Embed presentation
Downloaded 10 times




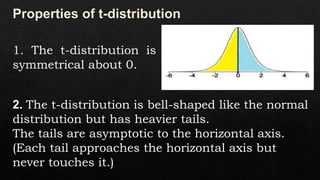







The document discusses the t-distribution, which is used as an alternative to the normal distribution when sample sizes are small and/or the population variance is unknown. The t-distribution was developed by William Sealy Gosset using the pseudonym "Student" and accounts for uncertainty in population parameters by having heavier tails than the normal distribution. Key properties of the t-distribution include being symmetrical around 0, bell-shaped, and having tails that are asymptotic to the horizontal axis. The degree of freedom affects the shape, with lower freedom resulting in a lower peak and thicker tails.











