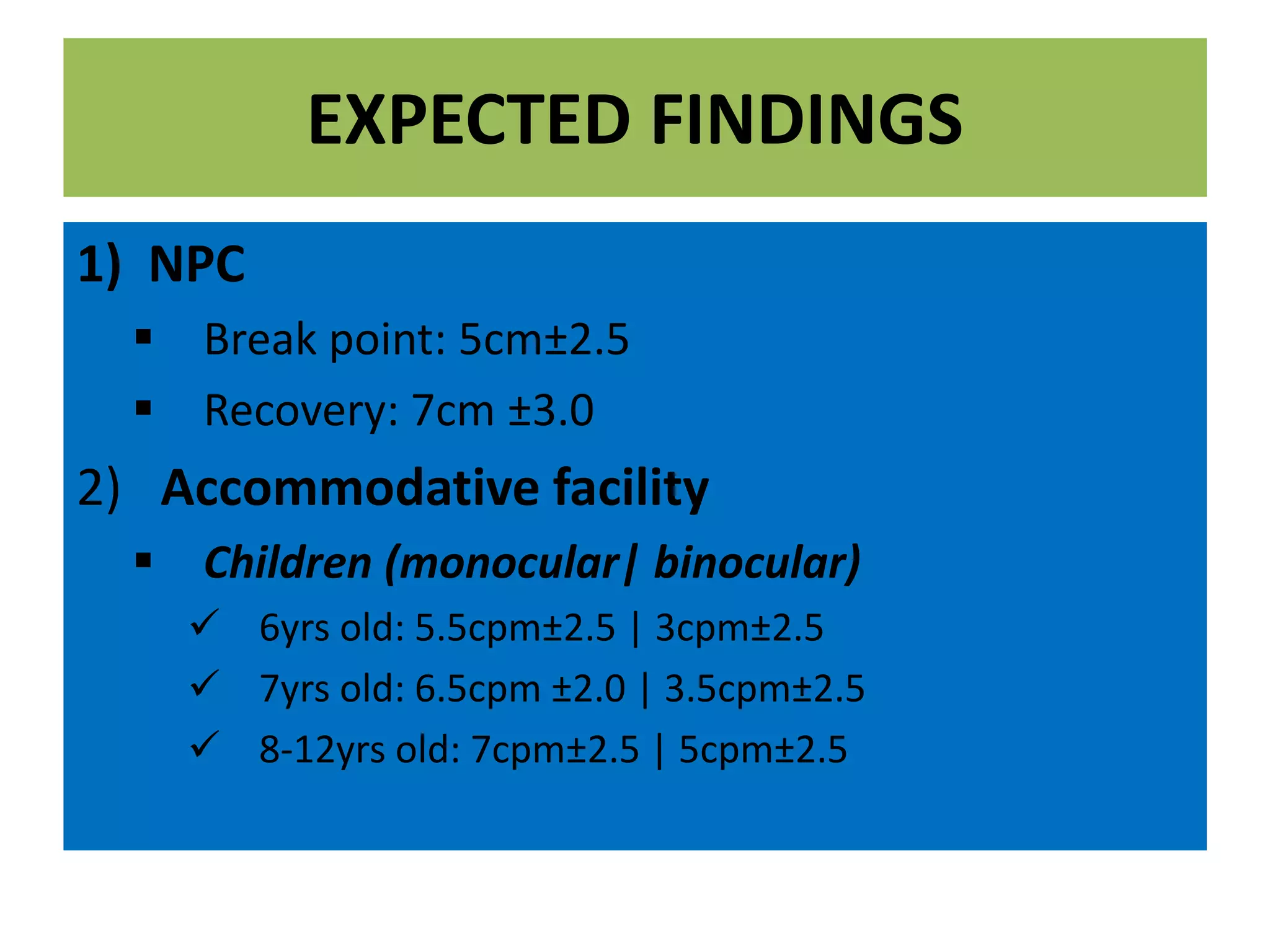
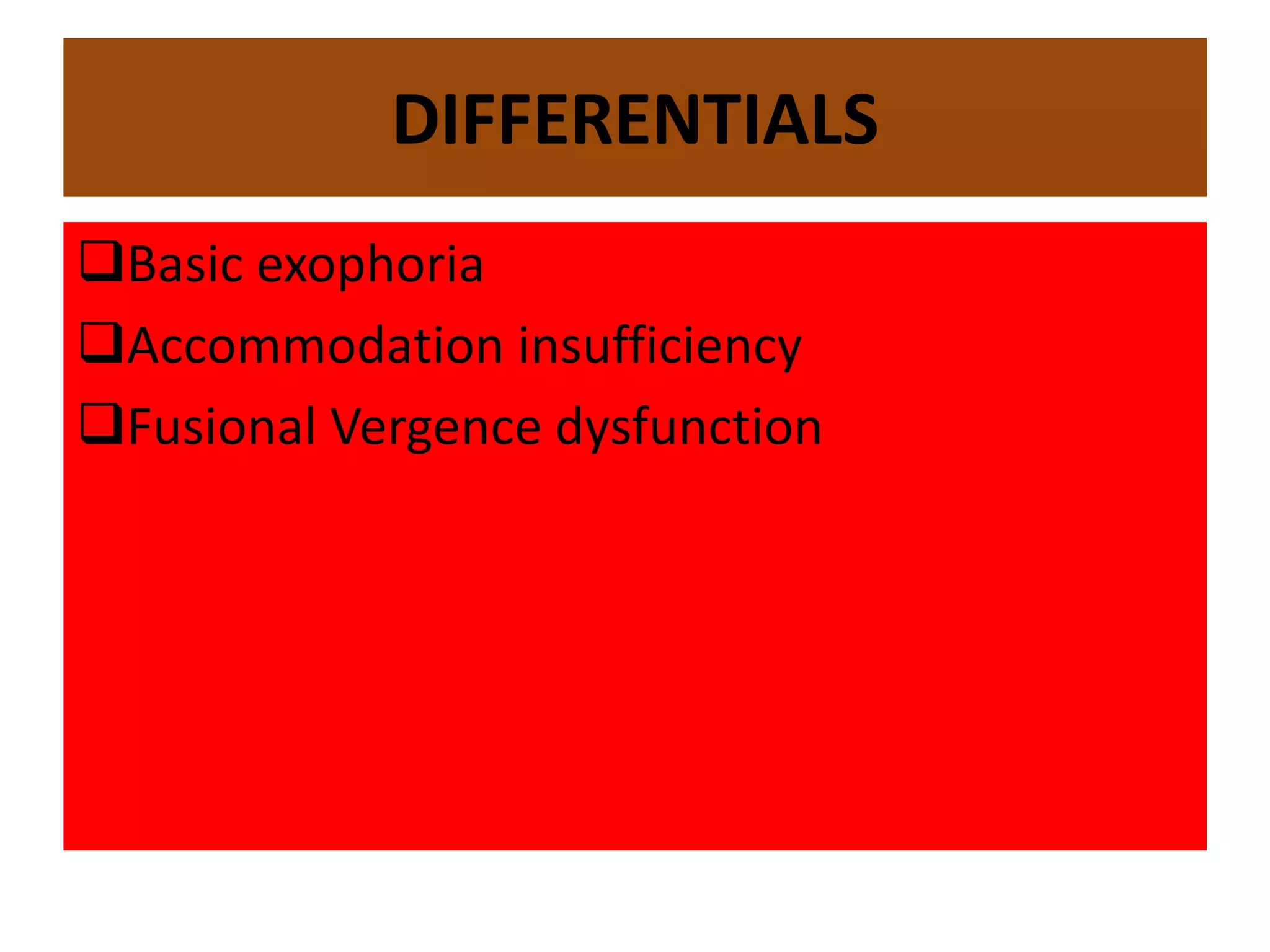
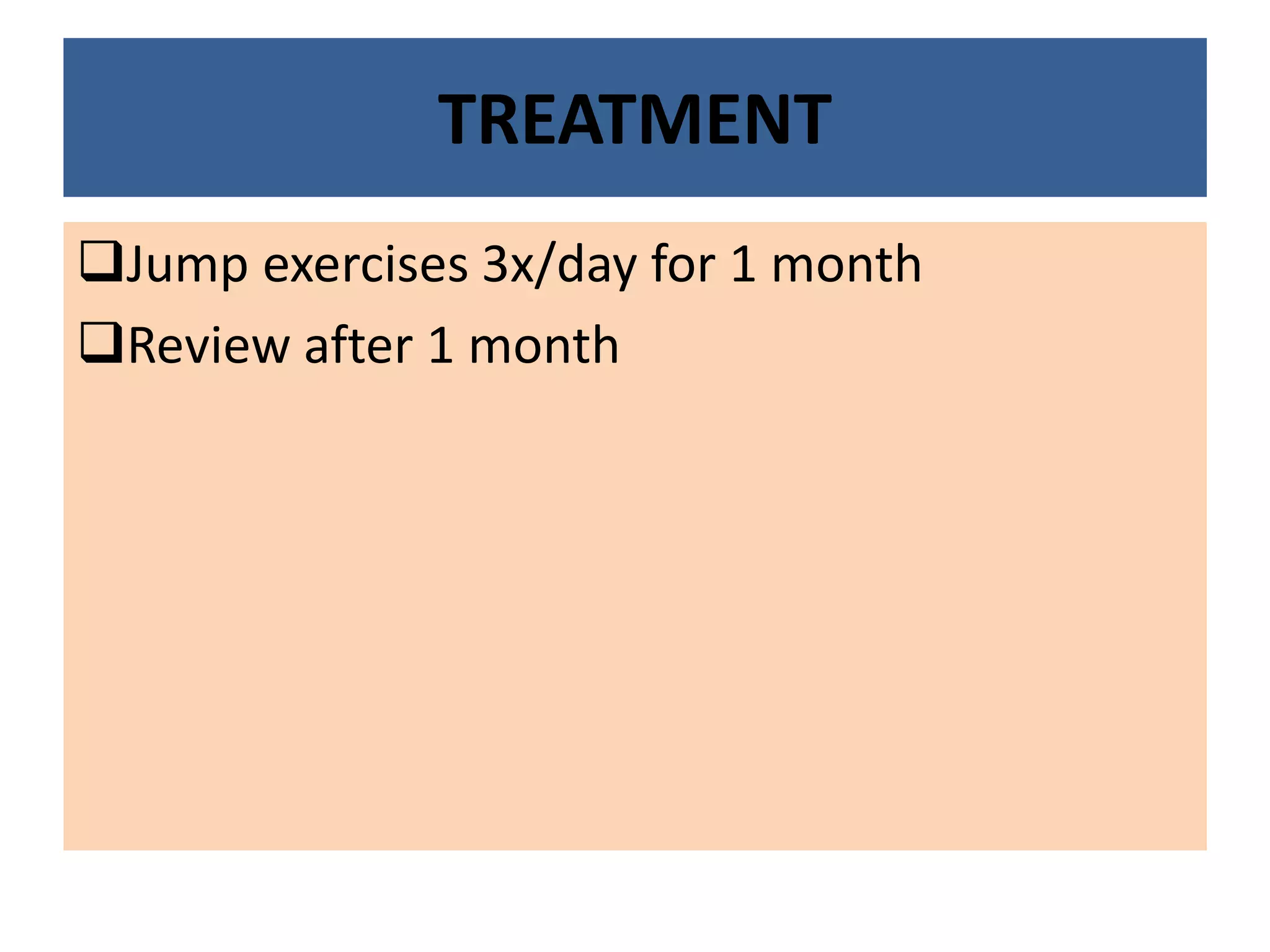
This document presents a case study of a 21-year-old female student complaining of tearing and eyestrain with prolonged near work. Her ocular examination results are within normal limits except for a low accommodative facility and binocular vision dysfunction. The patient is diagnosed with fusional vergence dysfunction based on her symptoms and examination findings. She is prescribed daily jump exercises for one month to treat her condition.








![CYCLOPLEGIC REFRACTION
OD:+0.25…6/6
OS: PLANO…6/6
CALCULATED AC/A RATIO
IPD (cm) + NFD (m) [Hn-Hf]
5.4:1](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ad6e4eda-f6a6-4533-98a8-92ad58186638-161207052713/75/CASE-PRESENTATION-BV-14-2048.jpg)