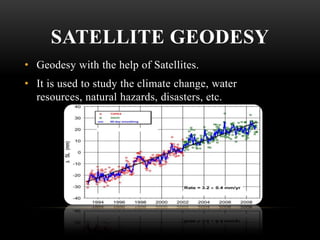
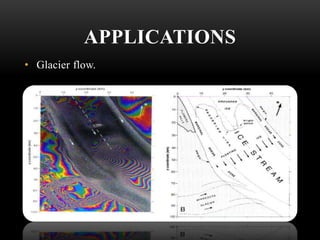
Geodesy is the science of measuring and representing the Earth, including its gravity field. It has applications in monitoring climate change, natural hazards, volcanoes, water resources, soil moisture, glaciers, and landslides using space-based technologies like GNSS, altimetry, and gravity missions. Some key technologies are GPS, GLONASS, altimetry missions like TOPEX and JASON-1, and gravity missions like GRACE and CHAMP. Geodesy has its origins in ancient Greece and has evolved into a modern discipline using satellites to study Earth systems and processes.



![DEFINITION OF GEODESY
• The classical definition:
Geodesy is the science of measuring, and portraying the
earth’s surface.
[Helmert, 1880].
• The modern definition:
Robert
Helmert
(1843 - 1917)
Geodesy is discipline that deals with the measurement and
representation of the earth, including it’s gravity field, in a
3D time varying space.
(International Association of Geodesy)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/geodesy-131204103430-phpapp02/85/Geodesy-4-320.jpg)