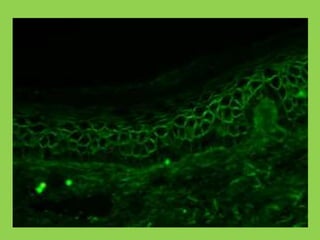
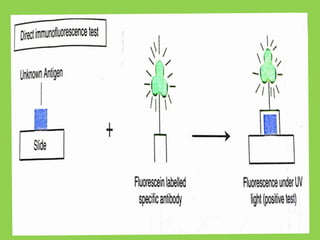
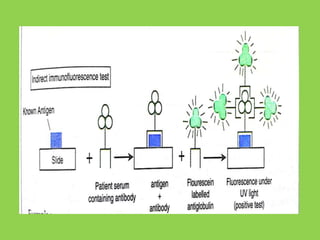
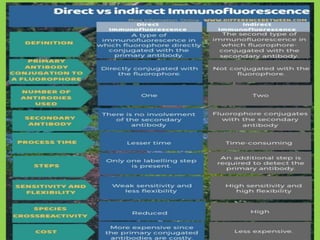
This document discusses immunofluorescence assays. It describes that immunofluorescence uses fluorescent dyes to detect the location of antigens or antibodies in tissue samples. There are two main types of immunofluorescence tests: direct and indirect. Direct tests use fluorescently-labeled antibodies to detect unknown antigens. Indirect tests detect antibodies in samples like serum by using a known antigen on a slide and fluorescently-labeled antibodies that bind to any human antibodies. The indirect test has the advantage of only requiring a single fluorescent conjugate that can detect antibodies to any antigen due to binding to all human antibodies.