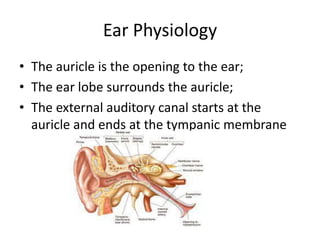
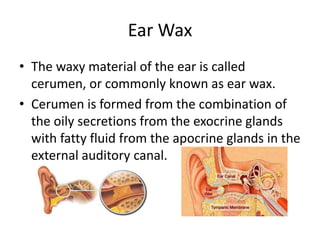
Otic preparations are pharmaceutical products used to treat conditions of the external and inner ear. They are applied inside, outside, or around the ear to exert therapeutic effects. Common conditions treated include bacterial infections, ear wax impaction, swimmer's ear, and skin disorders of the ear. Otic preparations contain various active ingredients like antibiotics, solvents, corticosteroids, and analgesics depending on the specific condition being treated.