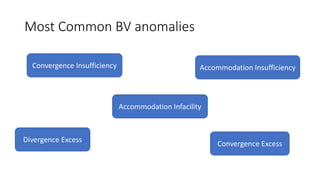
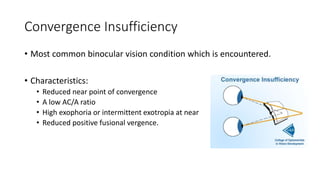
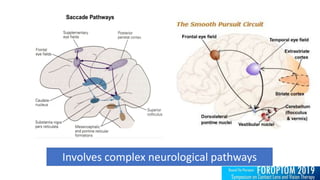
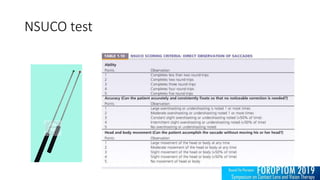
1) Common binocular vision disorders like convergence insufficiency, accommodative excess, and oculomotor dysfunctions are often neglected despite potentially having a significant negative impact on patients' lives.
2) Proper testing and diagnosis of these conditions is important, as treatment like vision therapy can help patients succeed academically and socially by improving their binocular vision.
3) Neglecting binocular vision issues can lead to problems like learning disabilities, loss of academic motivation, and potentially worsening eye alignment if left untreated.