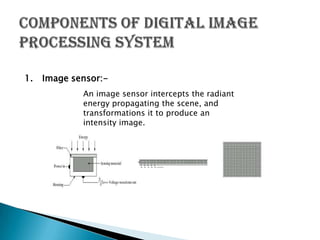
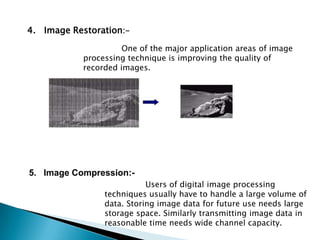
1. Digital image processing focuses on improving images for human interpretation and machine perception. It involves digitizing an image using sensors and processors then displaying the digital image.
2. The key stages of digital image processing are enhancement, restoration, compression, and registration. Registration involves mapping image frames for tasks like object recognition.
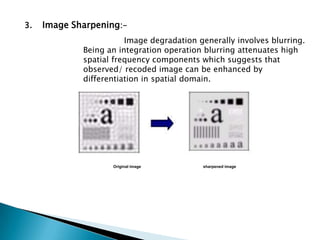
3. Common processing techniques include contrast intensification to improve poor contrast, smoothing to reduce noise, and sharpening to enhance blurred details.