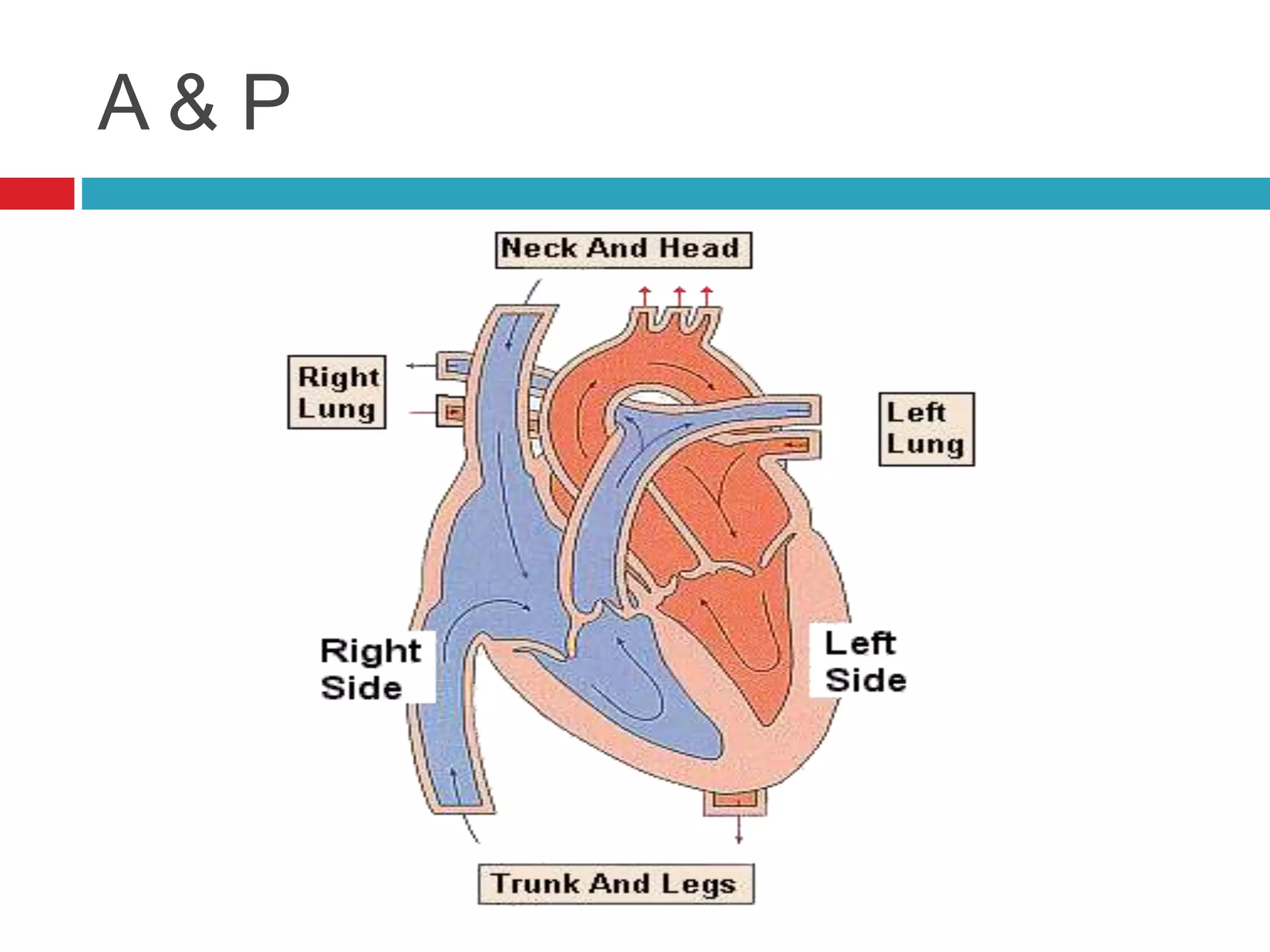
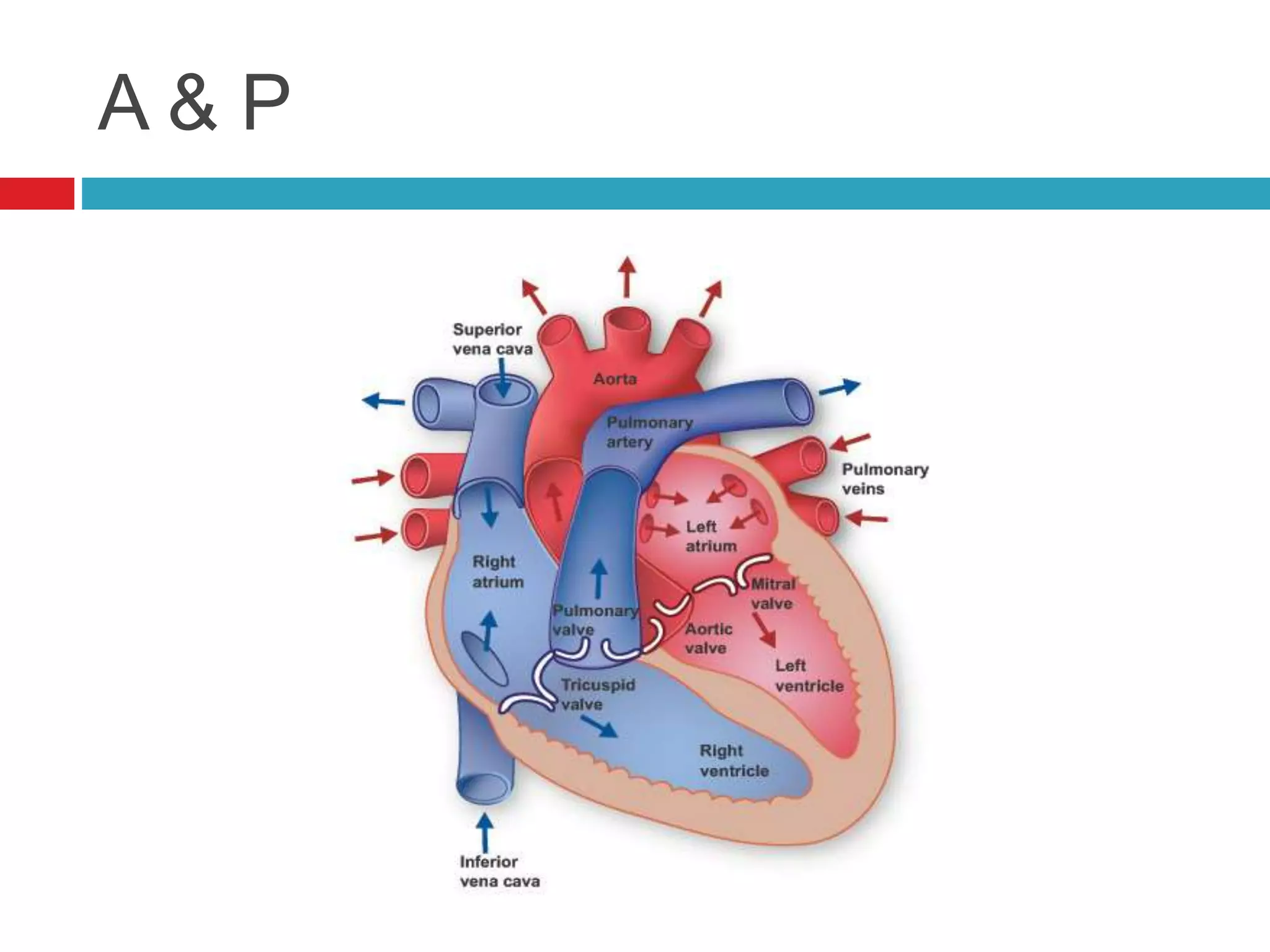
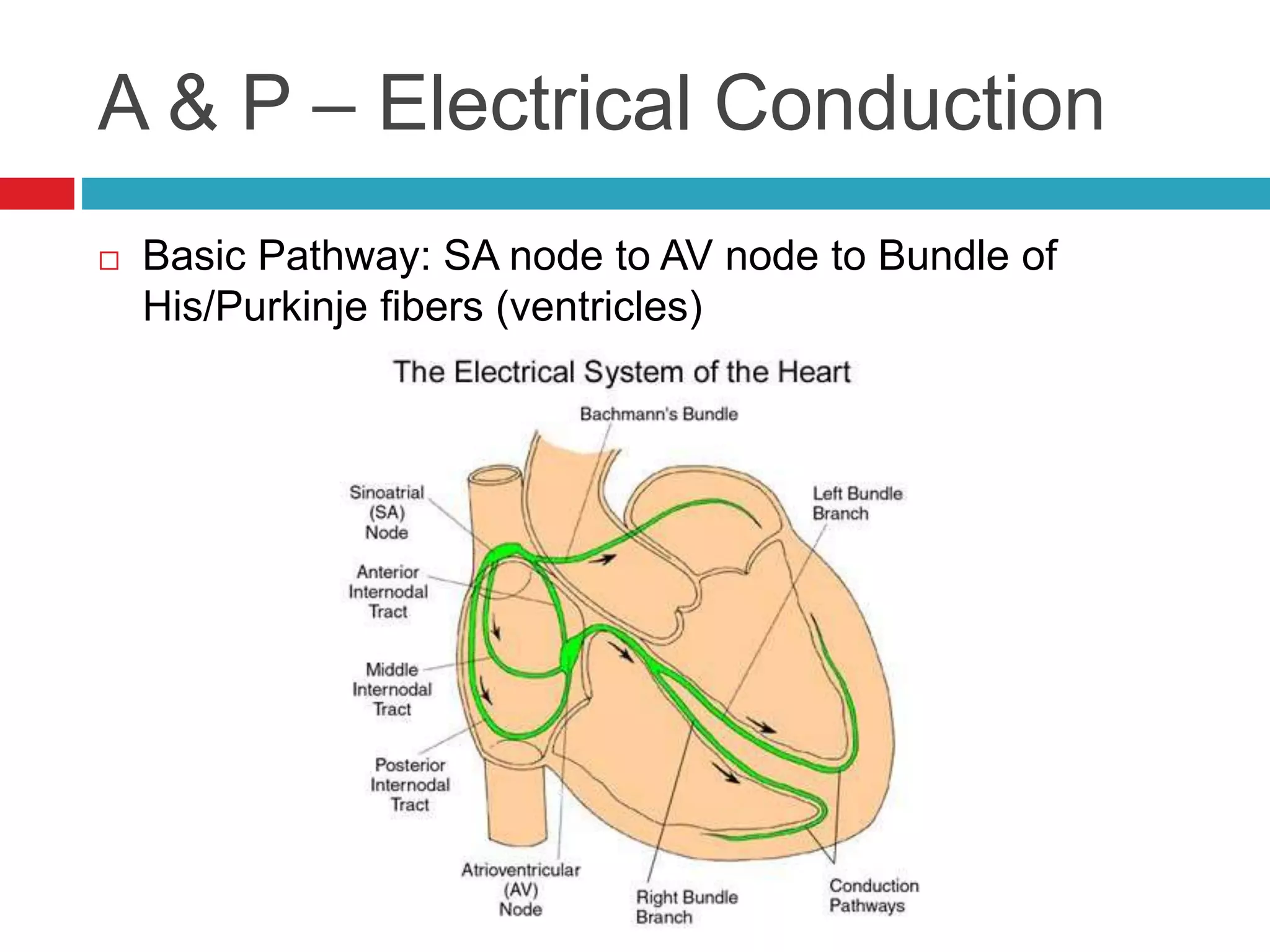
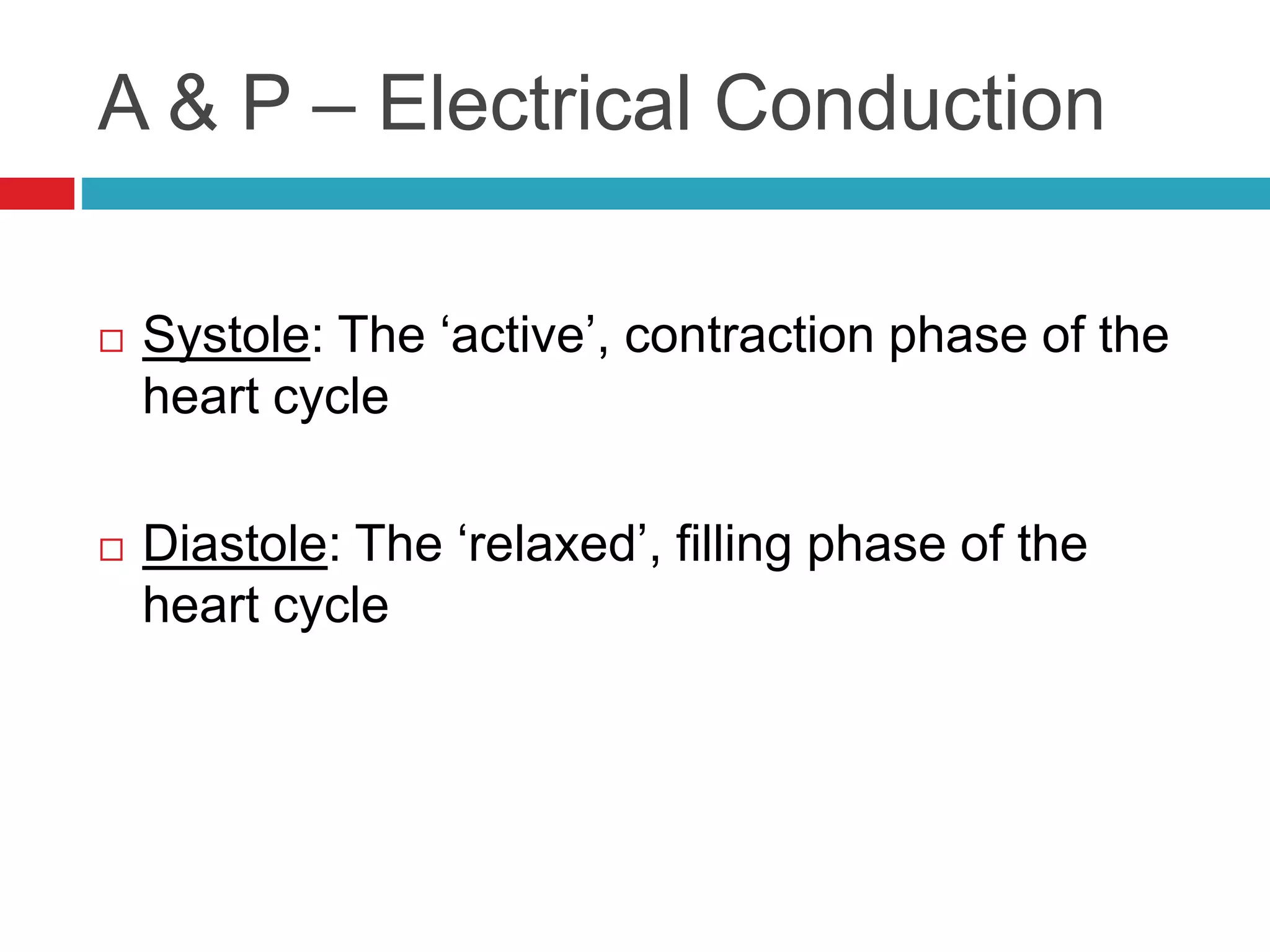
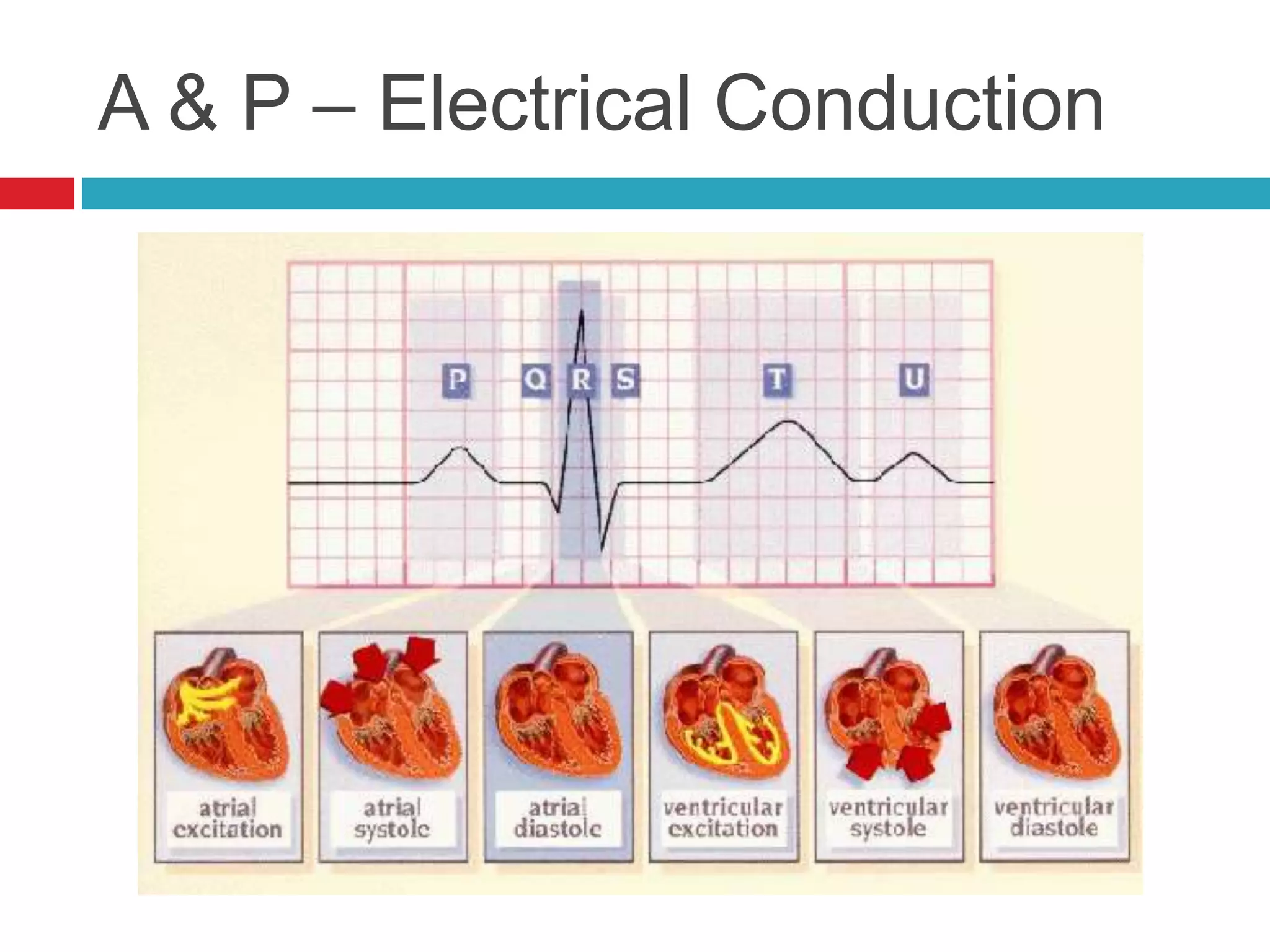
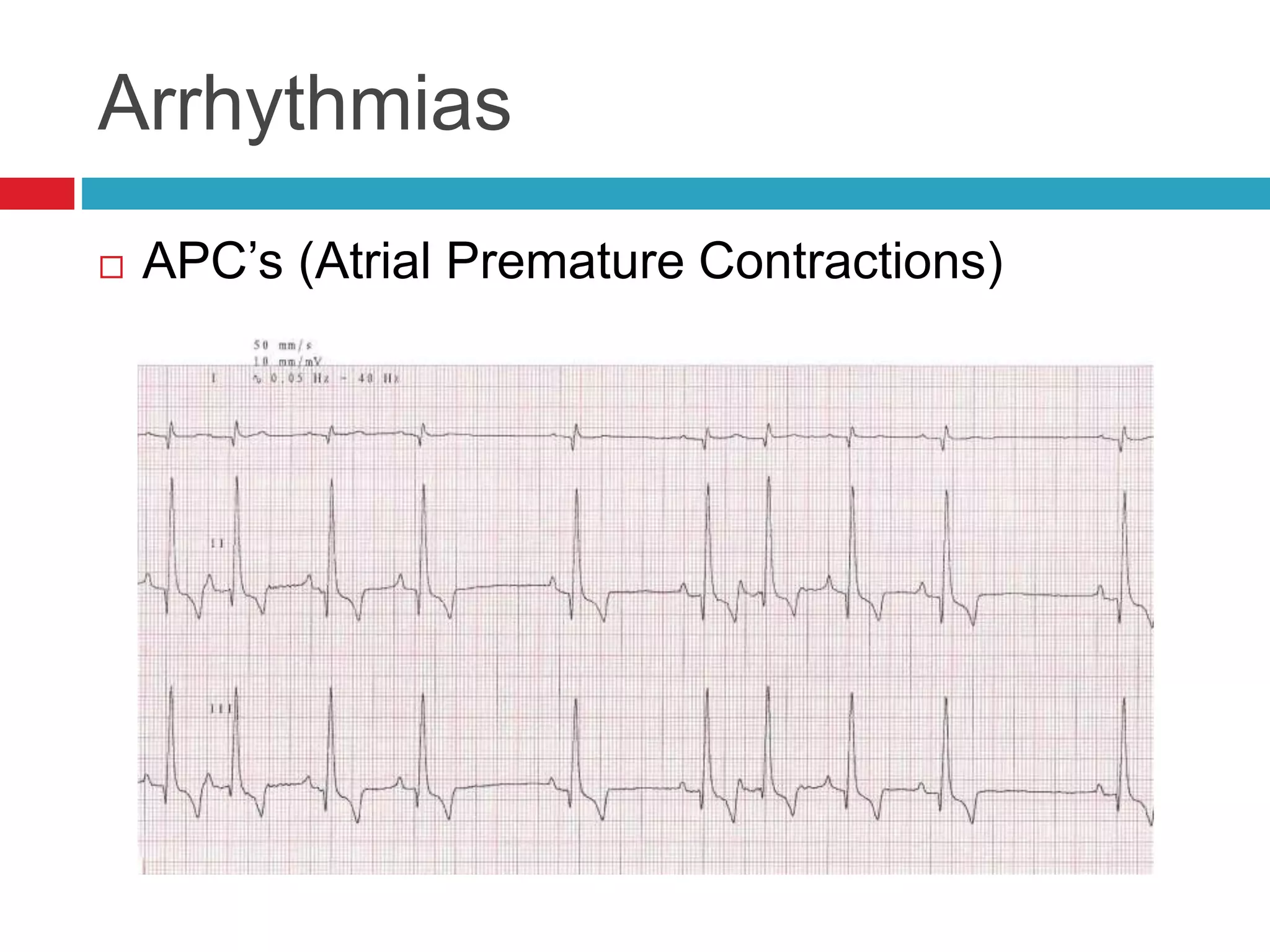
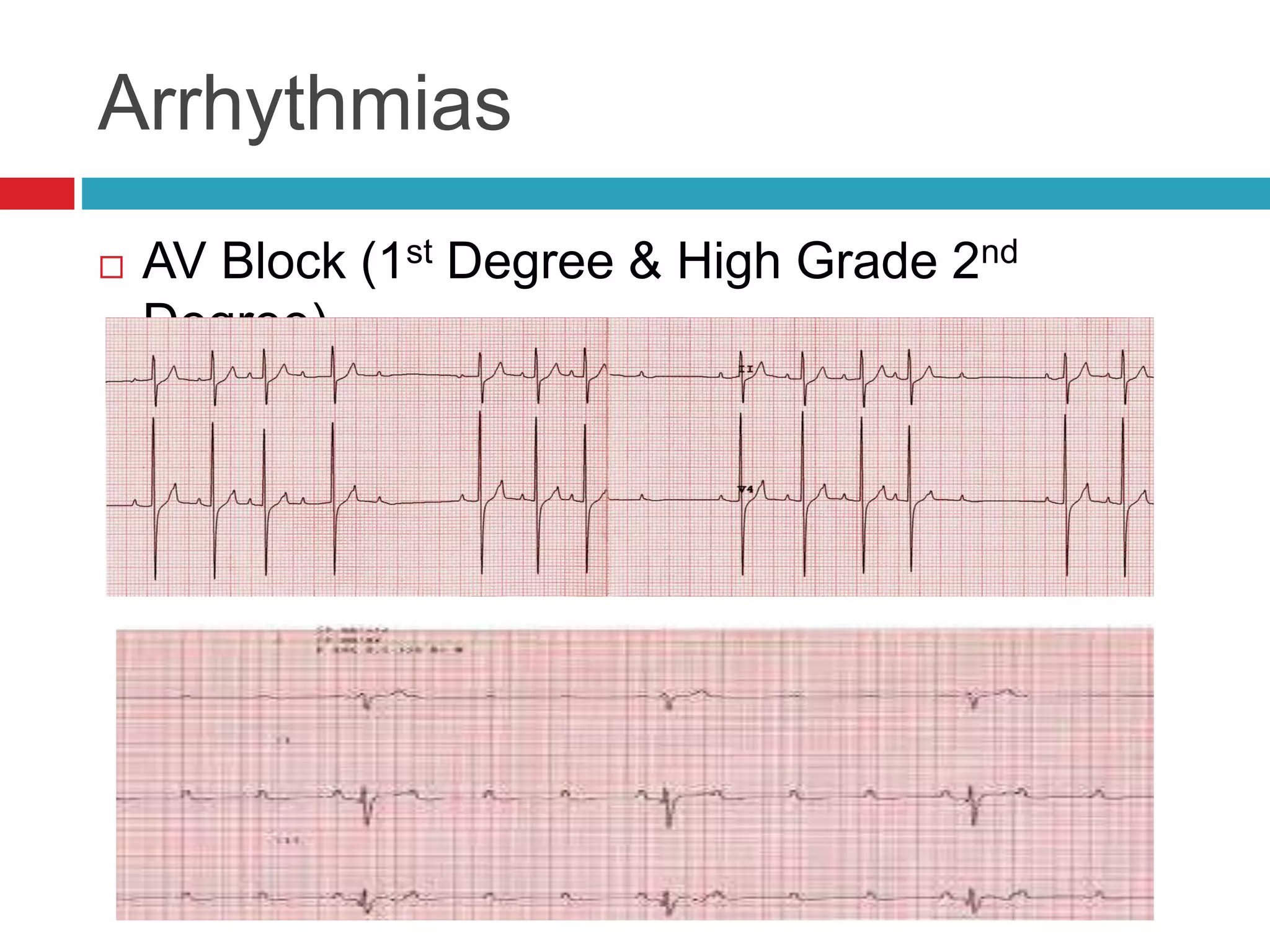
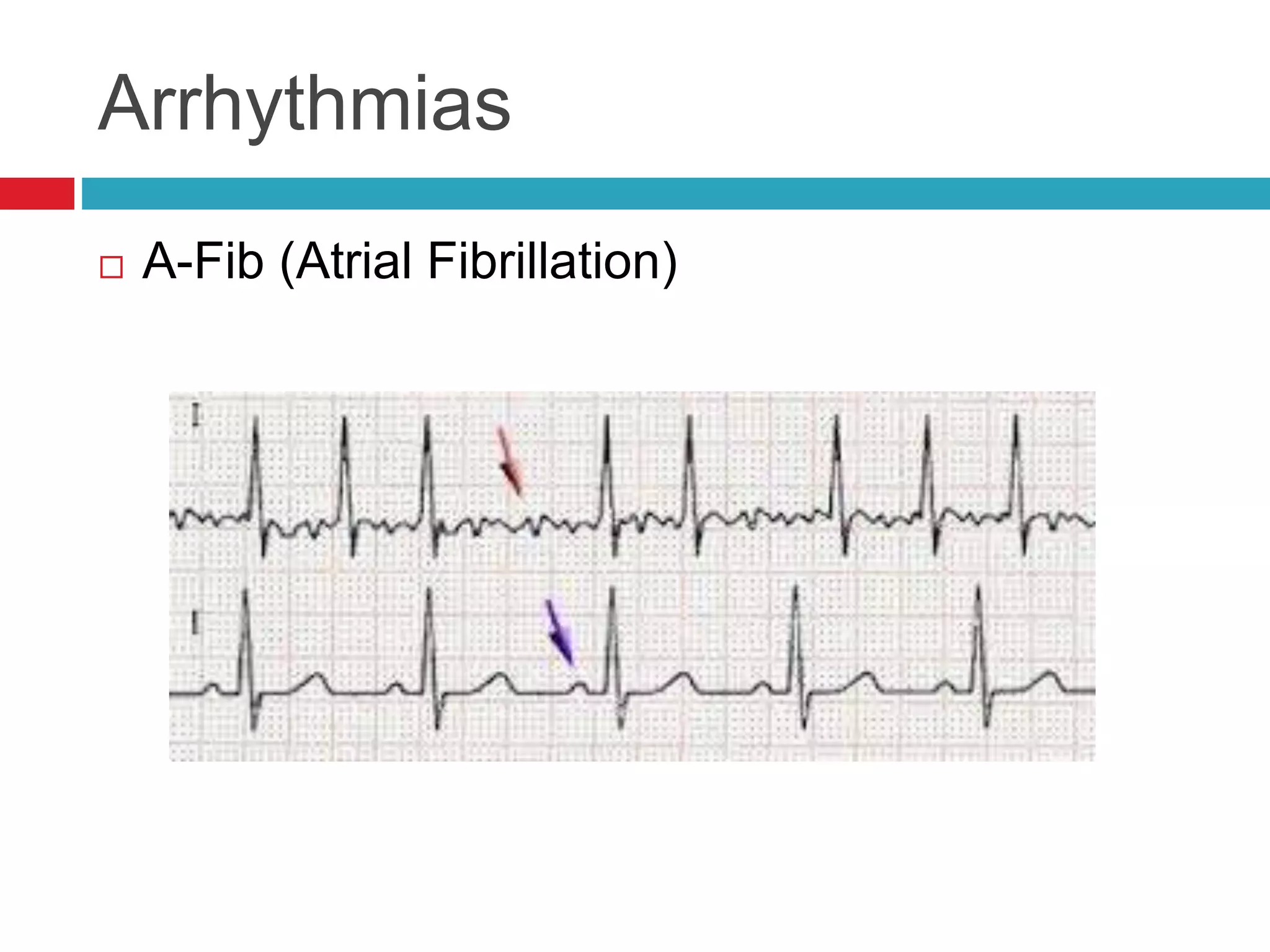
The document provides an overview of cardiology basics and the physical exam of the heart. It discusses the importance of the heart in pumping blood and removing waste. Key points include:
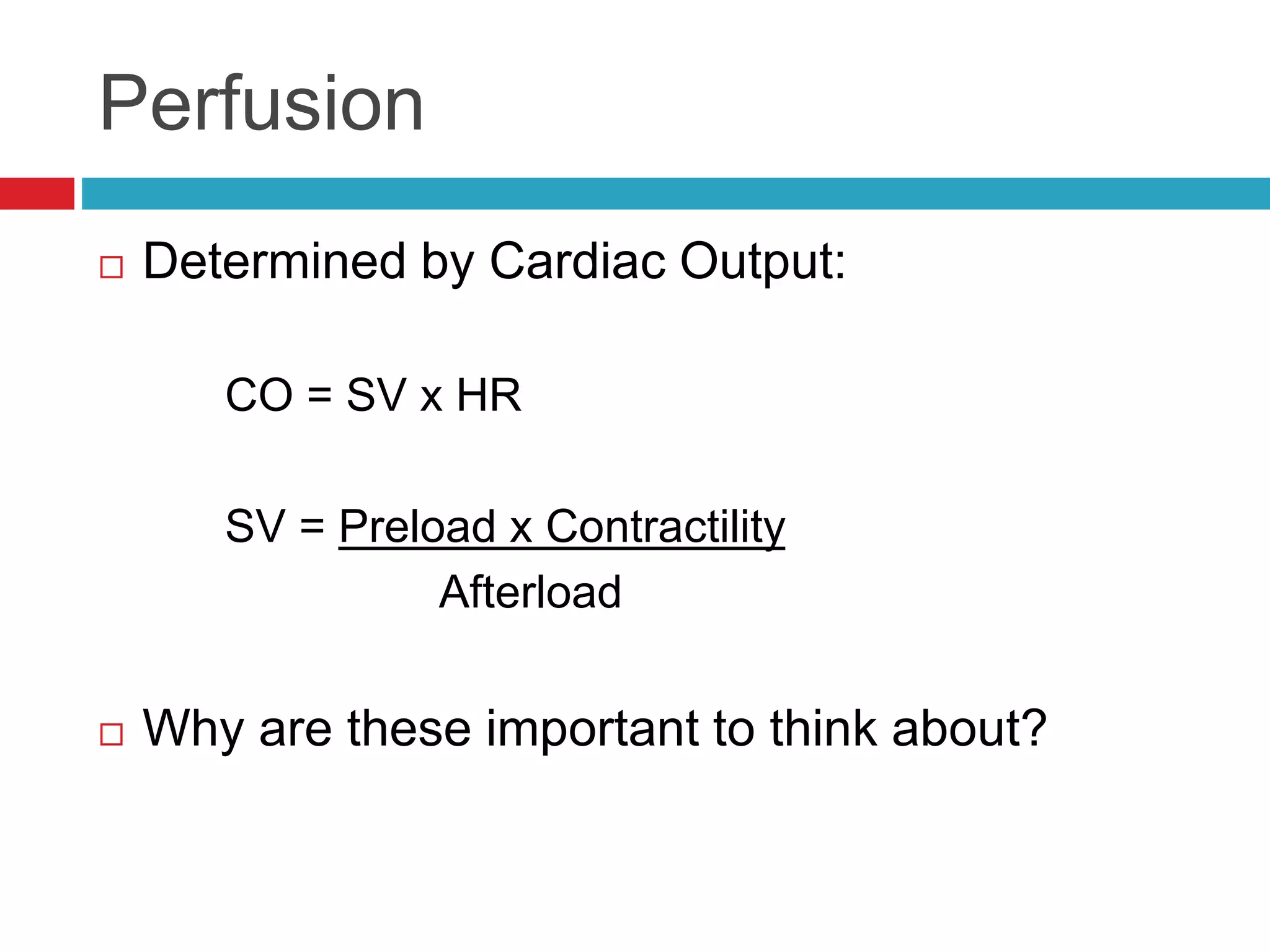
- The heart's function is determined by cardiac output, which depends on stroke volume and heart rate.
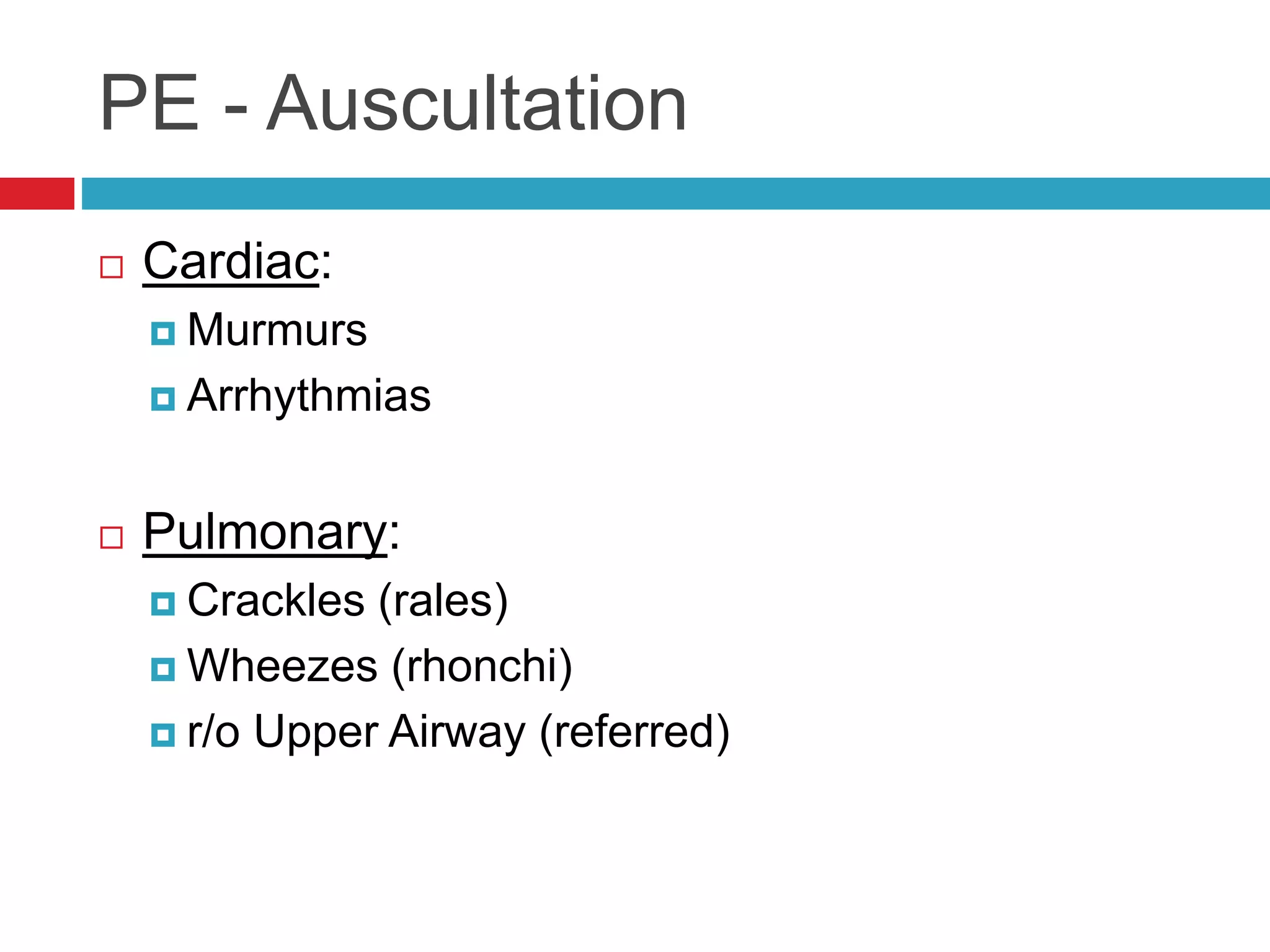
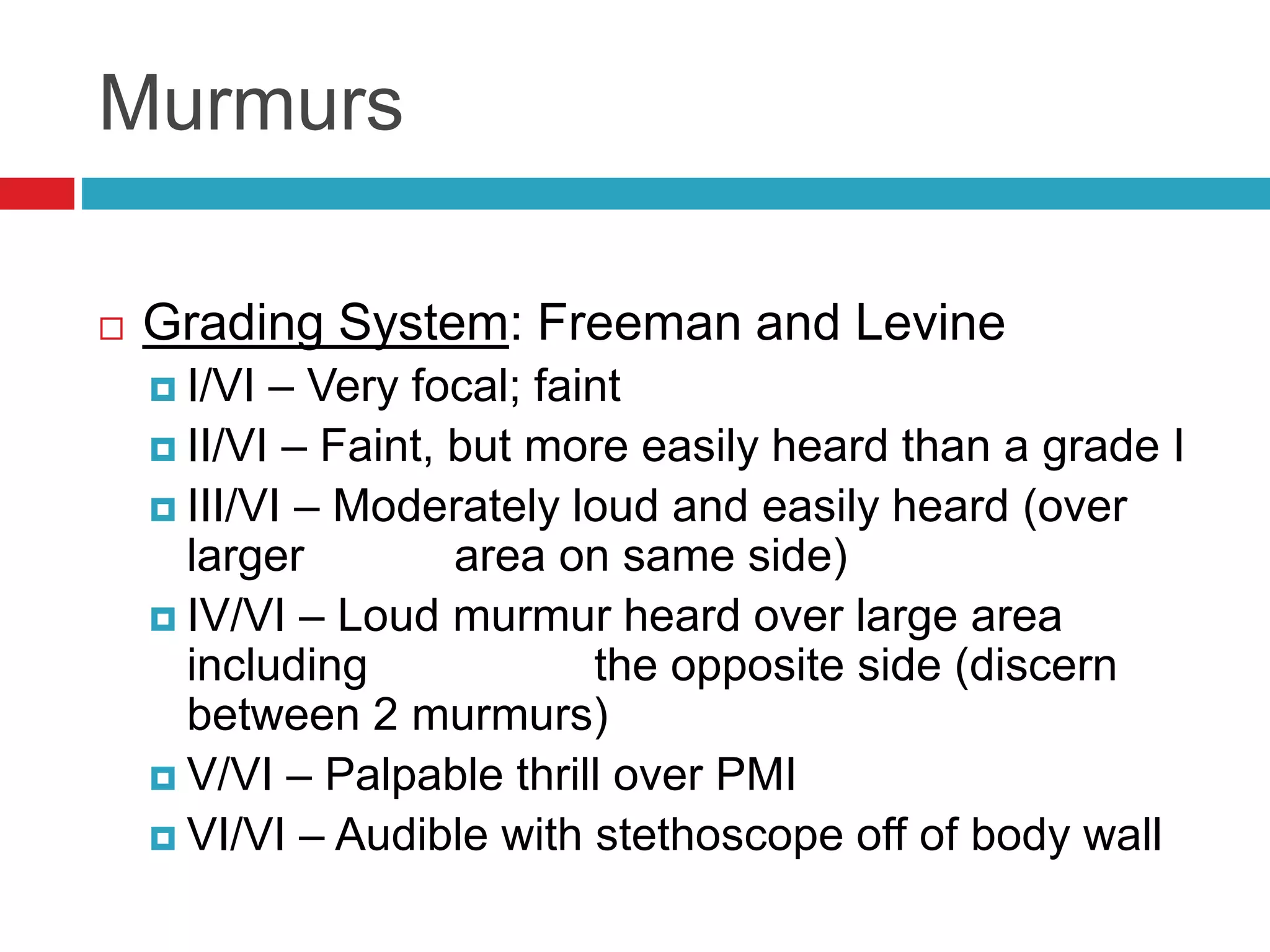
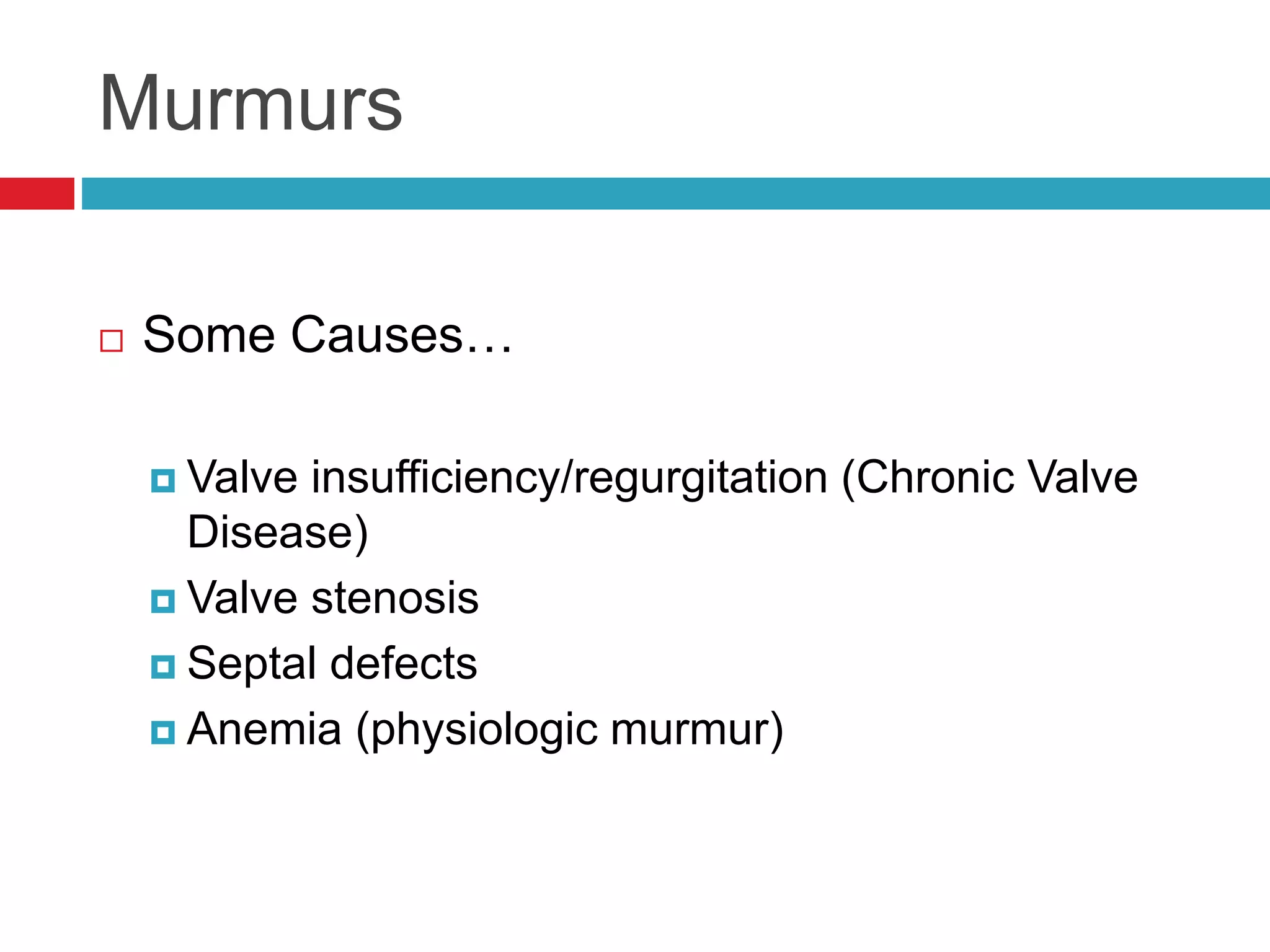
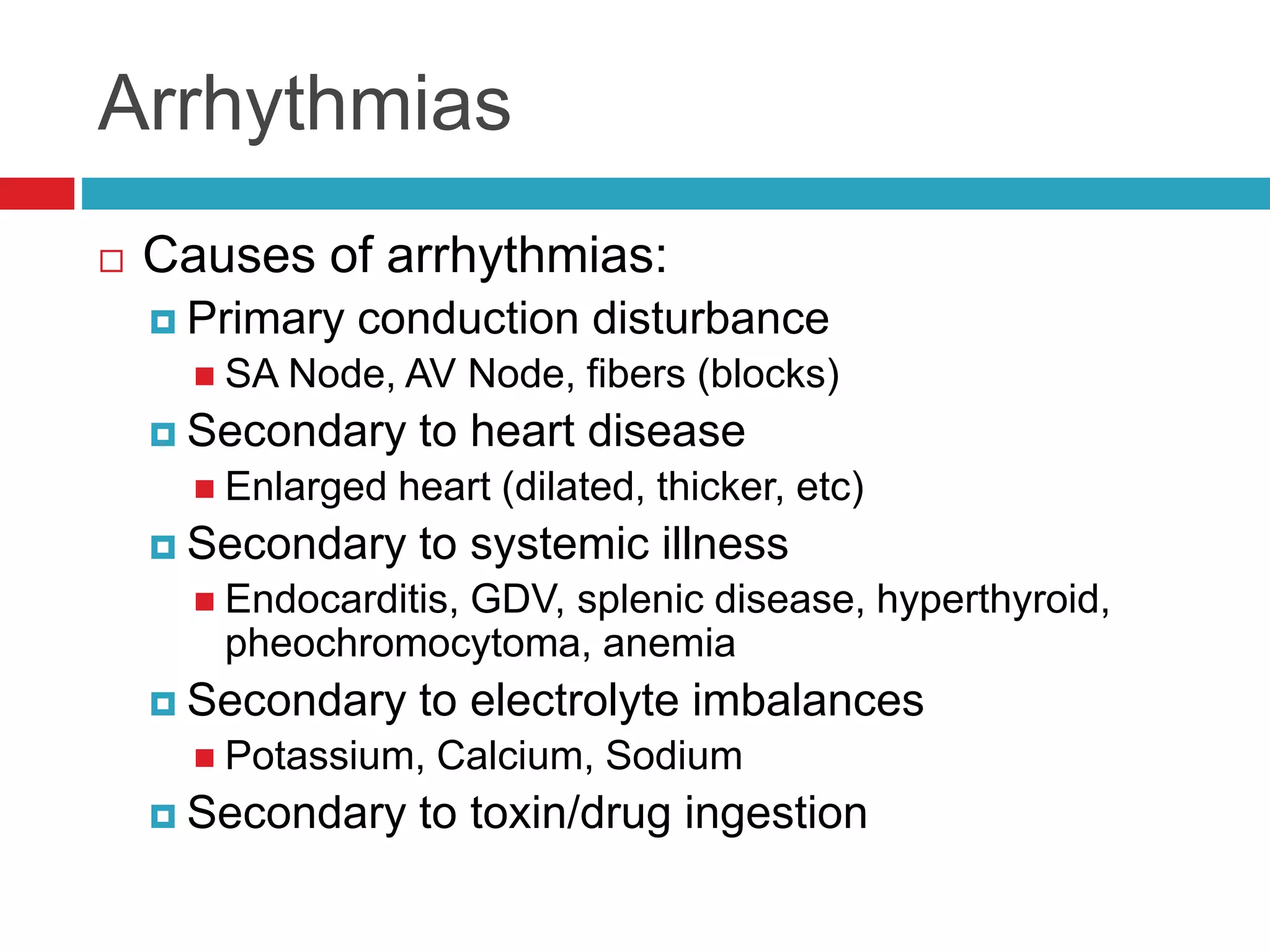
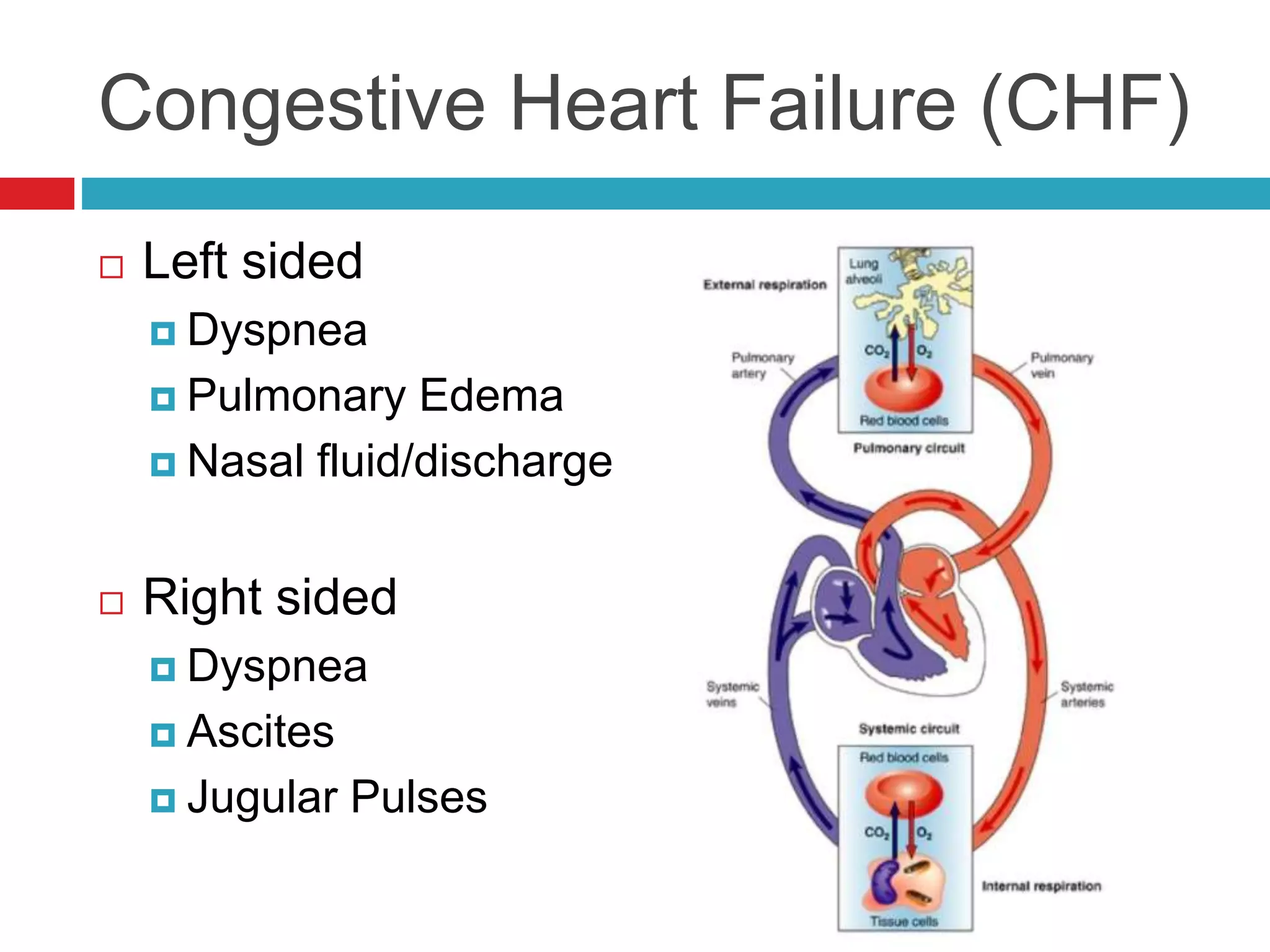
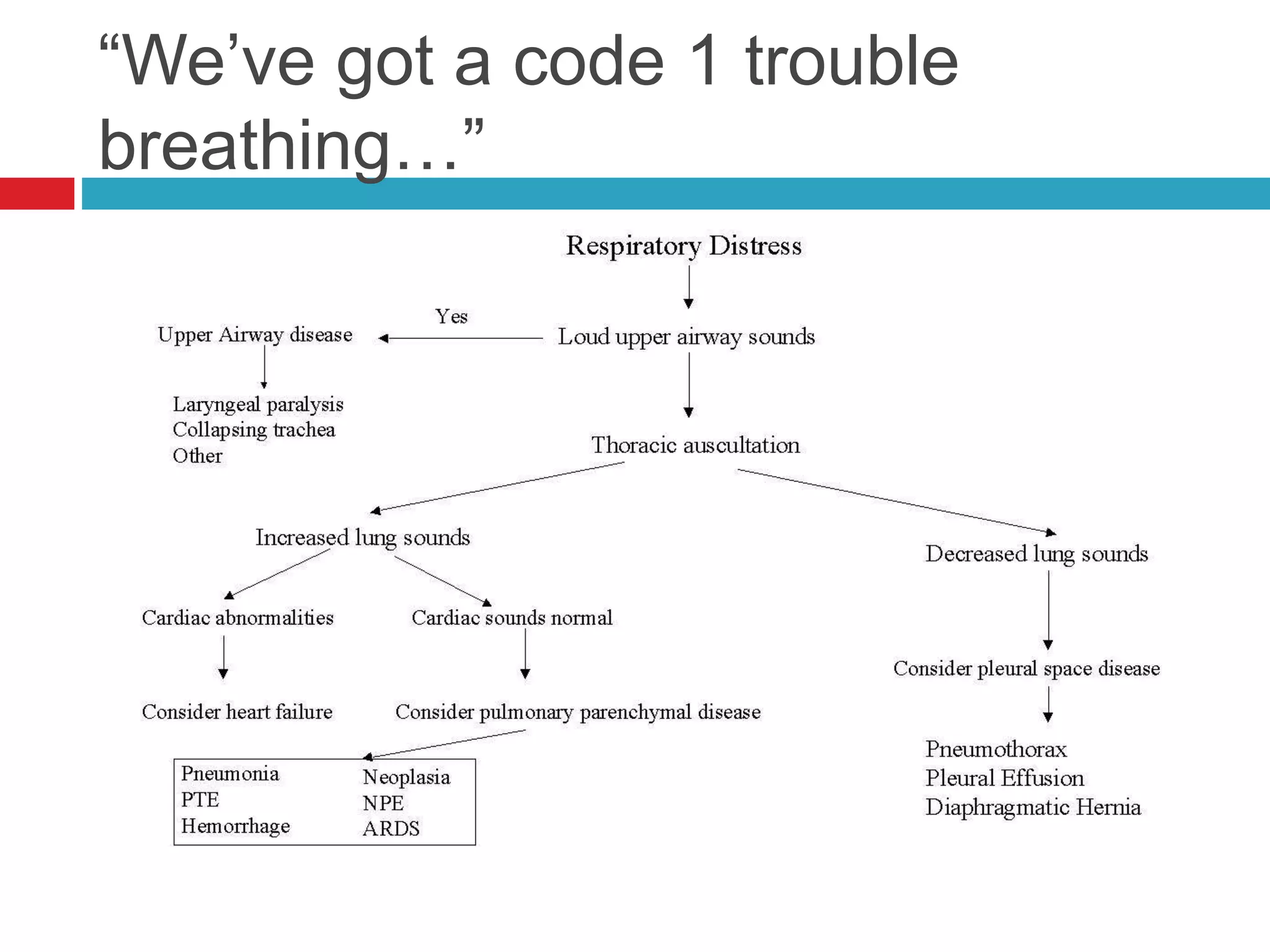
- Auscultation of heart sounds can detect murmurs or arrhythmias while lung sounds may reveal crackles or wheezes.
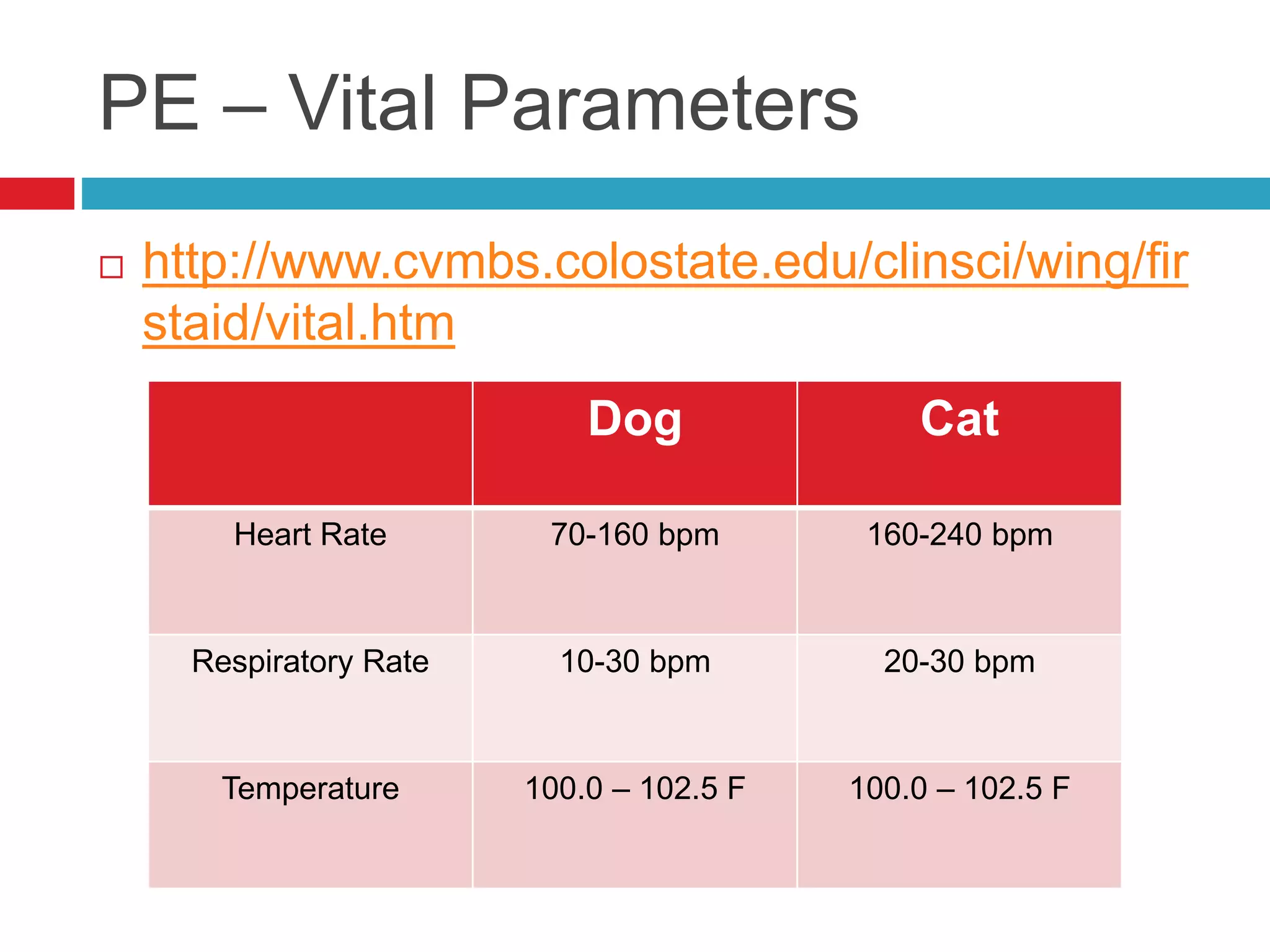
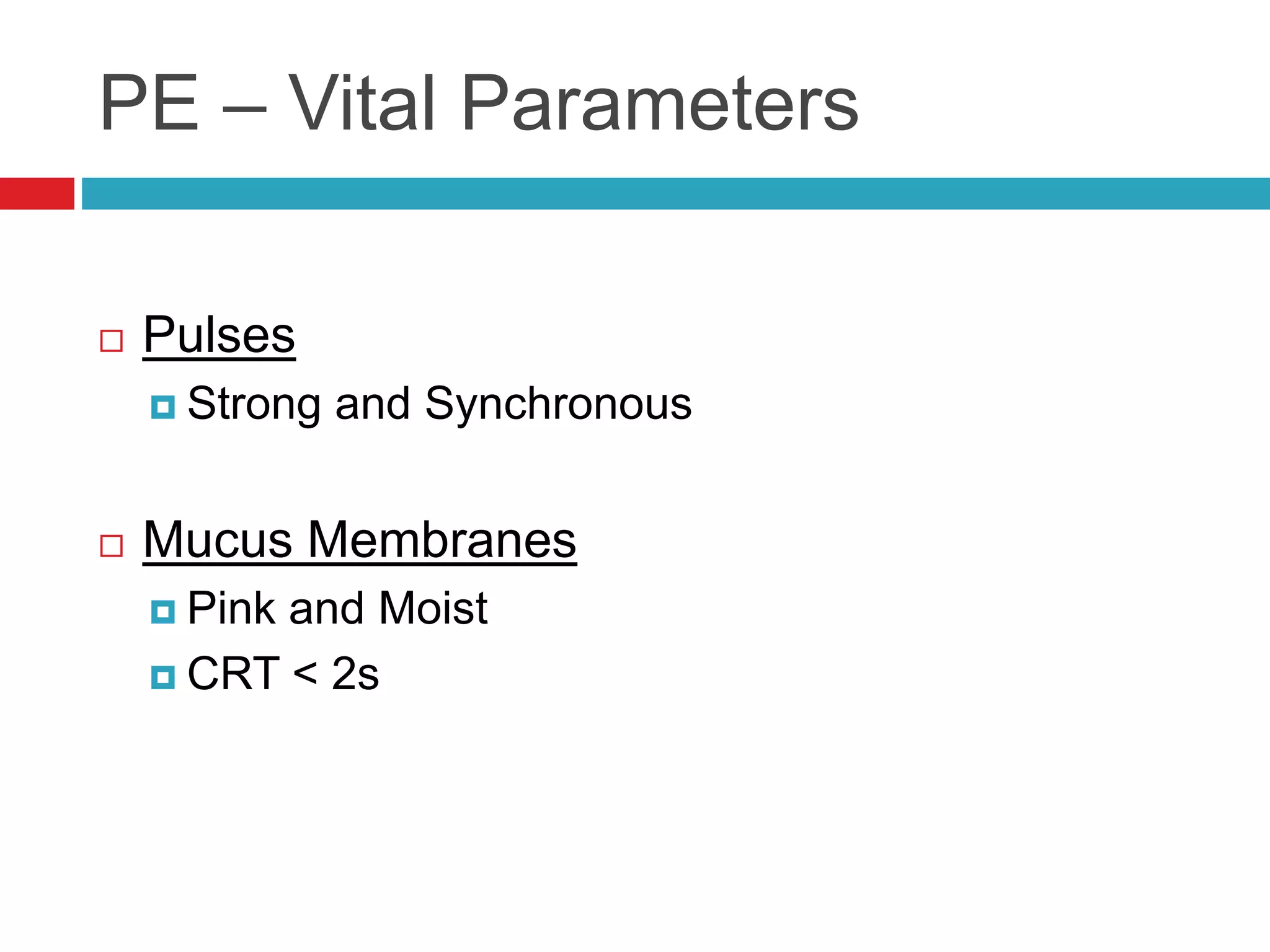
- Physical exam also involves assessing vital parameters and looking for signs of dyspnea or weakness.
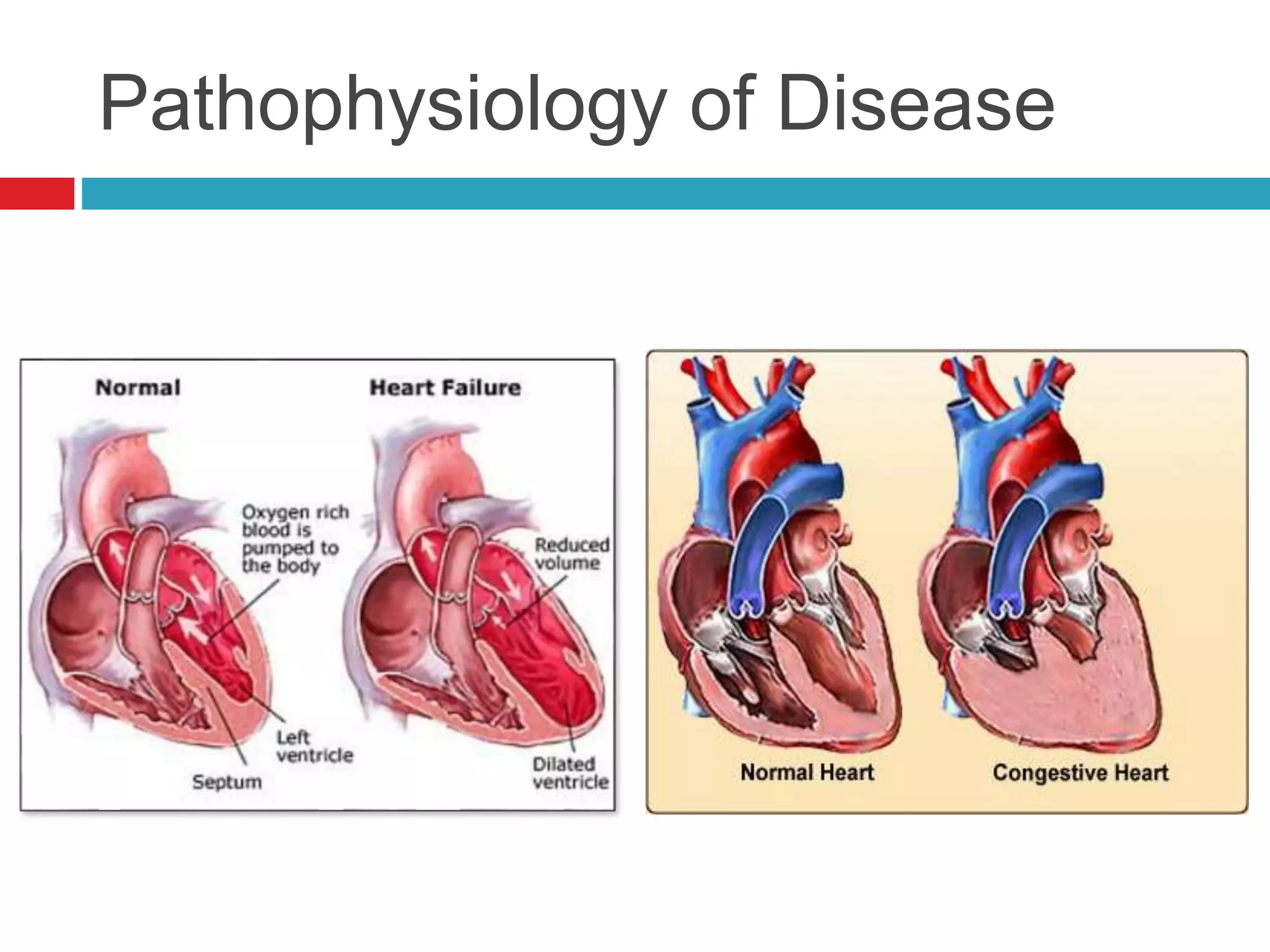
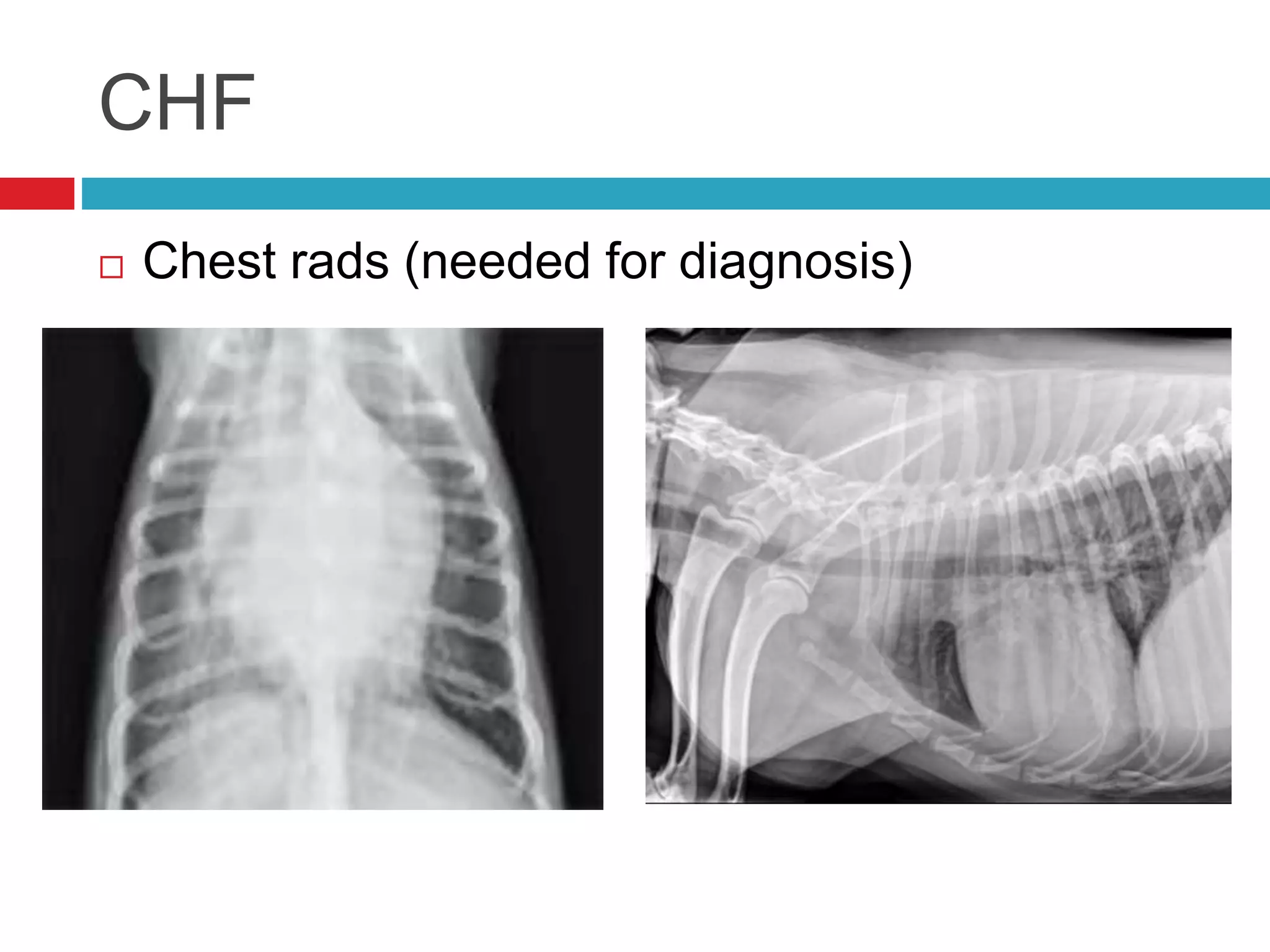
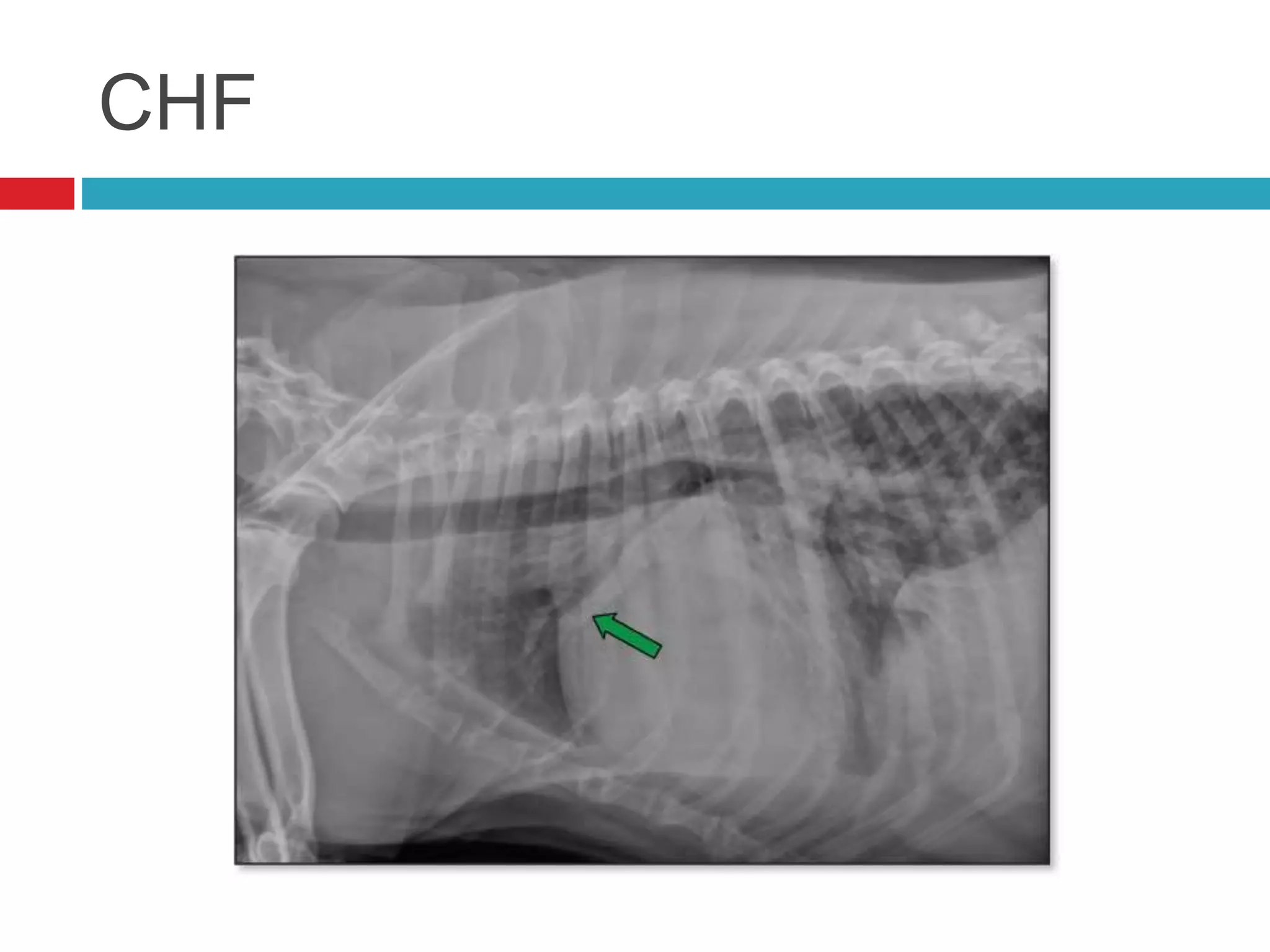
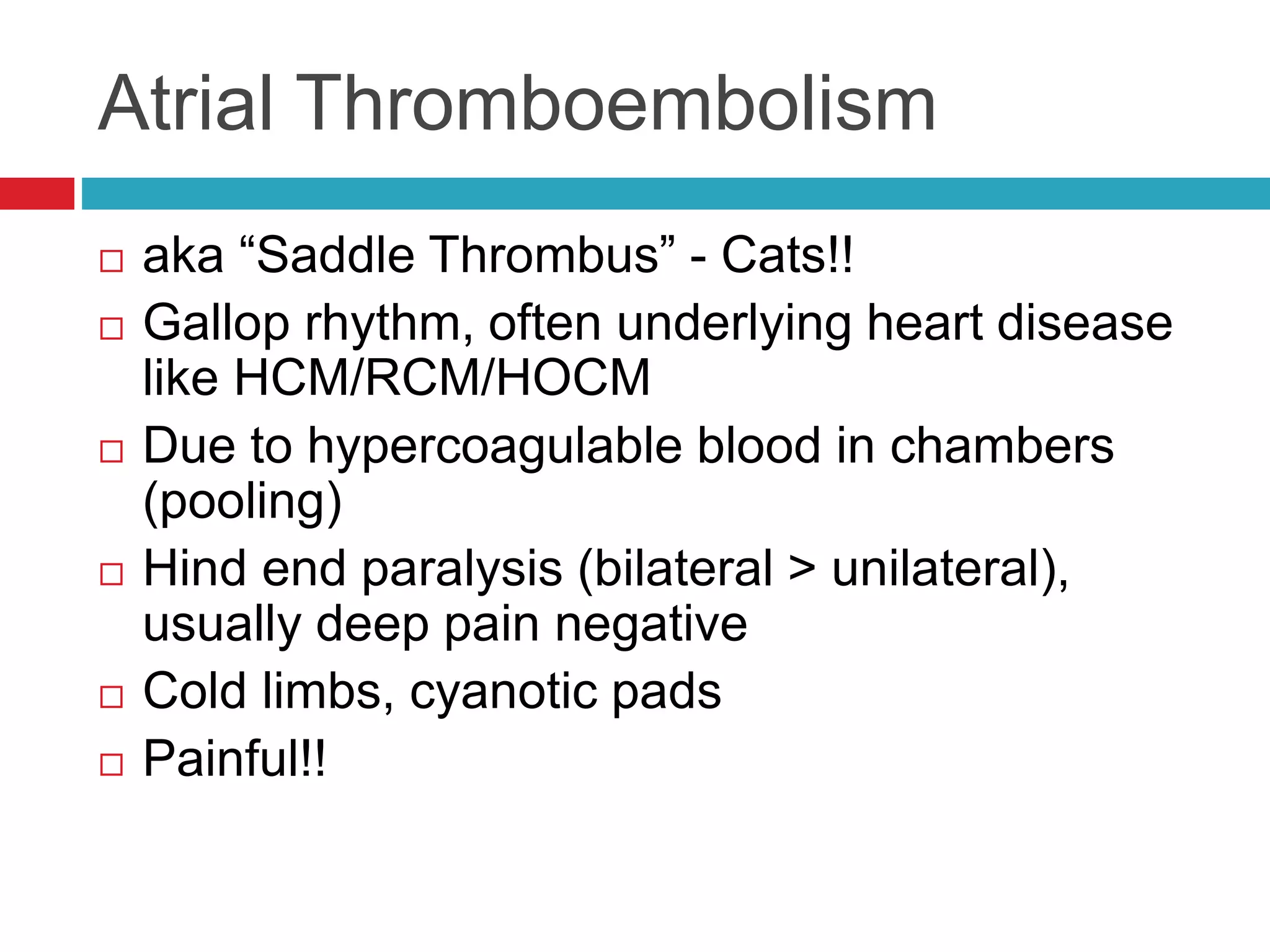
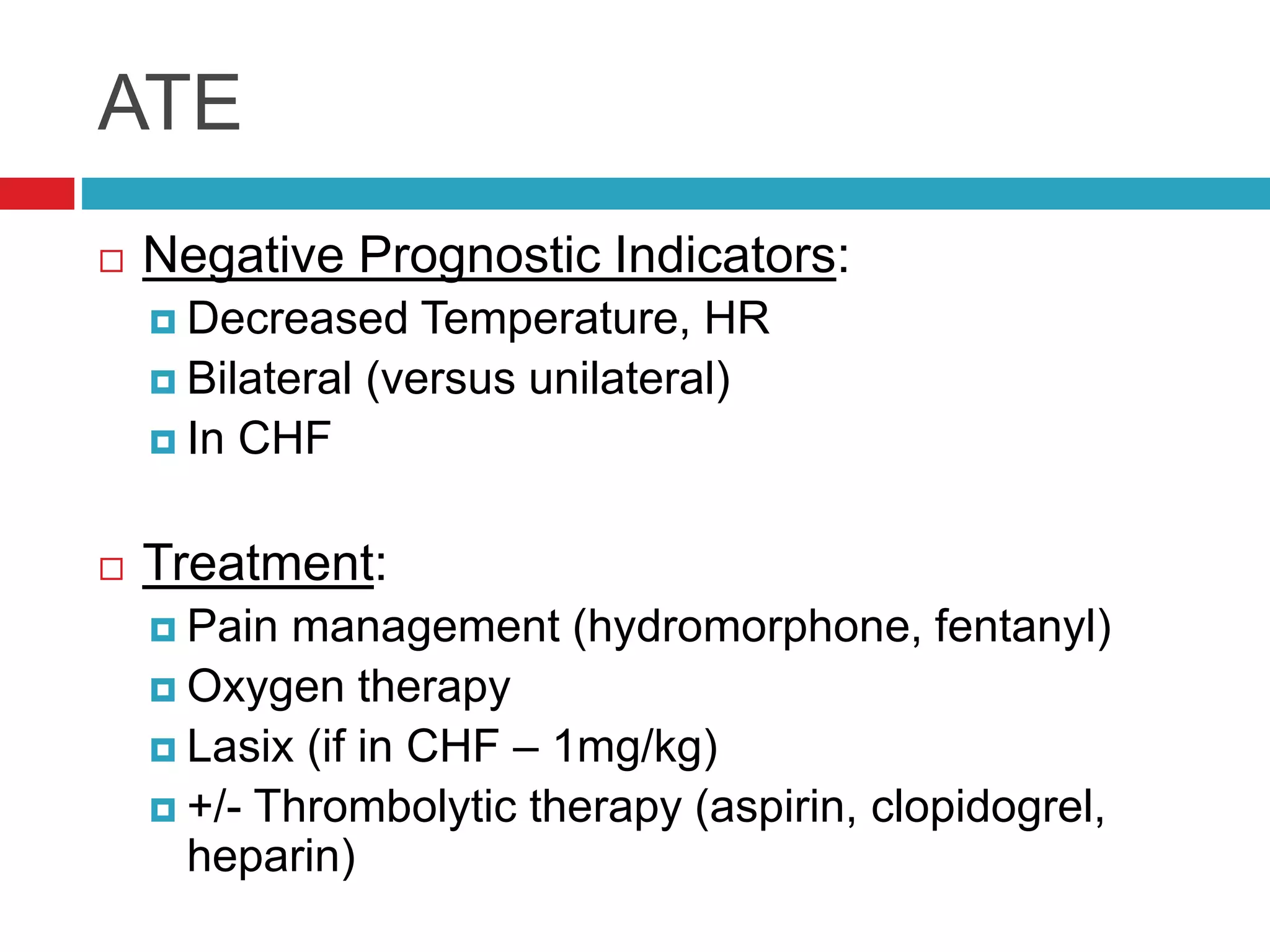
- Common cardiac conditions addressed include murmurs, arrhythmias, congestive heart failure, and atrial thromboembolism in cats.