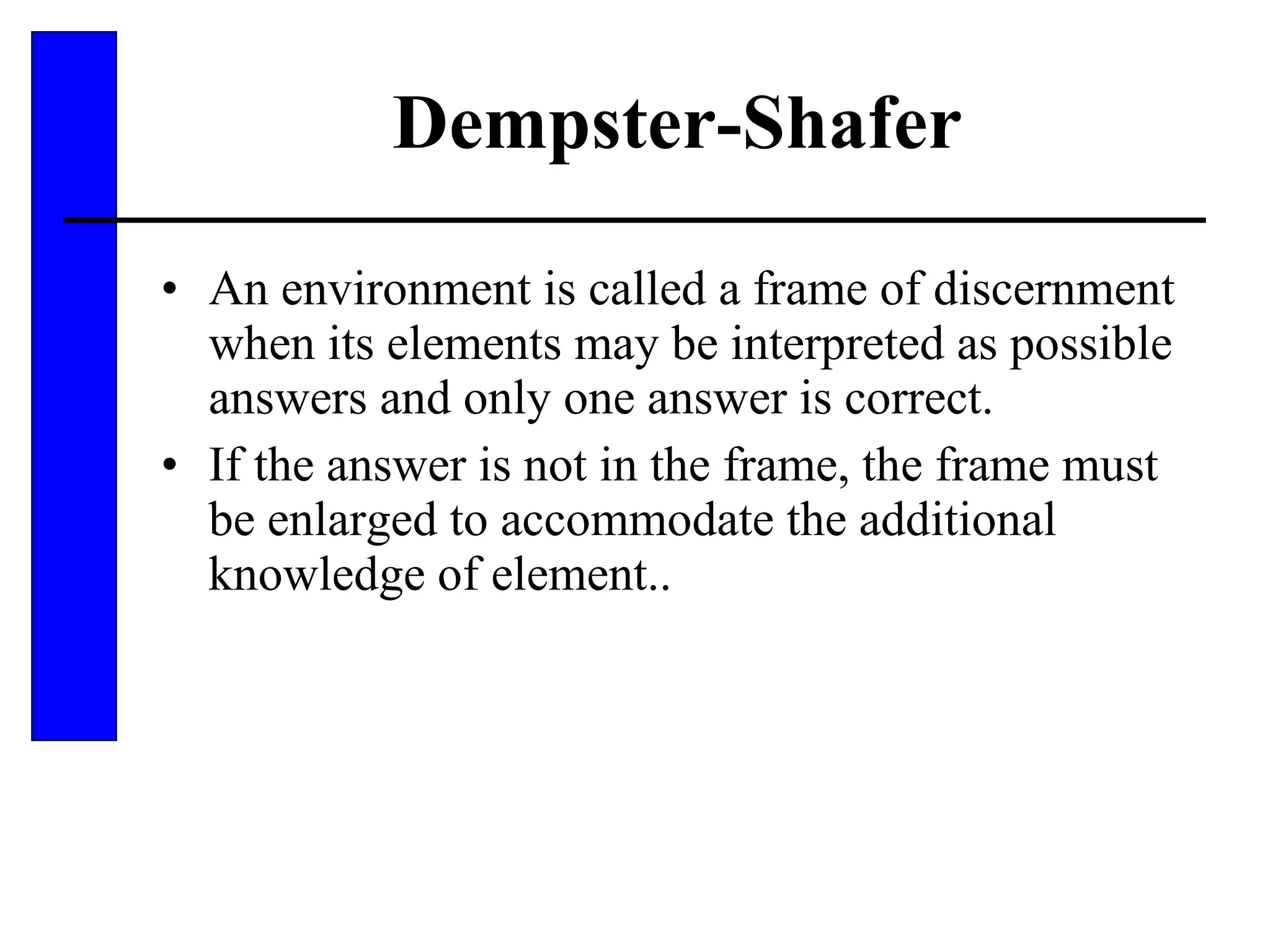
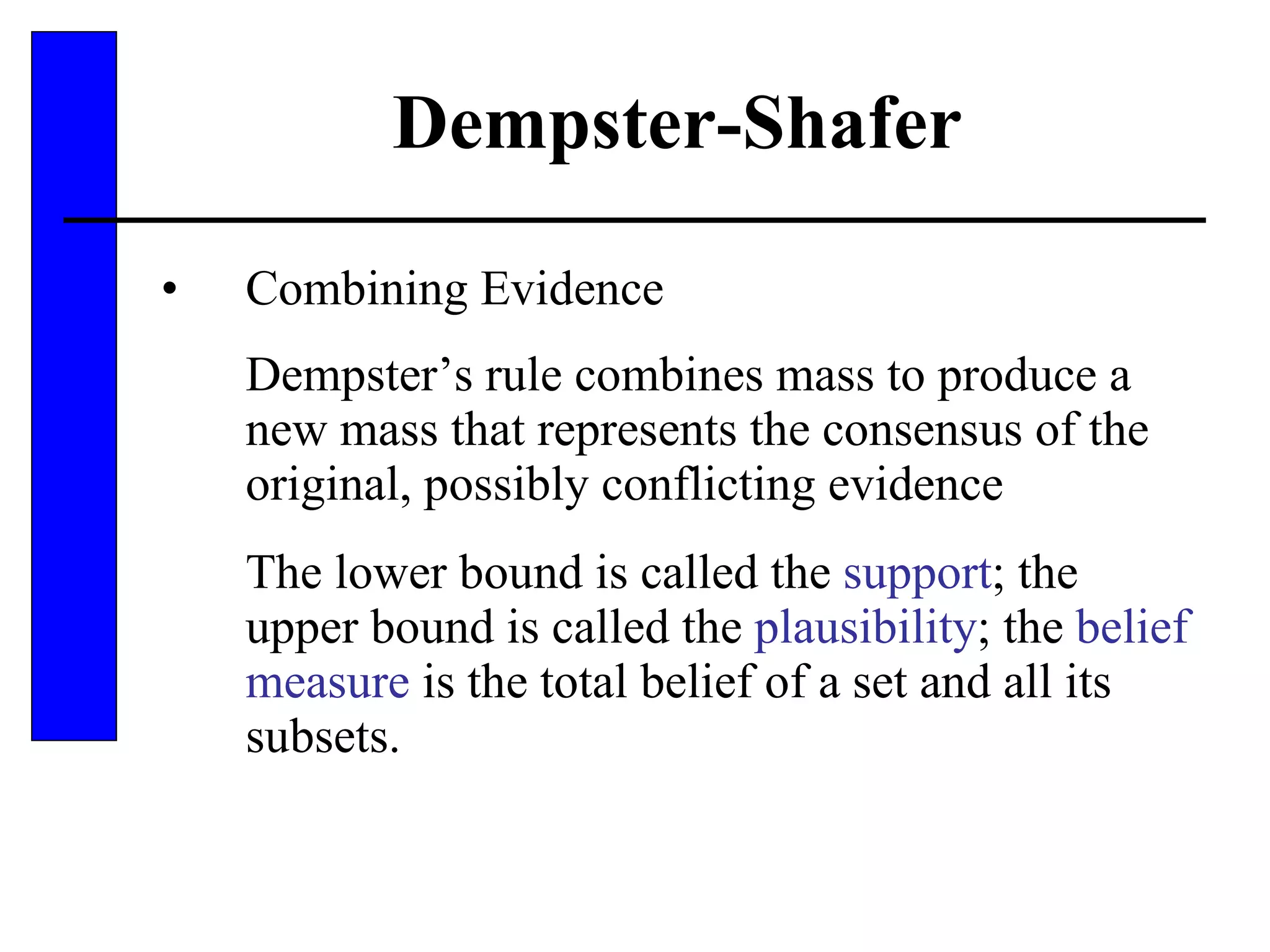
This document discusses various forms of inexact knowledge and reasoning, including uncertainty, incomplete knowledge, defaults and beliefs, contradictory knowledge, and vague knowledge. It provides examples of how probabilistic reasoning, fuzzy logic, truth maintenance systems, certainty factors, and other approaches can be used to represent and reason with inexact knowledge. Key concepts covered include uncertainty, incomplete knowledge, defaults, beliefs, contradictory knowledge, and vague knowledge.





















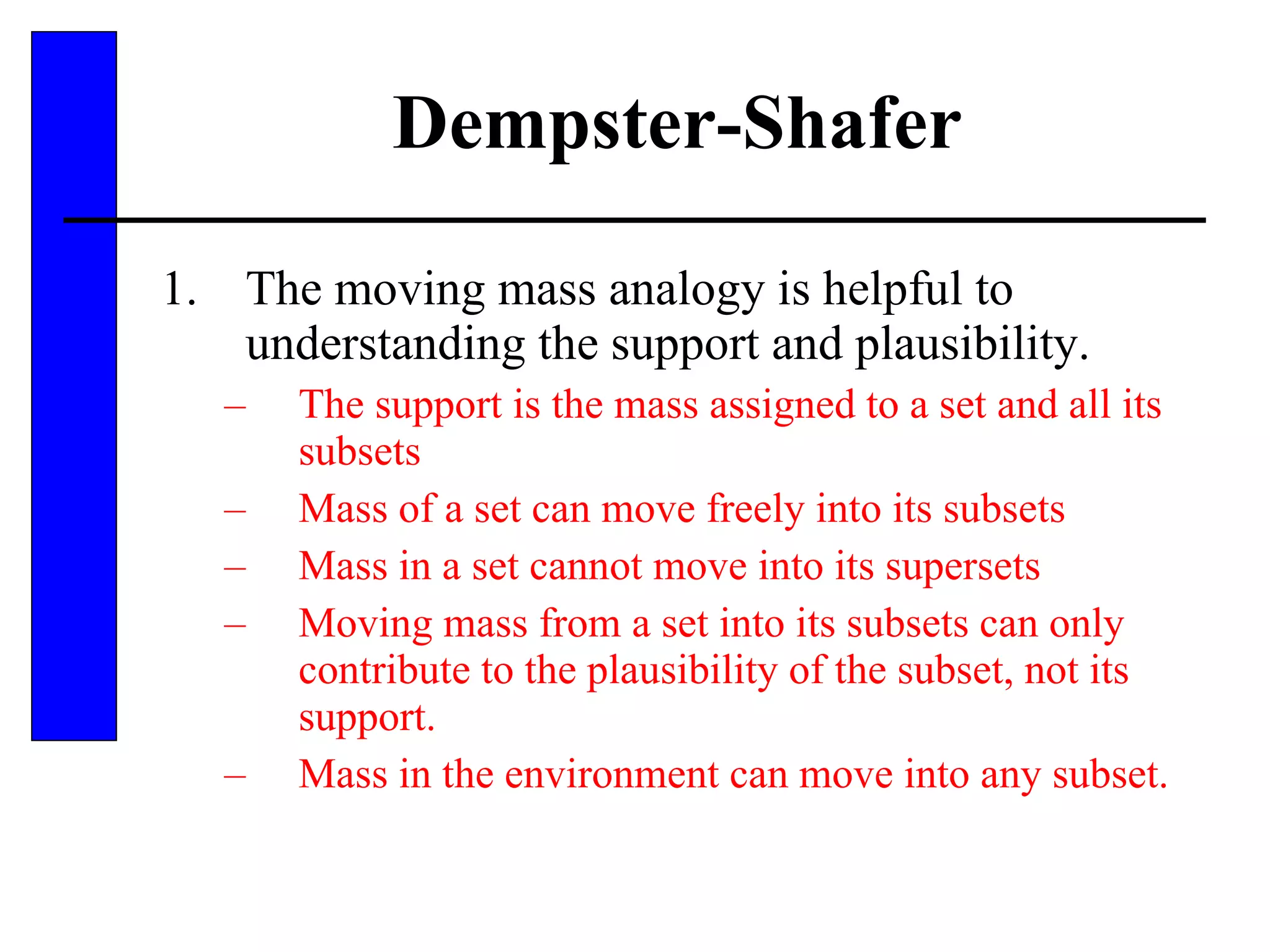
![Dempster-Shafer Dempster-Shafer does not force belief to be assigned to ignorance – any belief not assigned to a subset is considered no belief (or non-belief) and just associated with the environment. Every set in the power set of the environment which has mass > 0 is a focal element. Every mass can be thought of as a function: m: P ( ) [0, 1]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/inexactreasoning-111103003807-phpapp02/75/Inexact-reasoning-37-2048.jpg)



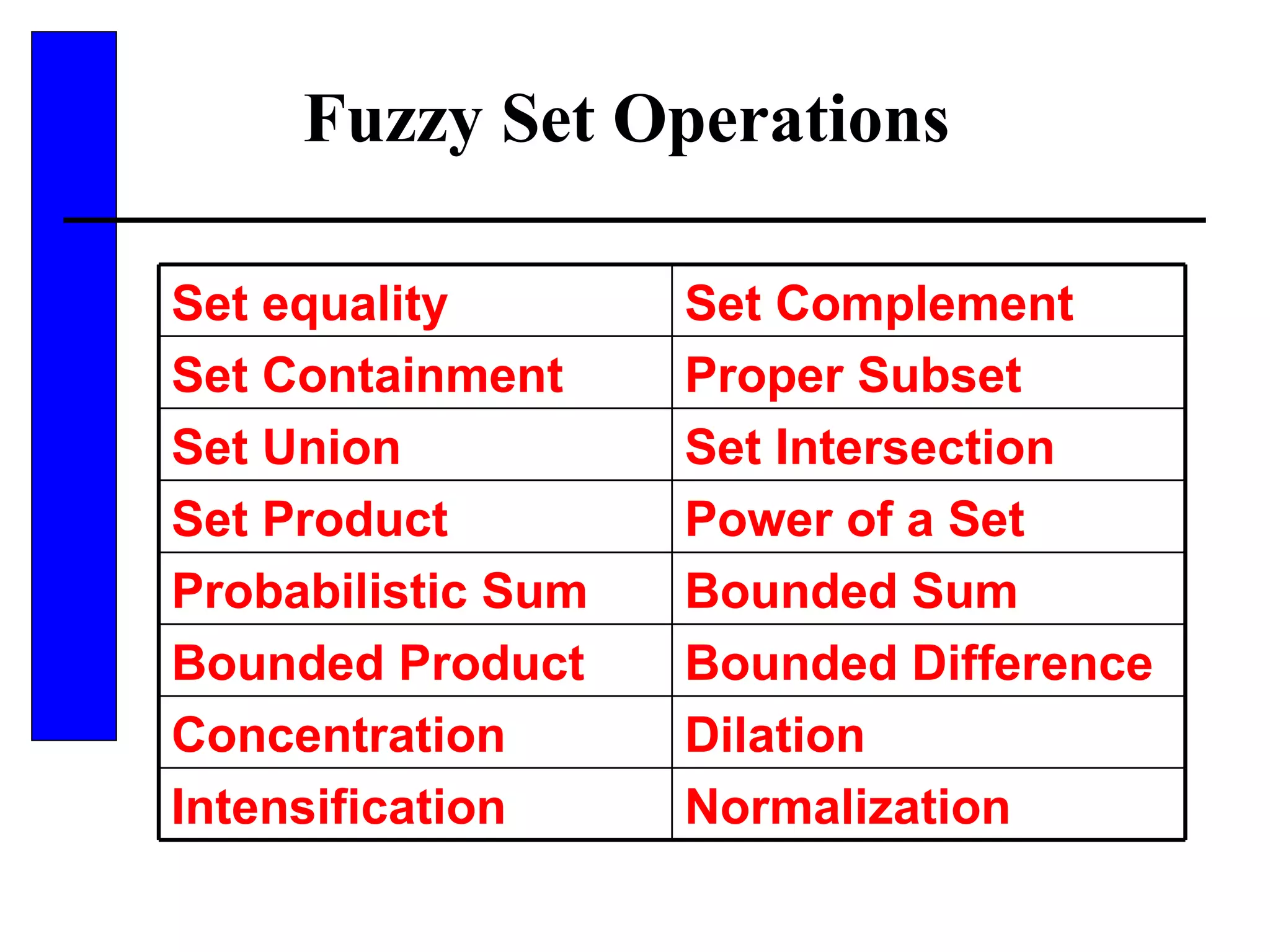
![Fuzzy Set Operations An ordinary crisp set is a special case of a fuzzy set with membership function [0, 1]. All definitions, proofs, and theorems of fuzzy sets must be compatible in the limit as the fuzziness goes to 0 and the fuzzy sets become crisp sets.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/inexactreasoning-111103003807-phpapp02/75/Inexact-reasoning-43-2048.jpg)