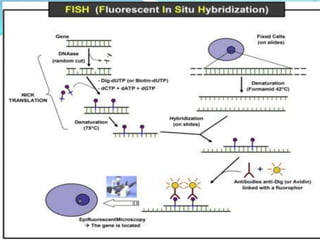
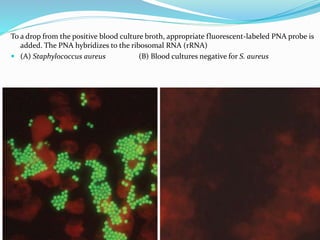
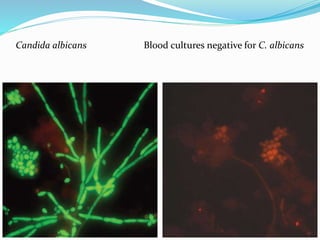
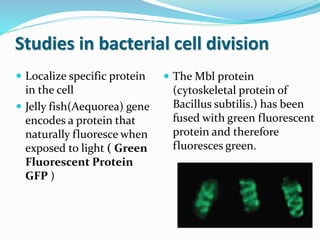
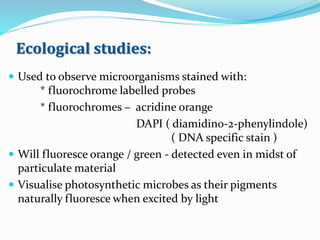
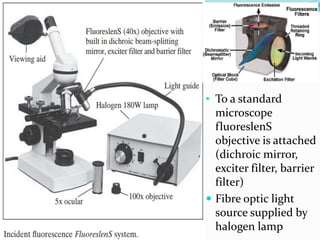
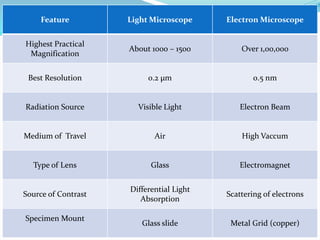
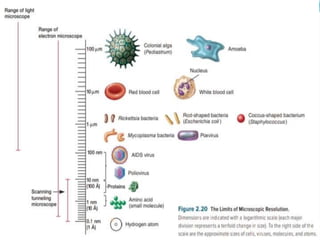
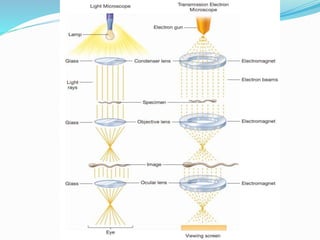
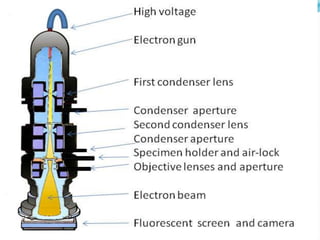
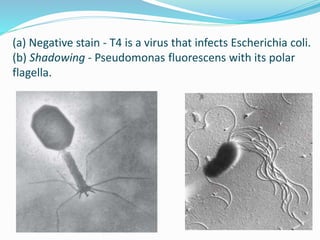
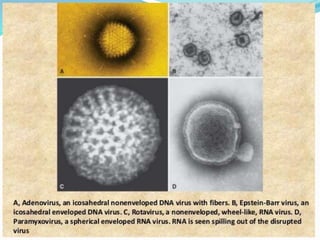
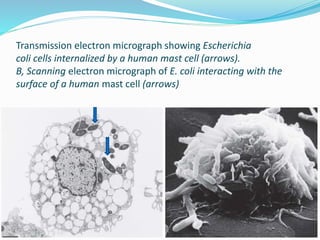
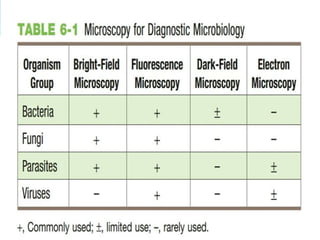
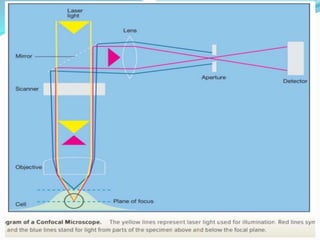
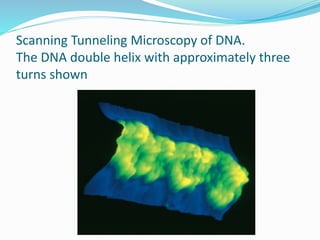
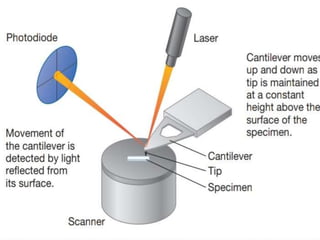
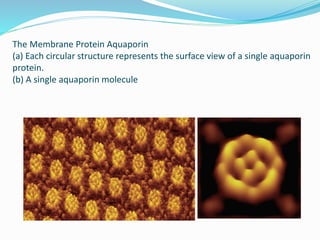
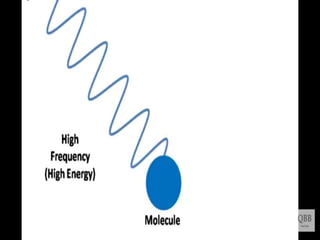
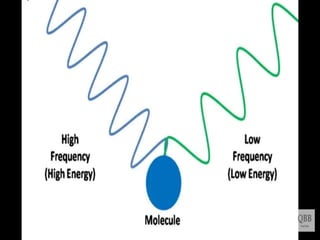
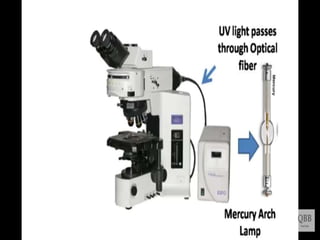
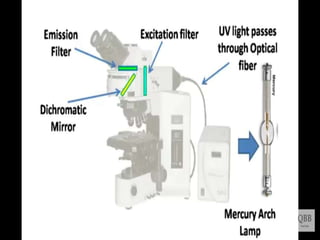
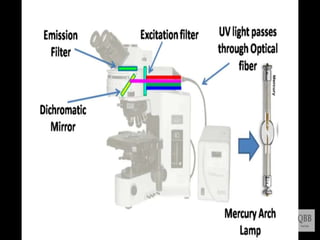
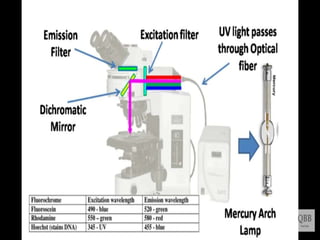
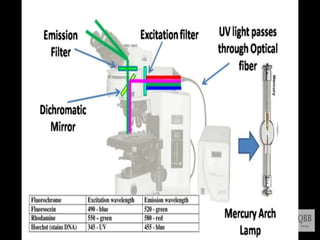
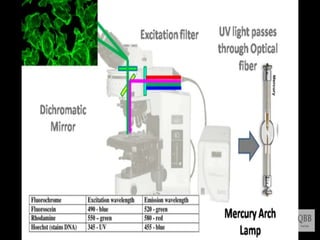
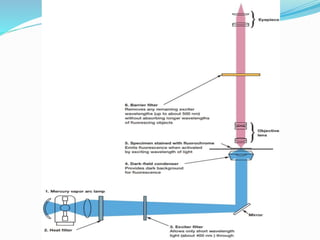
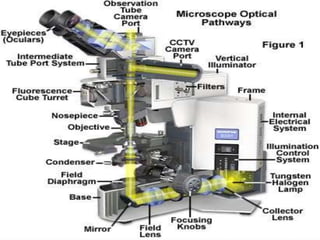
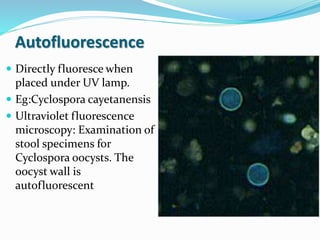
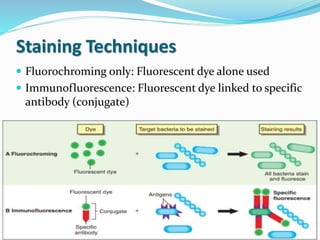
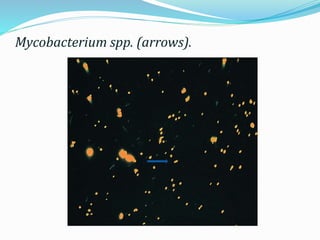
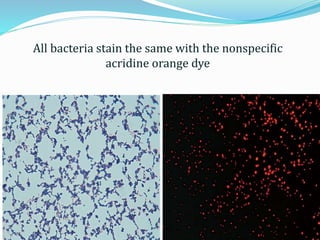
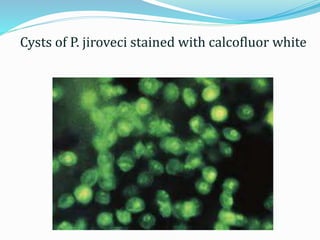
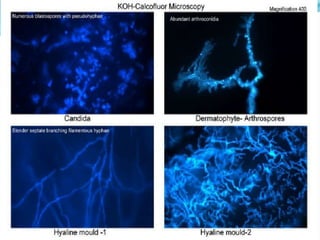
This document provides information on fluorescence microscopy. It discusses how fluorescence microscopy works by using fluorochromes or fluorescent dyes that absorb light of shorter wavelengths and emit light of longer wavelengths. These dyes are used to stain specimens so that they glow under fluorescence microscopy. The document also describes different types of fluorescence microscopy like epifluorescence, transmitted light fluorescence, and confocal microscopy. It discusses applications in microbiology like staining bacteria and fungi, immunofluorescence, and fluorescent in situ hybridization.





















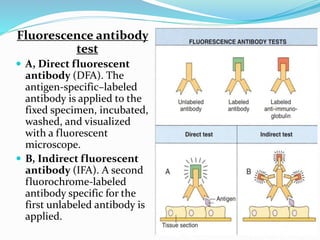

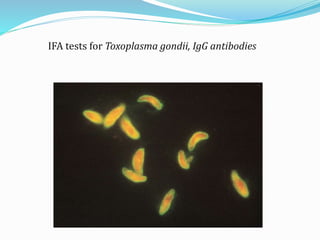
![Indirect Fluorescent Antibody Test
Two –step (sandwich) technique.
More sensitive than the DFA method,
DFA method is faster(single incubation).
Widely applied method of detecting diverse antibodies.
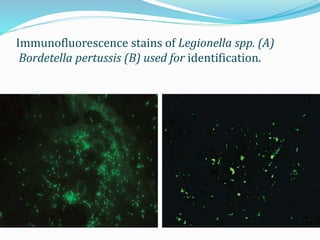
Legionella spp., Borrelia burgdorferi, T. gondii, VZV,
CMV, EBV capsid antigen, HSV types 1 and 2,
rubella virus, Mycoplasma pneumoniae, T. pallidum
(the fluorescent treponemal antibody absorption test
[FTA-ABS])](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/microscope-210304063742/85/Microscope-44-320.jpg)