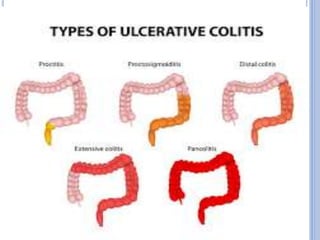
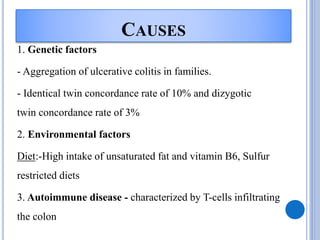
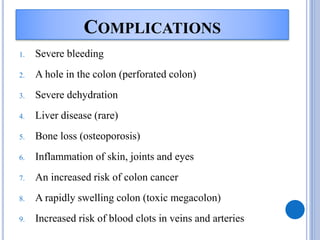
Ulcerative colitis is a type of inflammatory bowel disease that causes long-lasting inflammation and ulcers in the digestive tract, specifically the inner lining of the large intestine and rectum. It has various types defined by the parts of the colon affected. The causes include genetic and environmental factors such as diet as well as it being an autoimmune disease. Symptoms include bloody diarrhea, abdominal pain, and weight loss. Diagnosis involves medical history, physical exam, blood tests, stool culture, sigmoidoscopy, and biopsies. Treatment consists of medications to reduce inflammation and suppress the immune system, antibiotics, dietary changes, exercise and stress relief. Surgery may be required in severe cases to remove the colon. Nursing care focuses