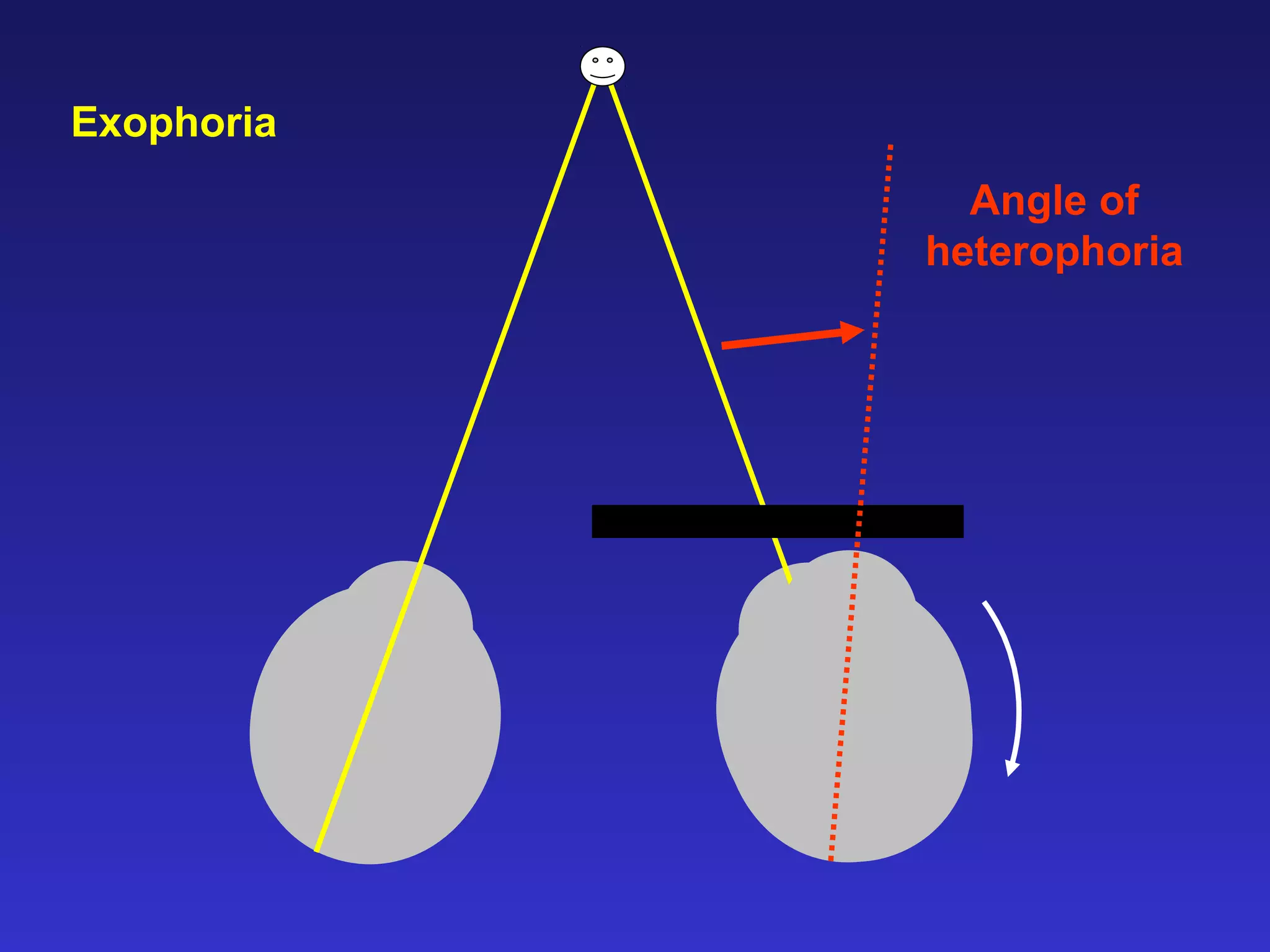
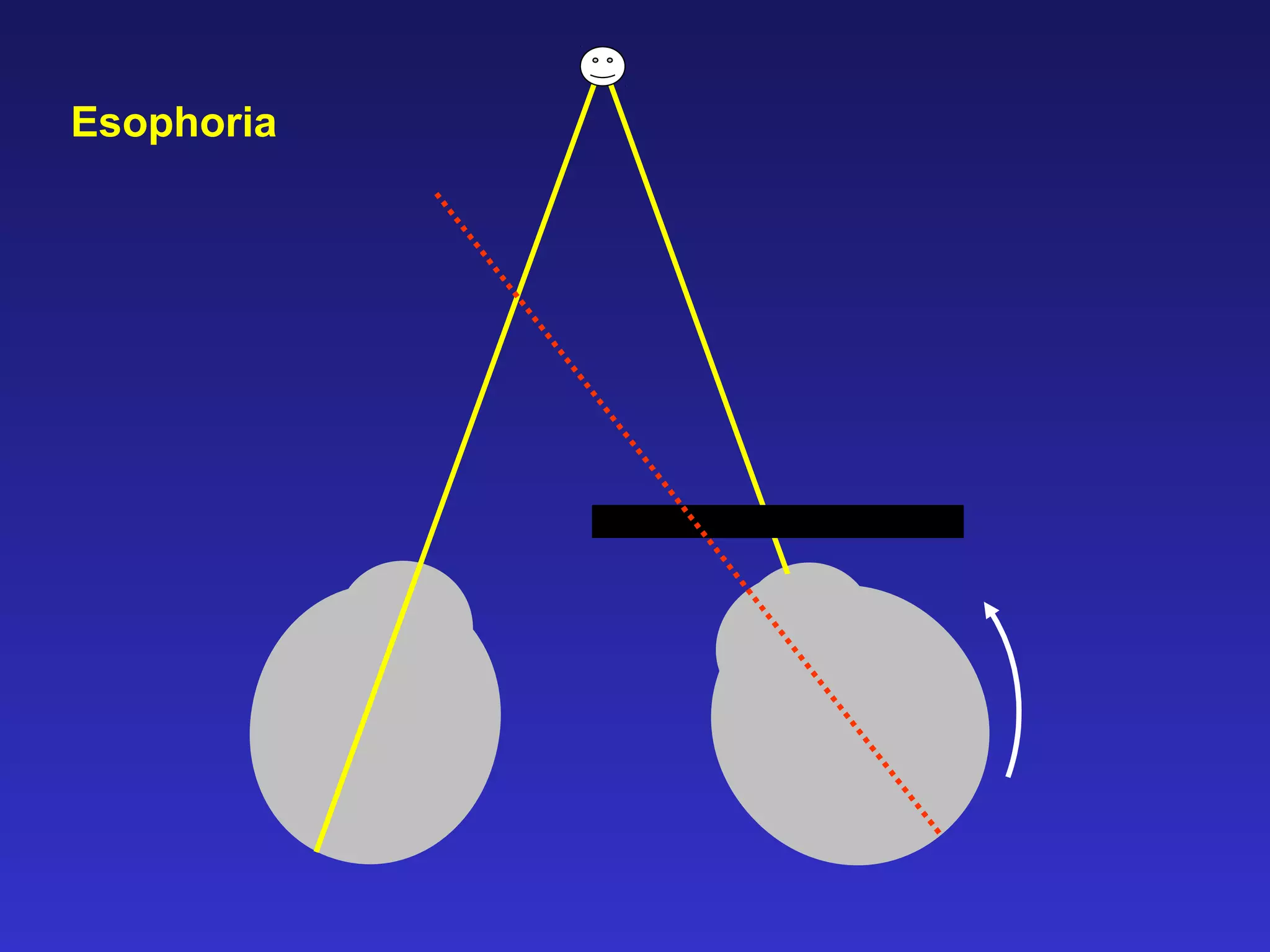
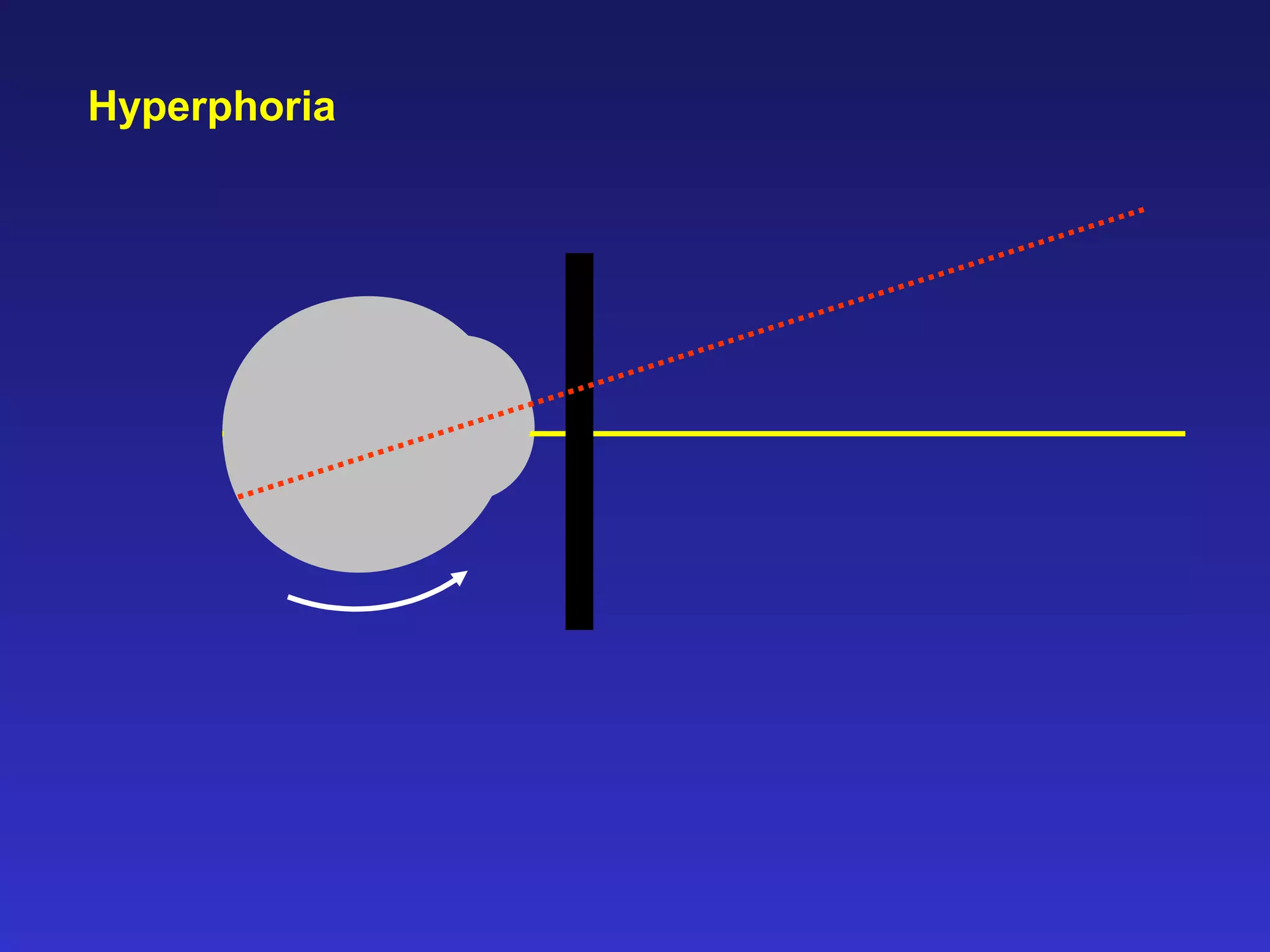
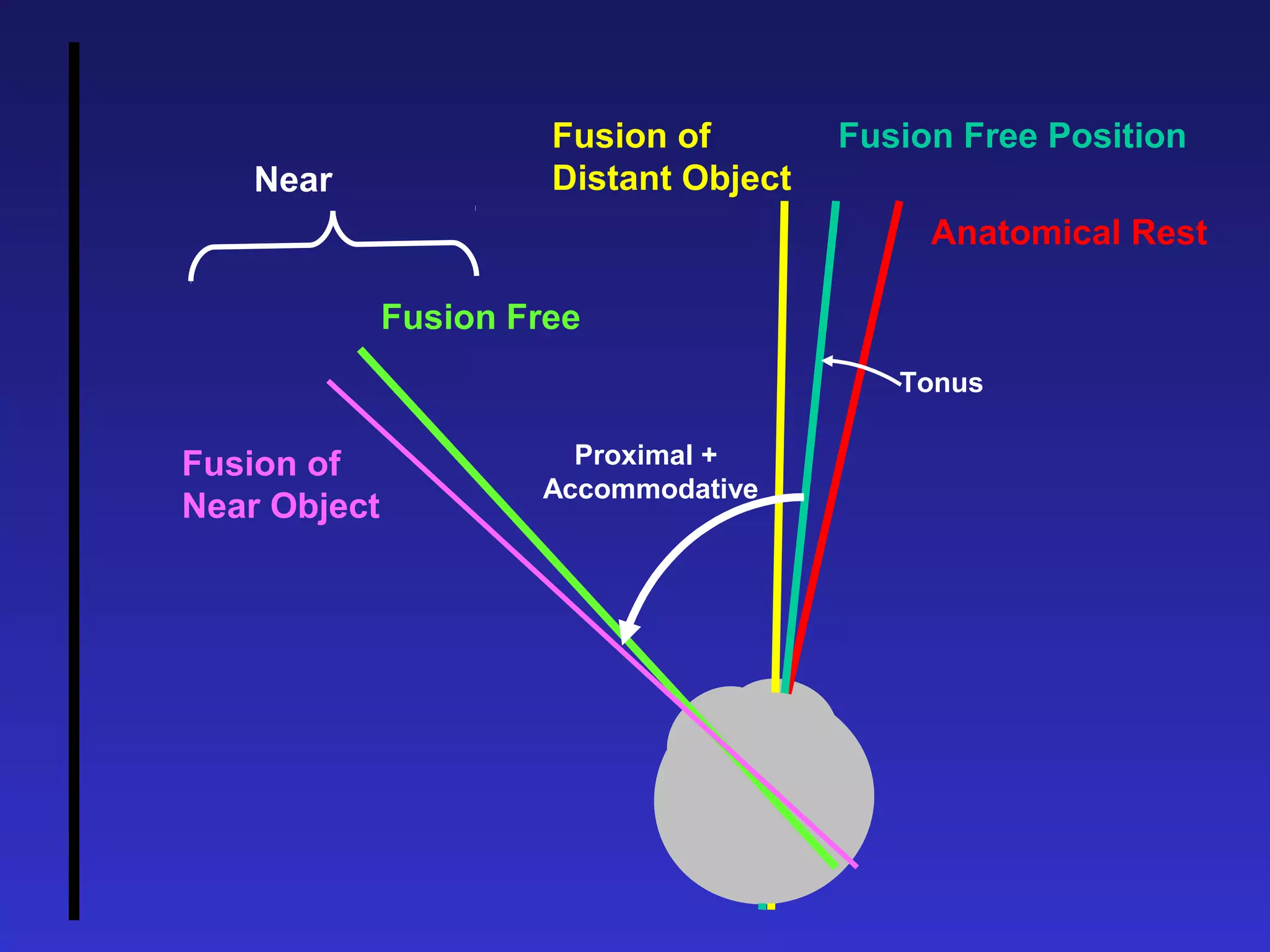
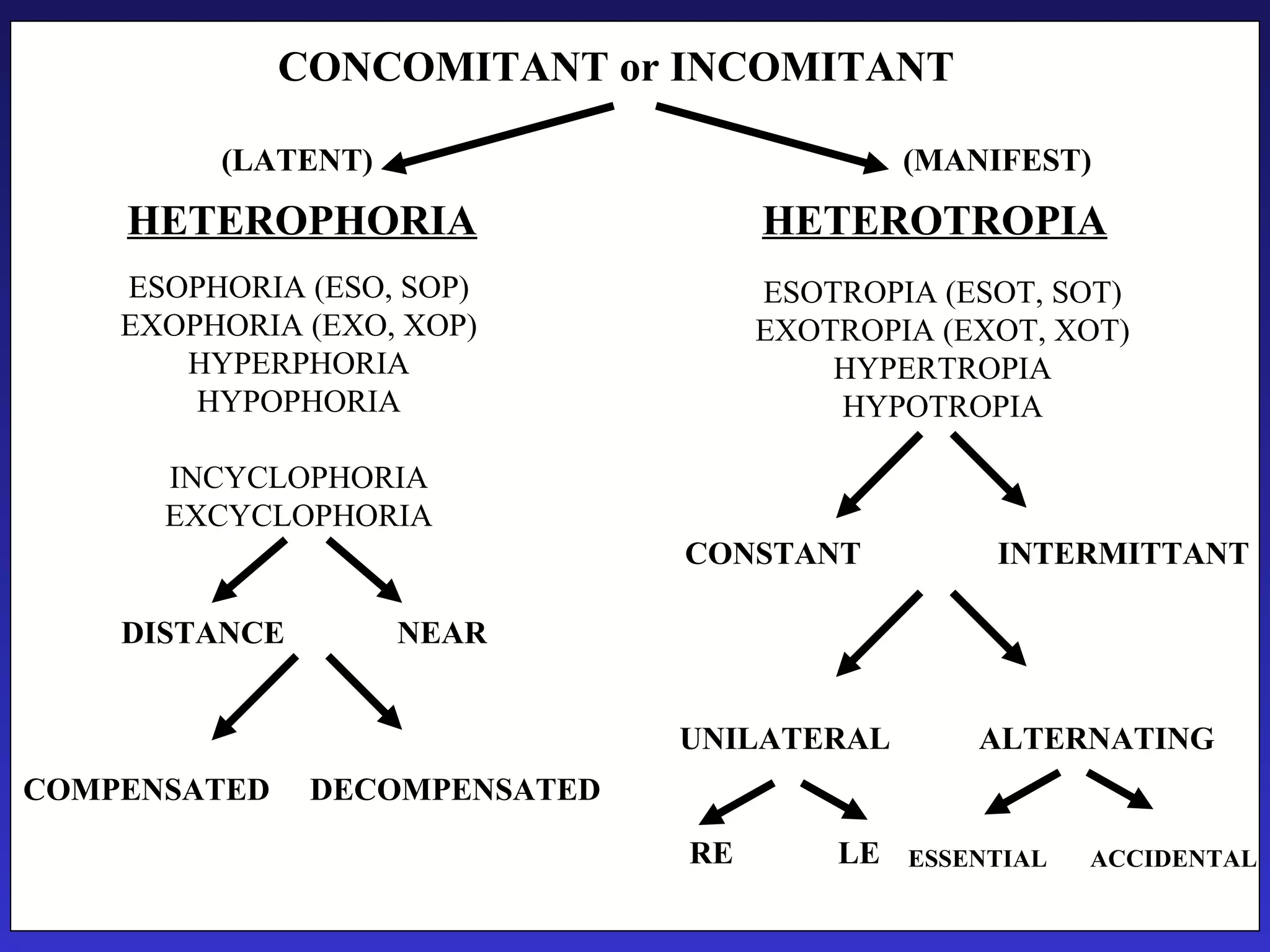
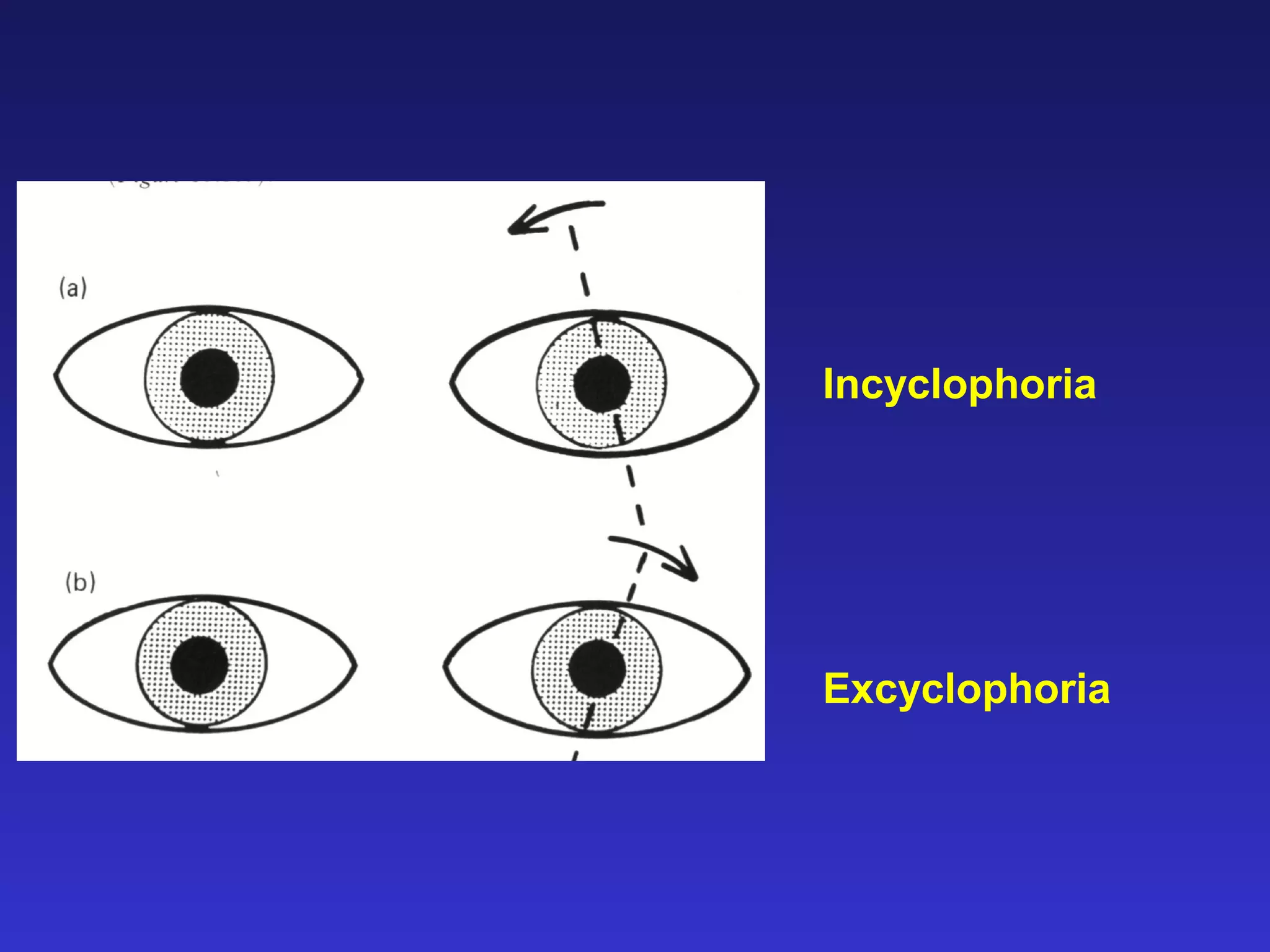
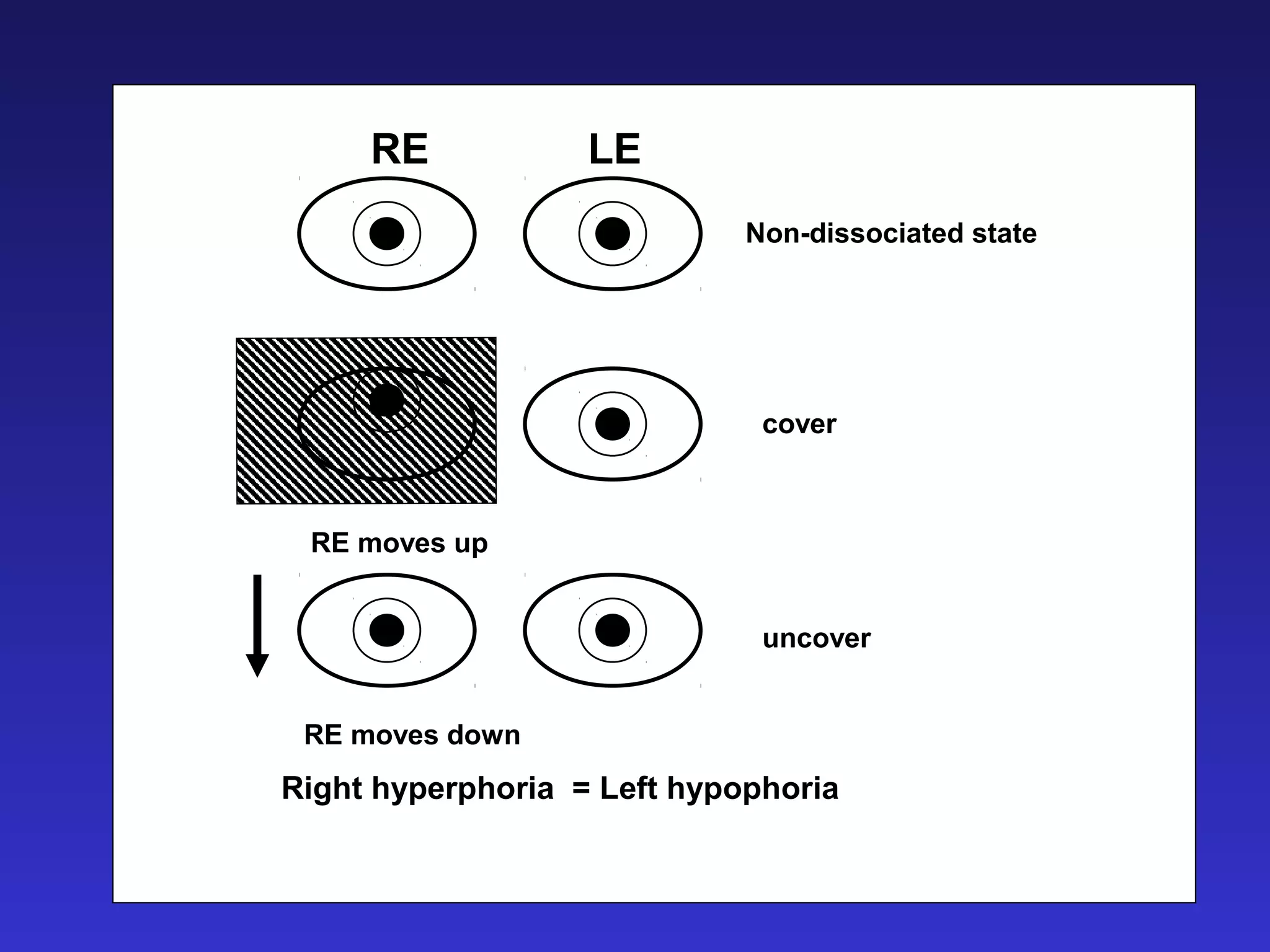
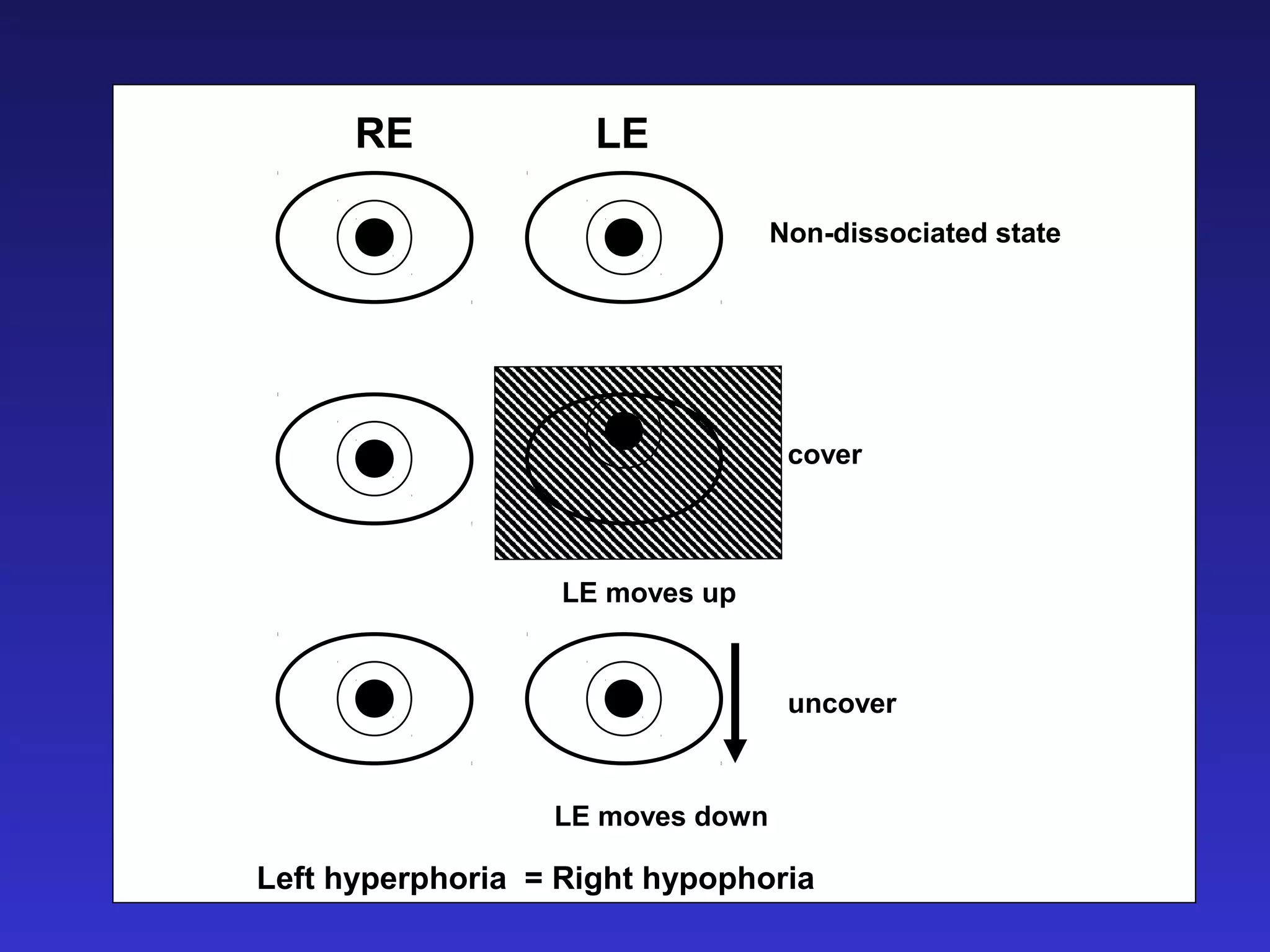
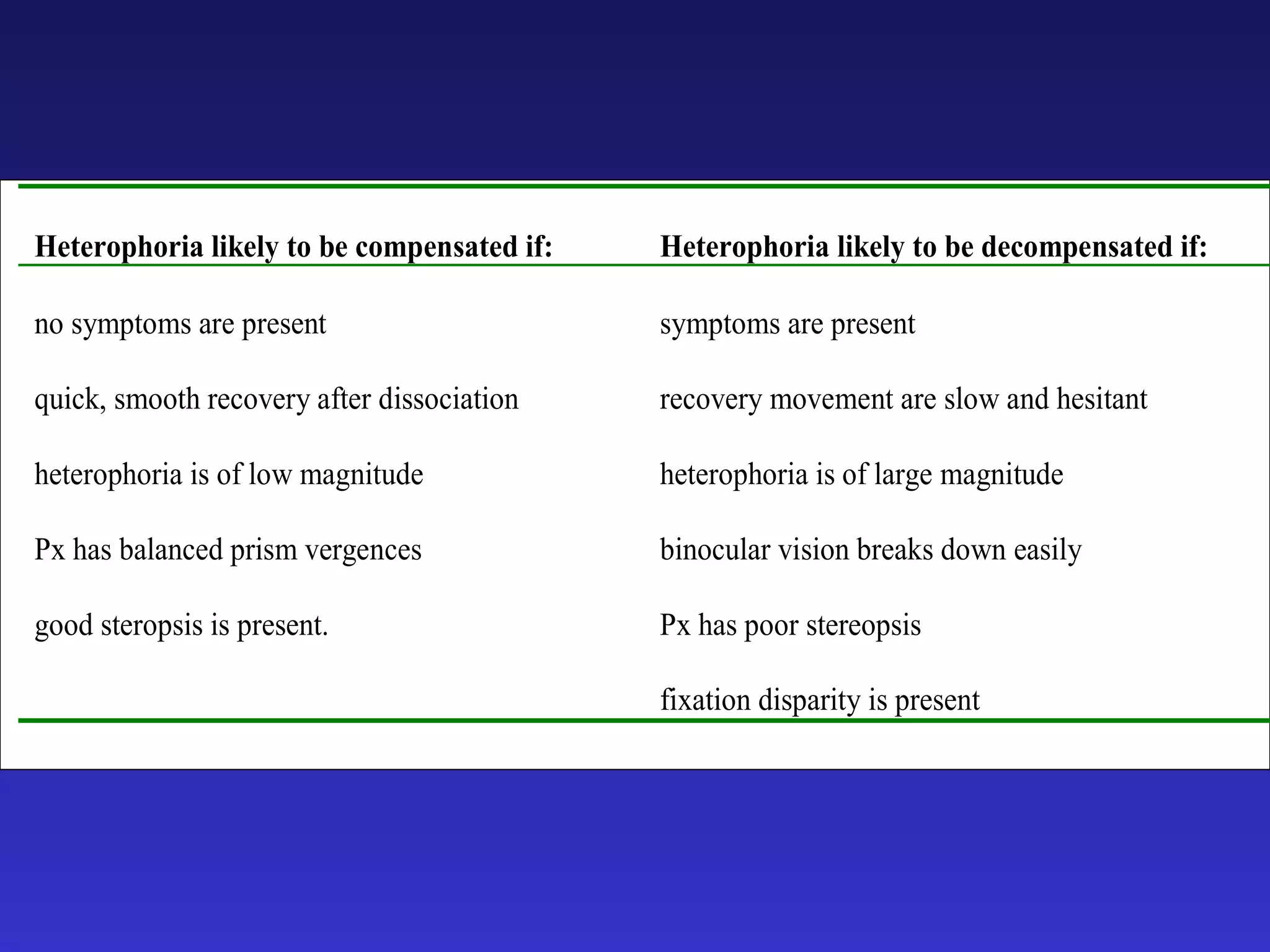
Heterophoria refers to a latent misalignment of the visual axes that is corrected by the fusion reflex. When fusion is suspended, the eyes adopt their "fusion free" position, which may involve esophoria, exophoria, or hyperphoria. Heterophorias can be classified based on direction, fixation distance, compensated vs decompensated state, and cause such as anatomical, neurogenic, or accommodative factors. Most people have some degree of heterophoria, though large or decompensated heterophorias may cause symptoms like asthenopia or headaches.