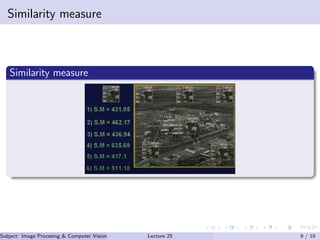
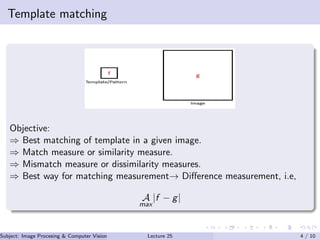
Image registration is a process that aligns pixels in two images to correspond to the same point in a scene. It allows images to be combined or focused in a way that improves information extraction. Some applications of image registration include stereo imaging, remote sensing, comparing images over time, and finding where a template matches an image. Template matching is used to find the best match between a template and image by measuring similarity or mismatch between them. Cross-correlation is commonly used as a similarity measure for template matching.


![Continued–
⇒ Second method (mismatch measure)
A
|f − g| ⇒
i j∈A
[|f (i, j) − g(i, j)|]
⇒ Third method (mismatch measure)
A
(f − g)2
⇒
i j∈A
[|f (i, j) − g(i, j)|]2
Also
A
(f − g)2
=
A
f 2
+
A
g2
− 2
A
fg
⇒ For a given template
A
f 2
remain fixed.
⇒ For a given image
A
g2
remain fixed.
Subject: Image Procesing & Computer Vision Dr. Varun Kumar (IIIT Surat)Lecture 25 5 / 10](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture25-201210143638/85/Image-Registration-Digital-Image-Processing-5-320.jpg)

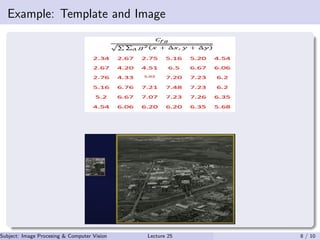
![Example
⇒
∞
−∞
∞
−∞f (x, y)g(x + ∆x, y + ∆y)dxdy → Cross correlation
⇒ We apply the normalized cross correlation
i,j∈A
[g2
(x + ∆x, y + ∆y)]1/2
Subject: Image Procesing & Computer Vision Dr. Varun Kumar (IIIT Surat)Lecture 25 7 / 10](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lecture25-201210143638/85/Image-Registration-Digital-Image-Processing-7-320.jpg)