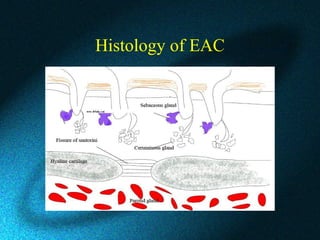
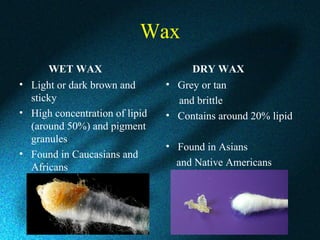
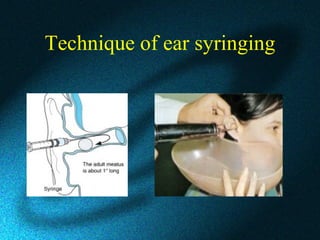
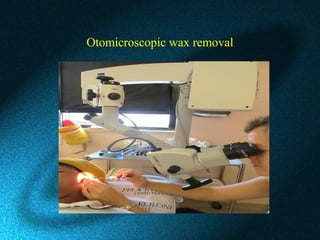
This document discusses earwax, also known as cerumen, and methods for removing impacted earwax. It describes the structure and composition of earwax, noting that it helps clean and lubricate the ear canal while also playing an antibacterial and antifungal role. When earwax becomes impacted, it can cause symptoms like a blocked ear sensation, discomfort, pain, tinnitus, and hearing impairment. The document outlines common techniques for removing impacted earwax, including using cerumenolytic drops to soften the wax, syringing the ear canal with water, and instrumental removal with tools like a cerumen hook. Complications from improper removal are also discussed.