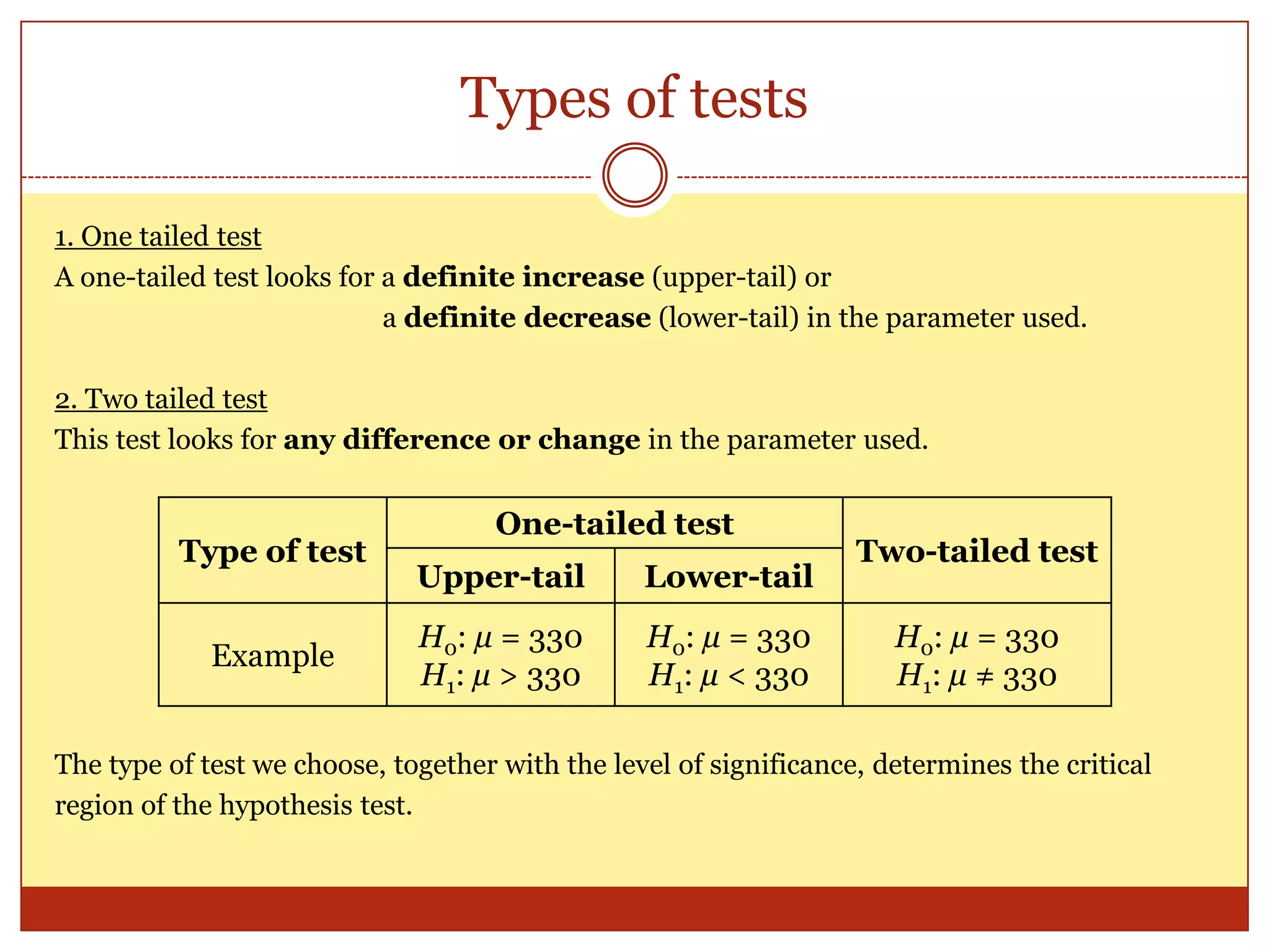
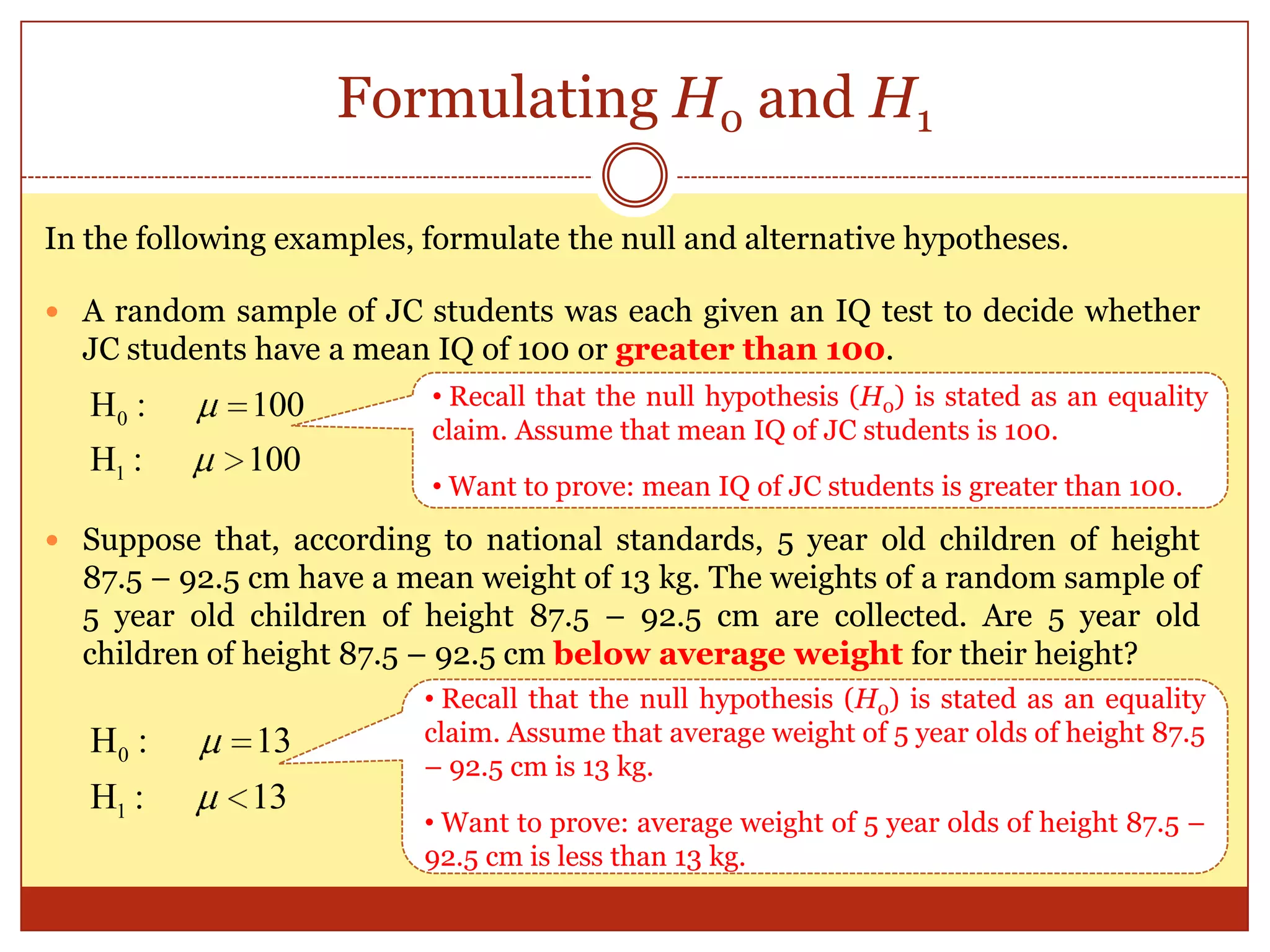
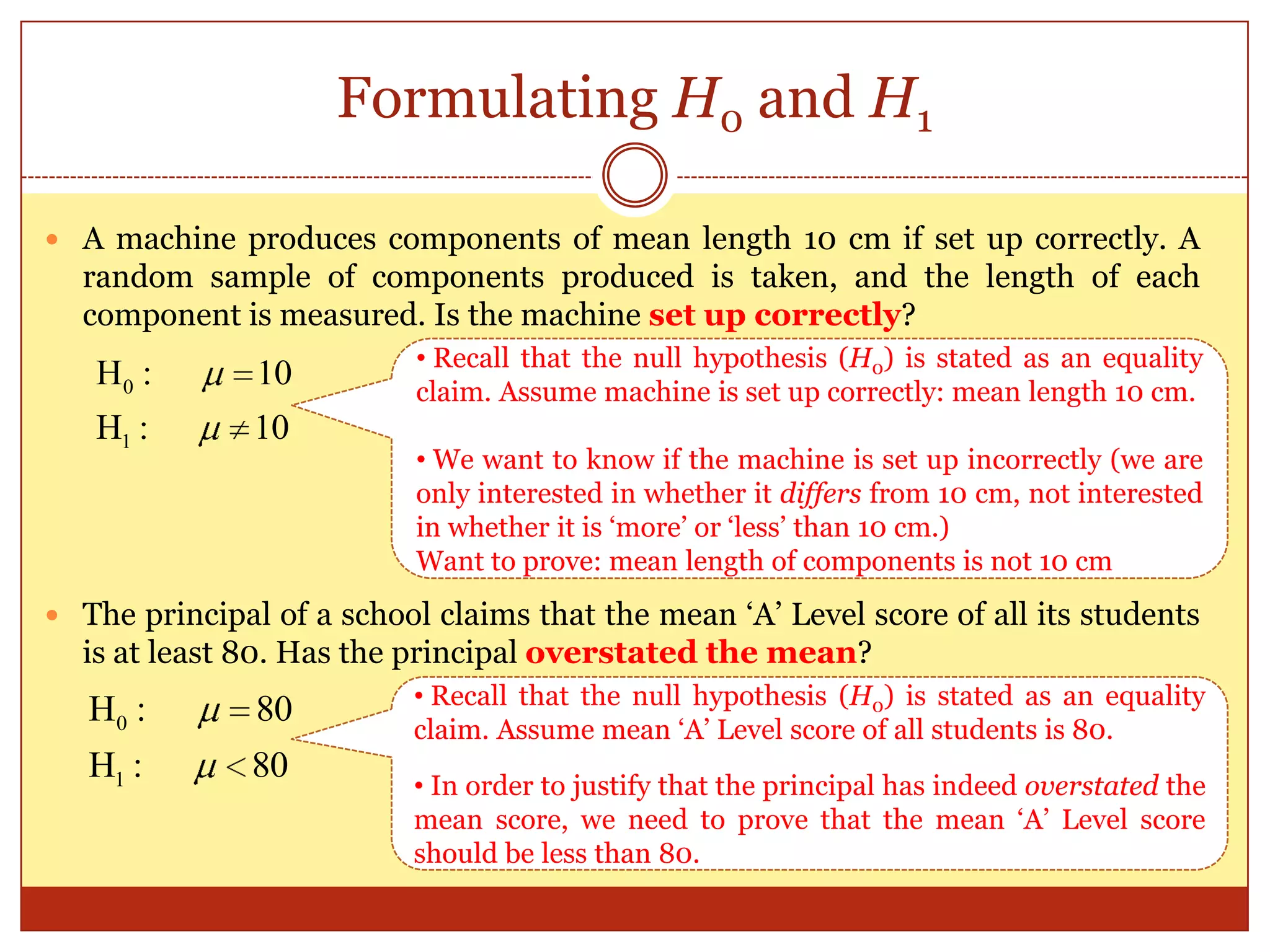
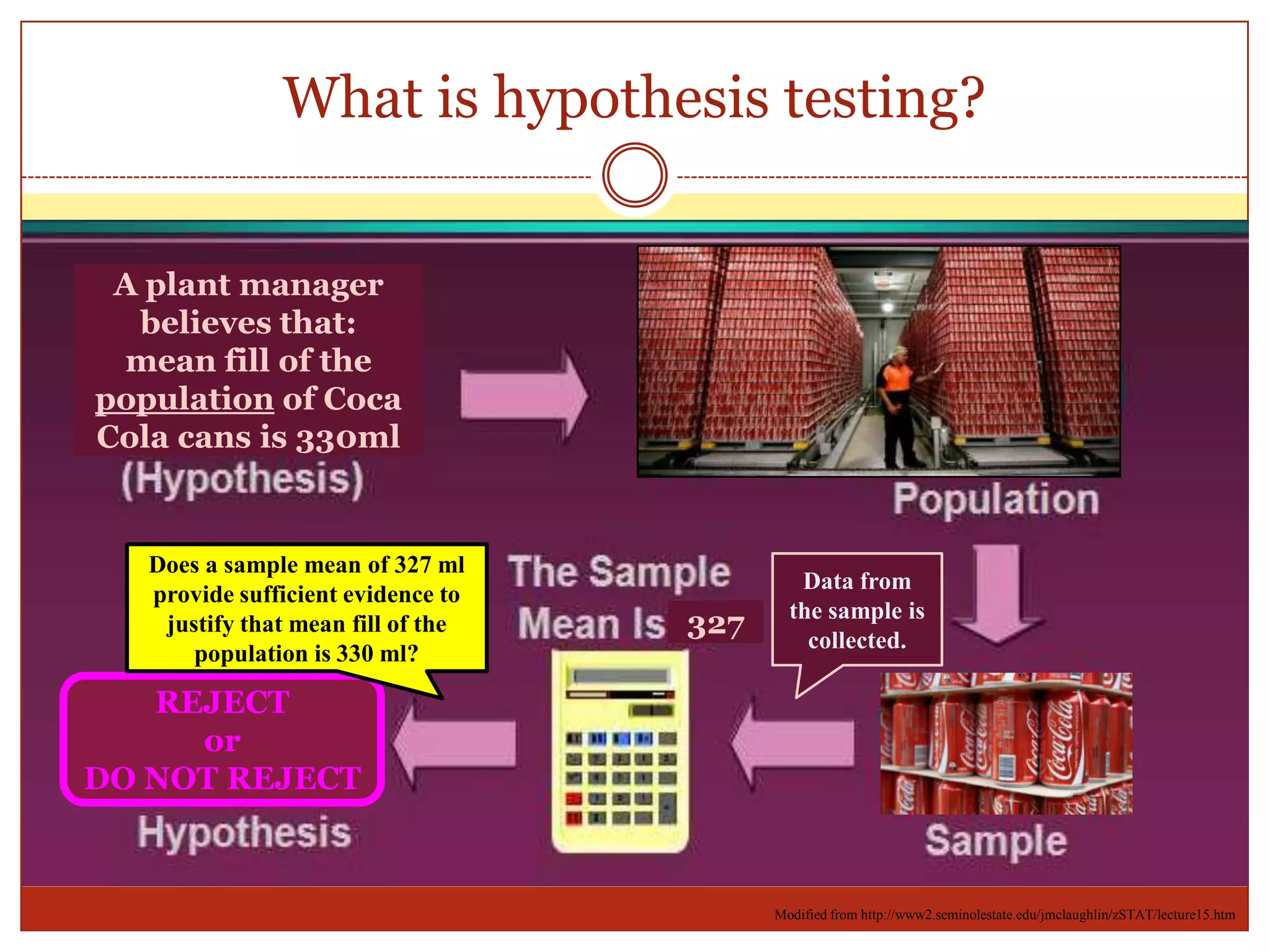
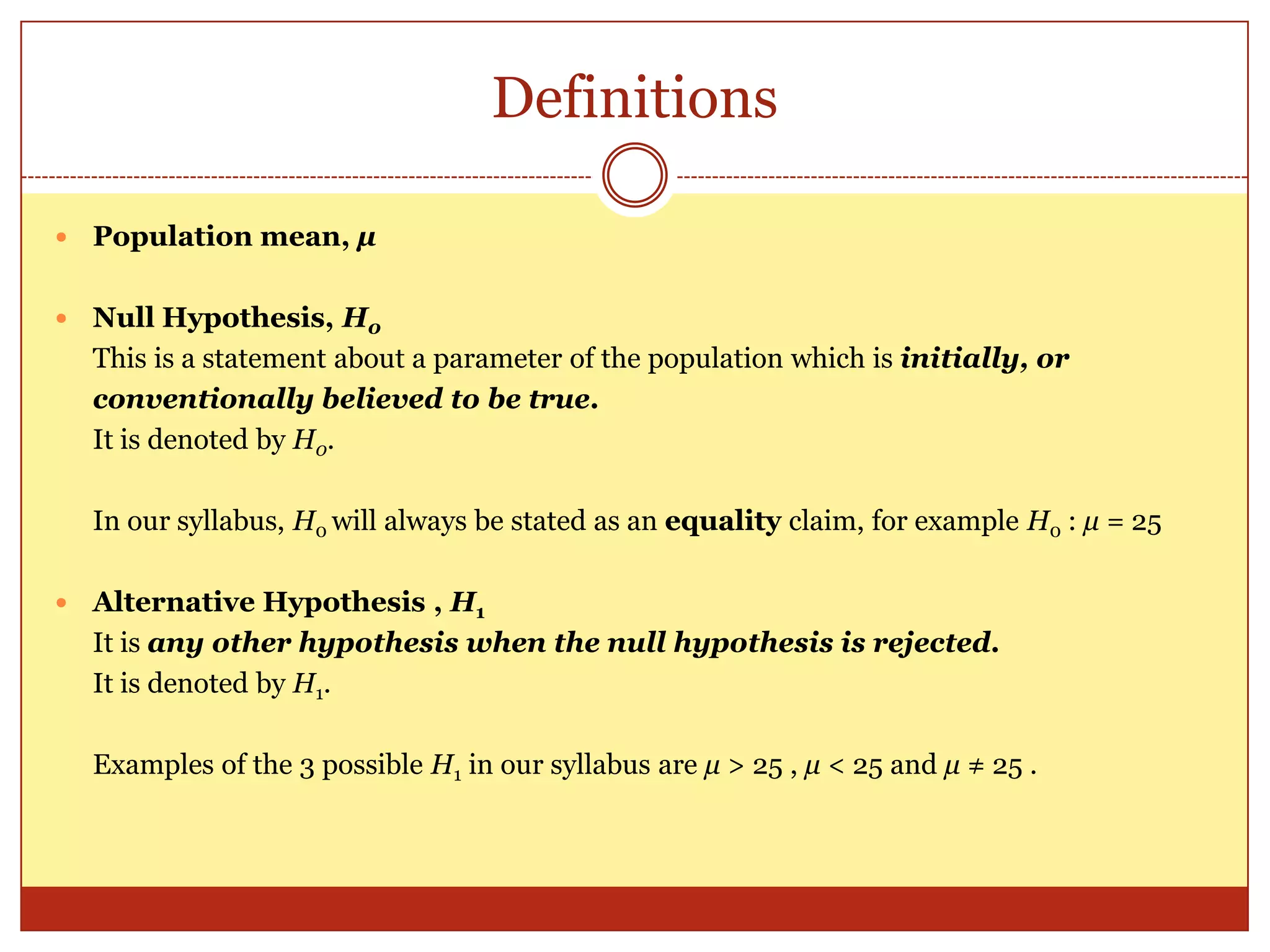
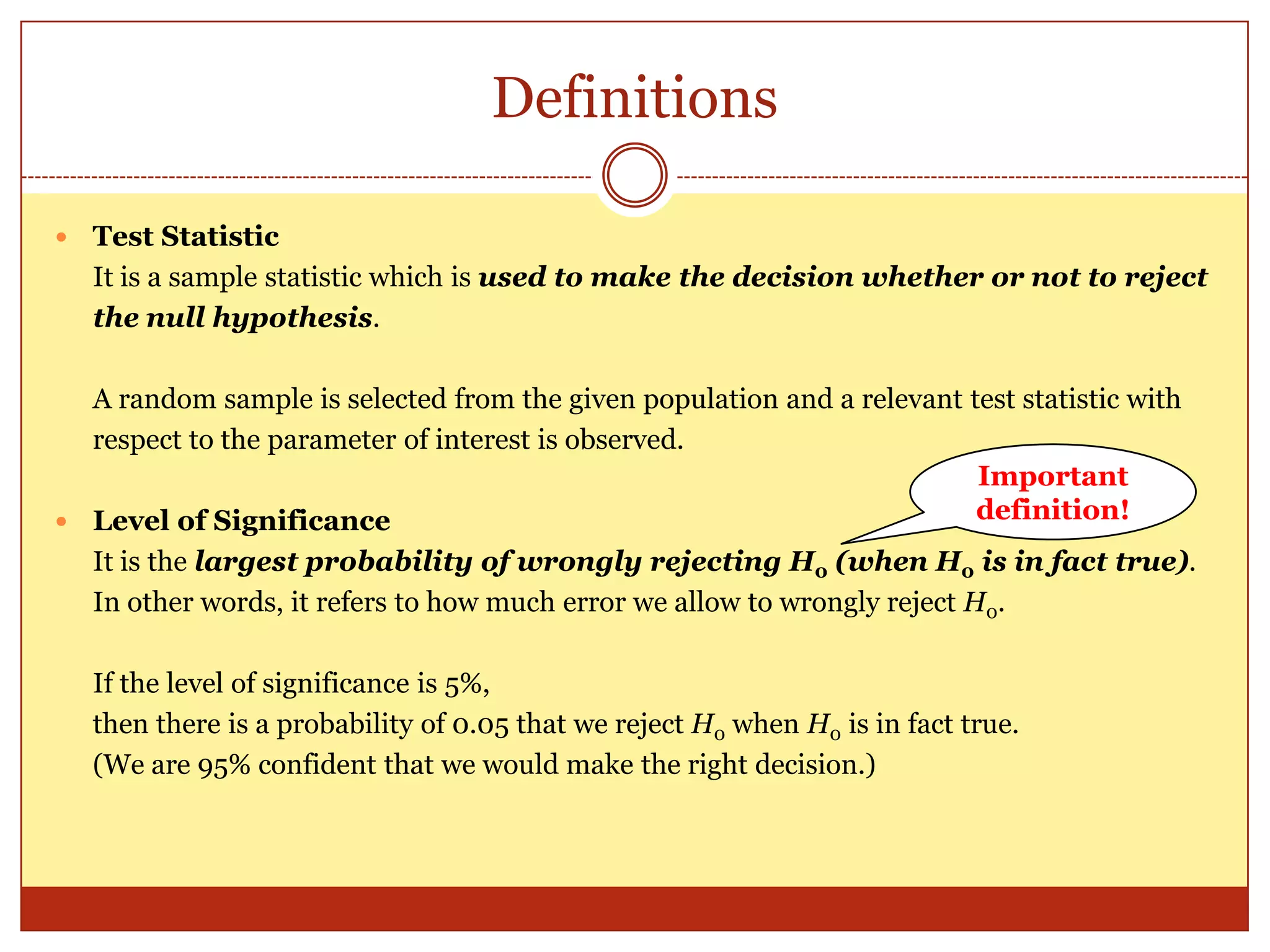
The document provides an introduction to hypothesis testing, including its real-life applications, key definitions, and structure. It defines hypothesis testing as the process of testing the validity of a statistical hypothesis based on a random sample from a population. The document outlines the common steps in hypothesis testing: 1) stating the null and alternative hypotheses, 2) choosing a significance level, 3) determining the test statistic and decision criteria, 4) rejecting or failing to reject the null hypothesis, and 5) drawing a conclusion. It also defines important terminology like population mean, null and alternative hypotheses, test statistic, significance level, critical region, and p-value. Real-life examples from pharmaceutical testing and legal cases are provided to illustrate the motivation for hypothesis






![Structure
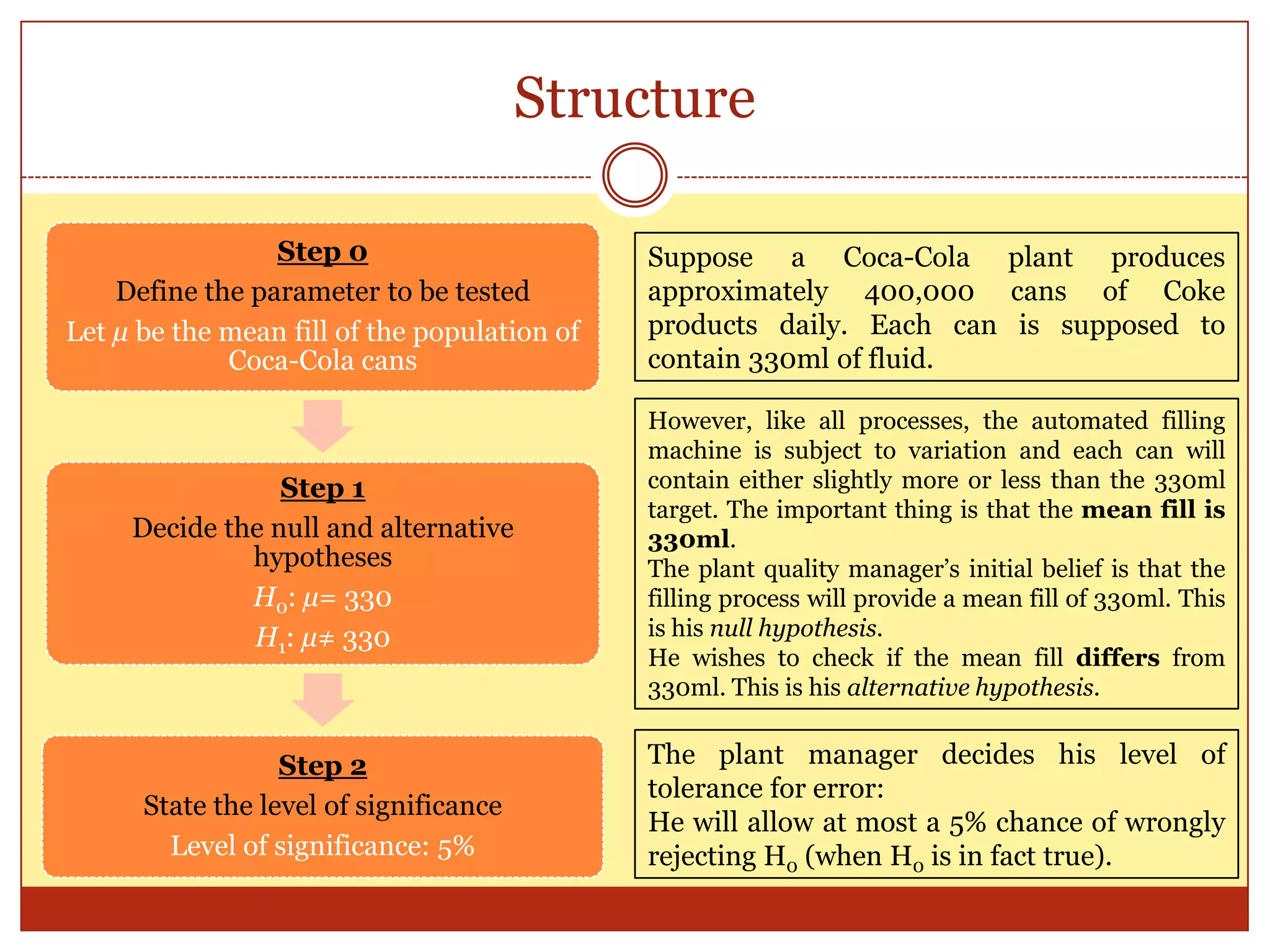
The mean fill of Coca Cola cans is normally
distributed with mean 330 and variance 2.6.
Step 3
State the distribution of the
population mean
[Apply Sampling Theory]
Let X be the fill of a Coca Cola can.
Under H0,
Step 4
State the test statistic
[Standardize the distribution of ]
2.6
~ N 330,
50
X
2.
330
,
6 /
N(0,1)
50/
Z
X X
Z
n
X
The plant quality manager selects a
random sample of 50 cans and
computes the sample mean, 327x](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hypothesistestinglesson1-140419034409-phpapp01/75/Hypothesis-Testing-Lesson-1-11-2048.jpg)
![Structure
Step 5
Decision Criteria
Calculate test statistic and p-value
[using the sample mean ]
More on this the next lesson
Step 6
Reject H0/Do not reject H0
Step 7
Conclude
327x
Based on the decision criteria,
there are two possible conclusions:
• Possibility #1
(the sample mean is “significantly” higher or
lower than 330ml)
Reject H0.
There is sufficient evidence at 5% level
of significance to conclude [H1 ] the mean
fill of Coke cans is not equal to 330ml.
• Possibility #2
(the sample mean is NOT “significantly”
higher or lower than 330ml)
Do not reject H0.
There is insufficient evidence at 5%
level of significance to conclude [H1 ] the
mean fill of Coke cans is not equal to 330ml.
Compare test
statistic with
critical value
Compare p-
value with level
of significance](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hypothesistestinglesson1-140419034409-phpapp01/75/Hypothesis-Testing-Lesson-1-12-2048.jpg)