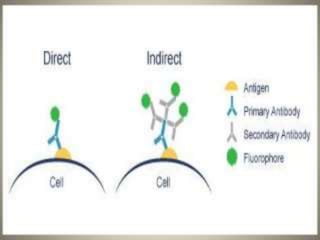
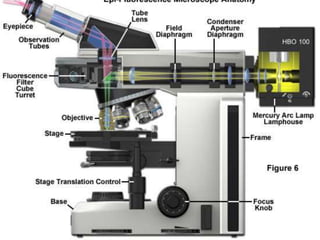
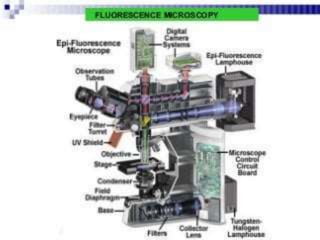
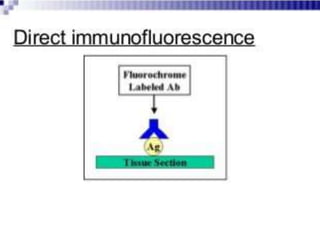
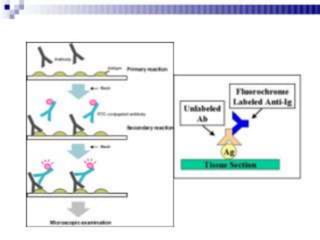
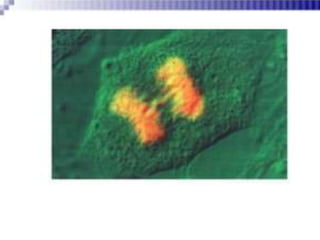
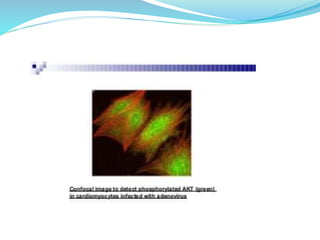
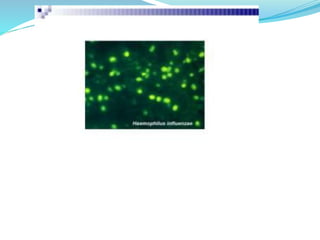
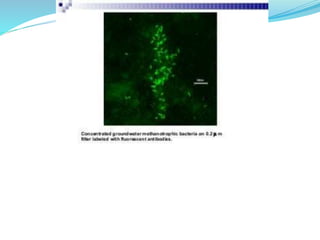
Immunofluorescence is a technique that uses fluorescent antibodies to visualize specific antigens in a sample. It works by binding antibodies that have been chemically conjugated with a fluorescent dye like FITC. When observed under ultraviolet light, the antibodies glow green, allowing the visualization of target molecules. There are two types: direct immunofluorescence uses antibodies directly labeled with fluorescent dye, while indirect uses a secondary antibody labeled with a fluorescent marker to recognize the primary antibody. Immunofluorescence is commonly used clinically to diagnose skin diseases by detecting antigen-antibody complexes.