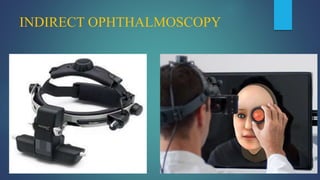
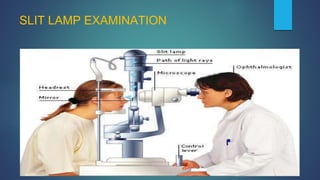
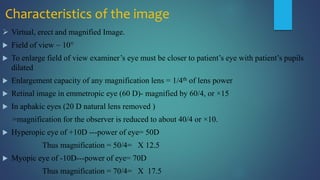
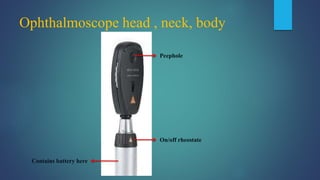
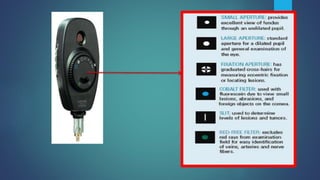
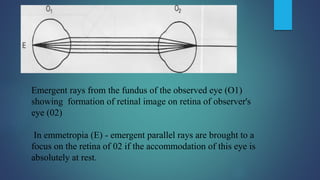
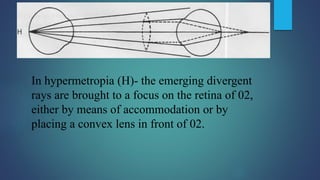
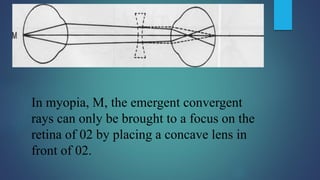
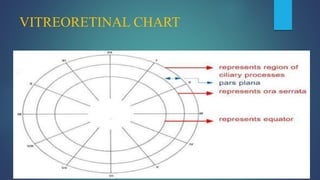
1. Direct ophthalmoscopy allows a magnified, erect, virtual image of the fundus to be seen by the examiner. It provides the greatest magnification of any examination technique but has limitations including a small field of view and lack of stereoscopic vision.
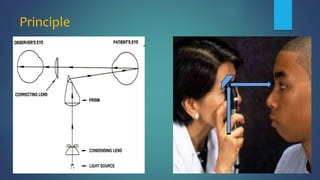
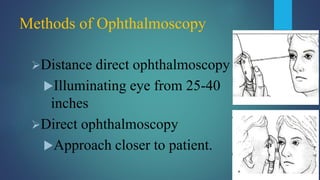
2. The examiner holds the direct ophthalmoscope in one hand and positions their eye close to the patient's eye to examine structures starting with the anterior segment and moving further back to the retina and optic disc.
3. Advantages are its portability and ability to examine a non-dilated pupil, while disadvantages are the limited field of view and lack of stereoscopic viewing compared to indirect techniques.