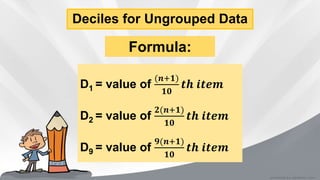
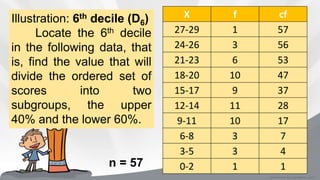
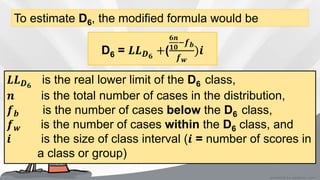
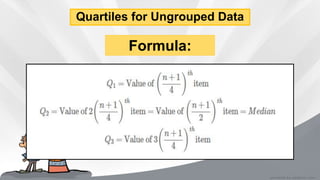
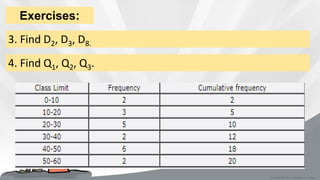
This document defines and provides formulas and examples for calculating quartiles and deciles from both ungrouped and grouped data. Quartiles and deciles are statistical measures used to divide a data set into four and ten equal parts, respectively. The document explains that quartiles are calculated as Q1, Q2, Q3 to divide the data into the lower 25%, middle 50%, and upper 25%. Deciles are calculated as D1-D9 to divide the data into ten equal parts. Modified formulas are provided to calculate quartiles and deciles from grouped frequency distribution data. Examples are included to demonstrate calculating these measures.