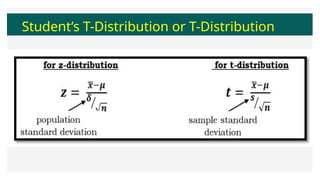
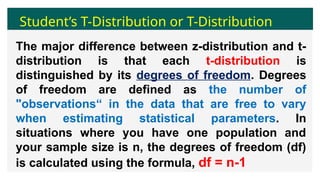
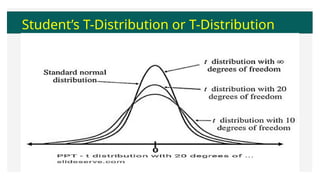
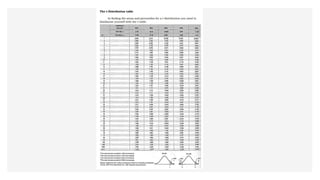
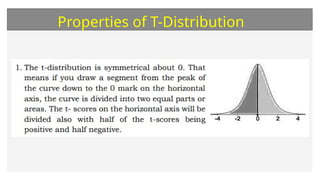
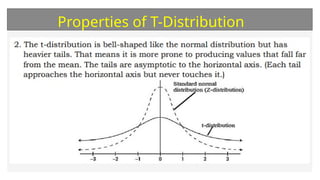
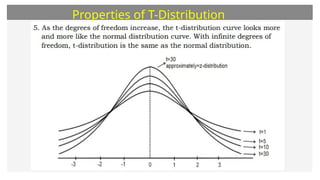
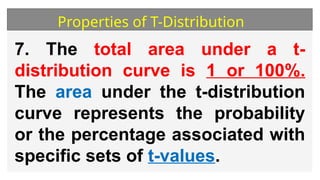
This document discusses the student's t-distribution, highlighting its properties, such as its application for small sample sizes and unknown population standard deviations. It explains the concept of degrees of freedom, which affects the distribution's shape and variance, and emphasizes that the means of t-distribution characteristics are zero with a variance greater than one. Additionally, it includes true/false assessments and sample problems related to the t-distribution and degrees of freedom.