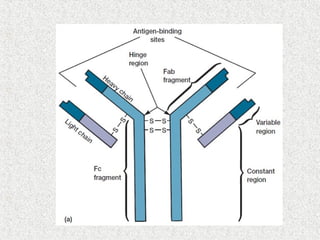
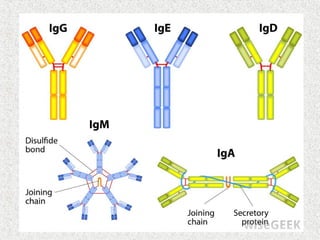
This document discusses immunoglobulins (antibodies) and their structure. It notes that antibodies are Y-shaped proteins produced by plasma cells to neutralize pathogens. Each antibody has two identical antigen-binding sites and consists of two light chains and two heavy chains joined by disulfide bonds. The variable regions at the ends of the Y arms form the antigen-binding site, while the constant stems and lower arms form the Fc region which interacts with immune cells and complement proteins.