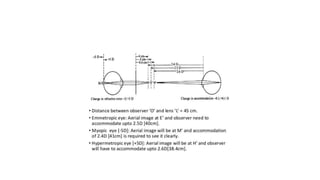
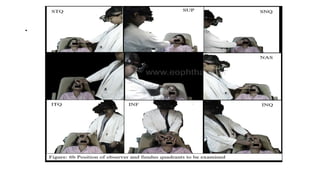
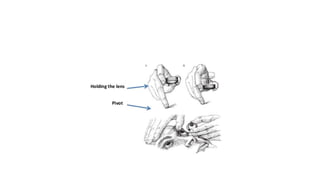
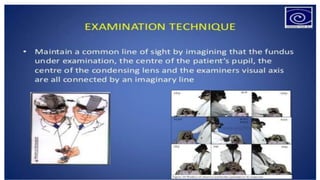
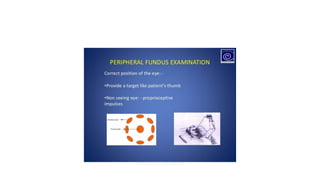
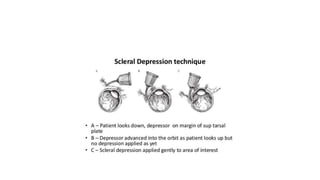
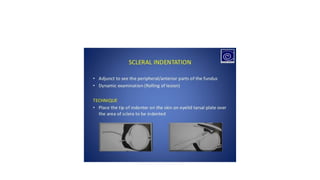
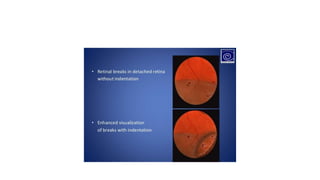
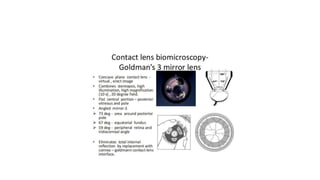
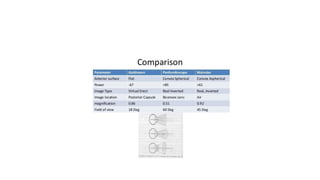
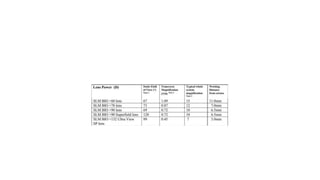
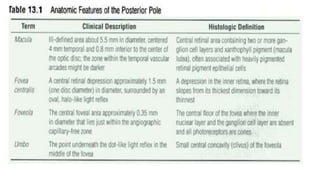
Indirect ophthalmoscopy is a technique used to examine the back of the eye. The key steps are:
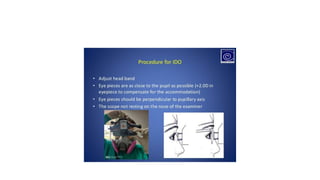
1) Adjusting the ophthalmoscope and positioning the patient lying down looking directly up.
2) The examiner stands to the side and holds the lens about 2 inches from the patient's eye to focus the view.
3) By tilting their head and walking around, the examiner views different parts of the retina, instructing the patient to look in various directions. The macula is examined last when cooperation may be reduced.