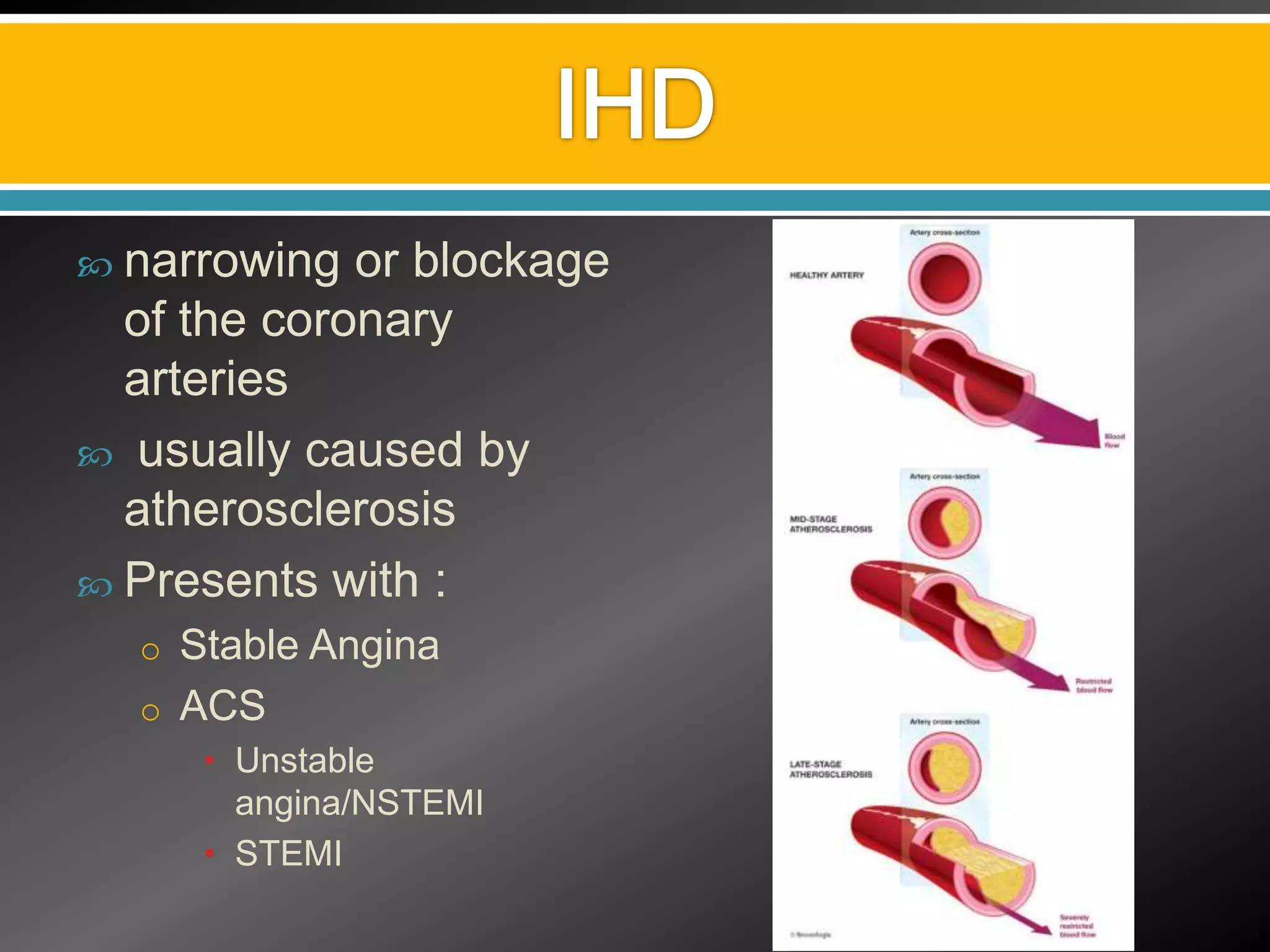
This document discusses various aspects of ischemic heart disease (IHD) including:
1) Causes, symptoms, and diagnostic tests for IHD including angiography, echocardiography, and exercise ECG.
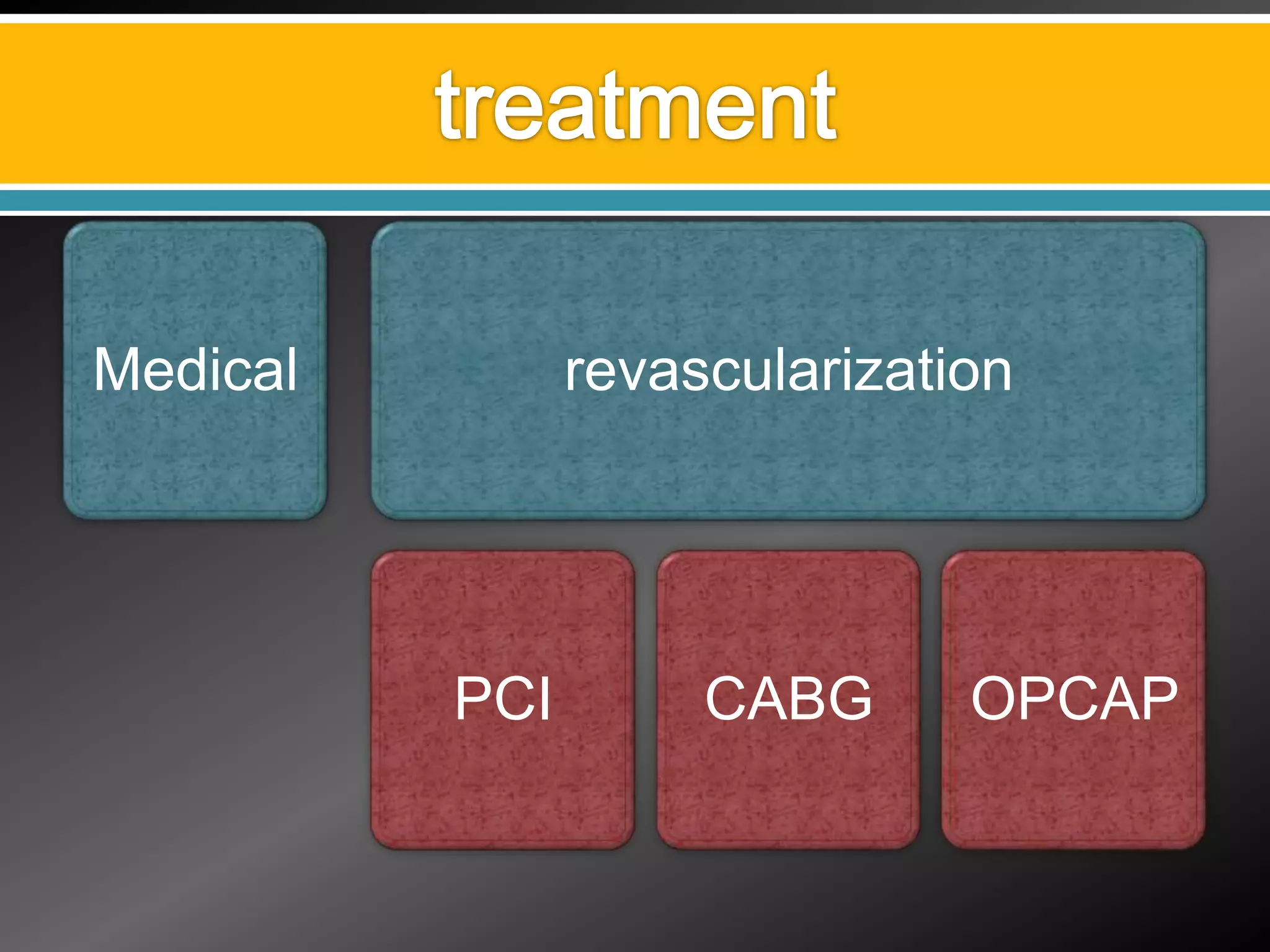
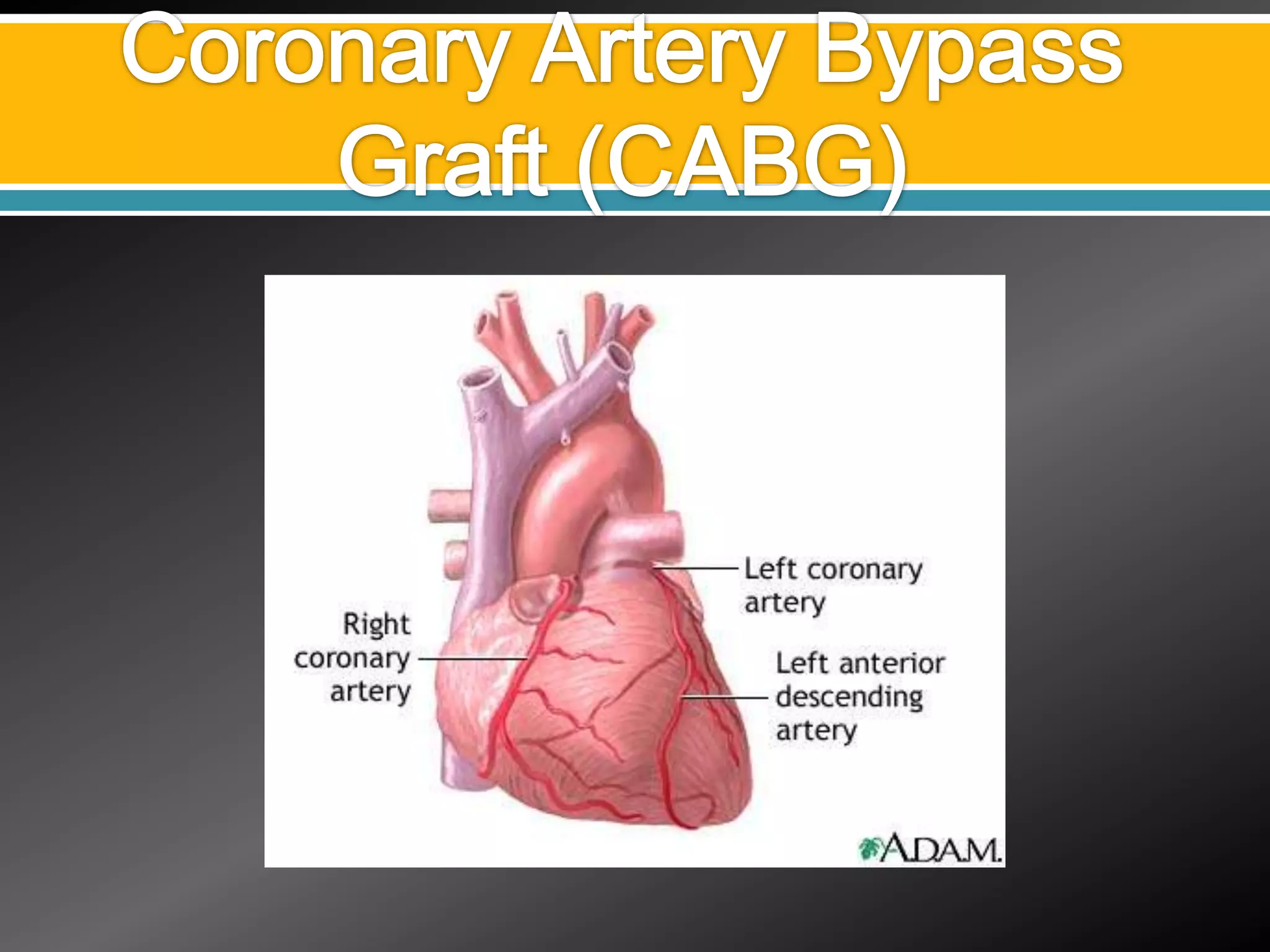
2) Treatment options for IHD including medical management, percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI), coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG), and off-pump CABG.
3) Surgical complications of IHD and their management through procedures like mitral valve repair, ventricular septal defect repair, and left ventricular aneurysm repair.