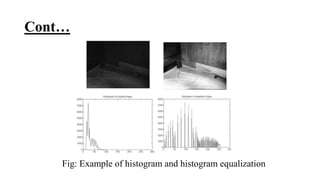
The document provides an overview of image enhancement techniques, focusing on methods from the spatial and frequency domains. It explains various procedures such as point operations, thresholding, and histogram equalization, which aim to improve image quality and highlight specific features. Applications of these techniques include sharpening image features and reducing noise to enhance visual appeal.


![Spatial domain methods:
• The term spatial domain refers to the aggregate of pixels composing
an image.
• Spatial domain methods are procedures that operate directly on these
pixels.
• Spatial Domain processes will be denoted by the expression ,
g(x,y)= T[f(x,y)]
Where, g is the output, f is the input image and T is an operation on f
defined over some neighborhood of (x,y)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/imageenhancementtechniques-181219105938/85/Image-enhancement-techniques-5-320.jpg)


![Point operation: Brightness modification
Increasing the brightness of an image:
g[m,n]=f[m,n]+k
Decreasing the brightness of an image:
g[m,n]=f[m,n]-k](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/imageenhancementtechniques-181219105938/85/Image-enhancement-techniques-8-320.jpg)









![Spatial operations:
• Operations performed on local neighborhoods of input pixels
• Image is convolved with [FIR] finite impulse response filter called
spatial mask .
• Techniques such as :
- Noise smoothing
- Median filtering
- LP and HP filtering
- Zooming](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/imageenhancementtechniques-181219105938/85/Image-enhancement-techniques-19-320.jpg)