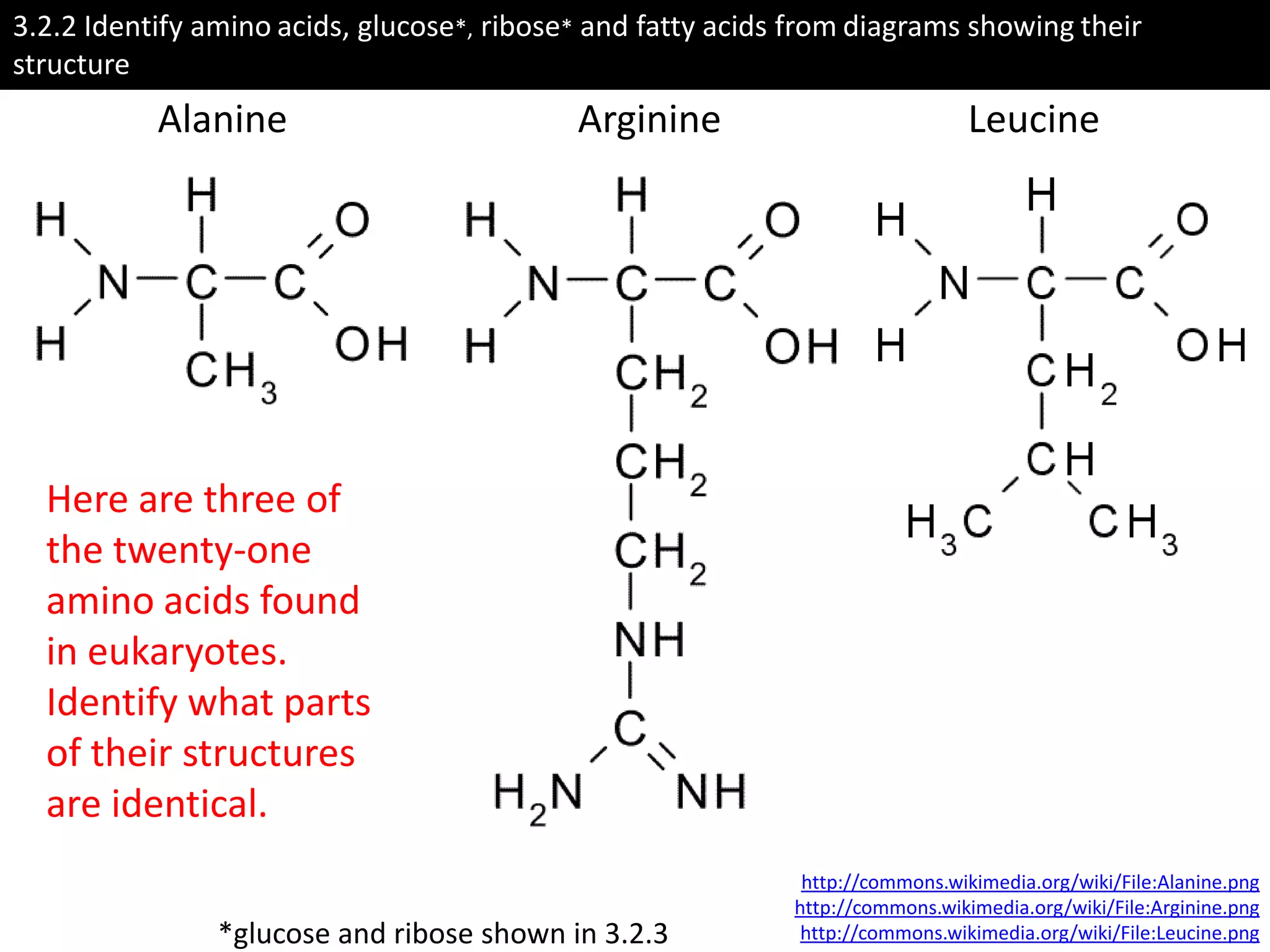
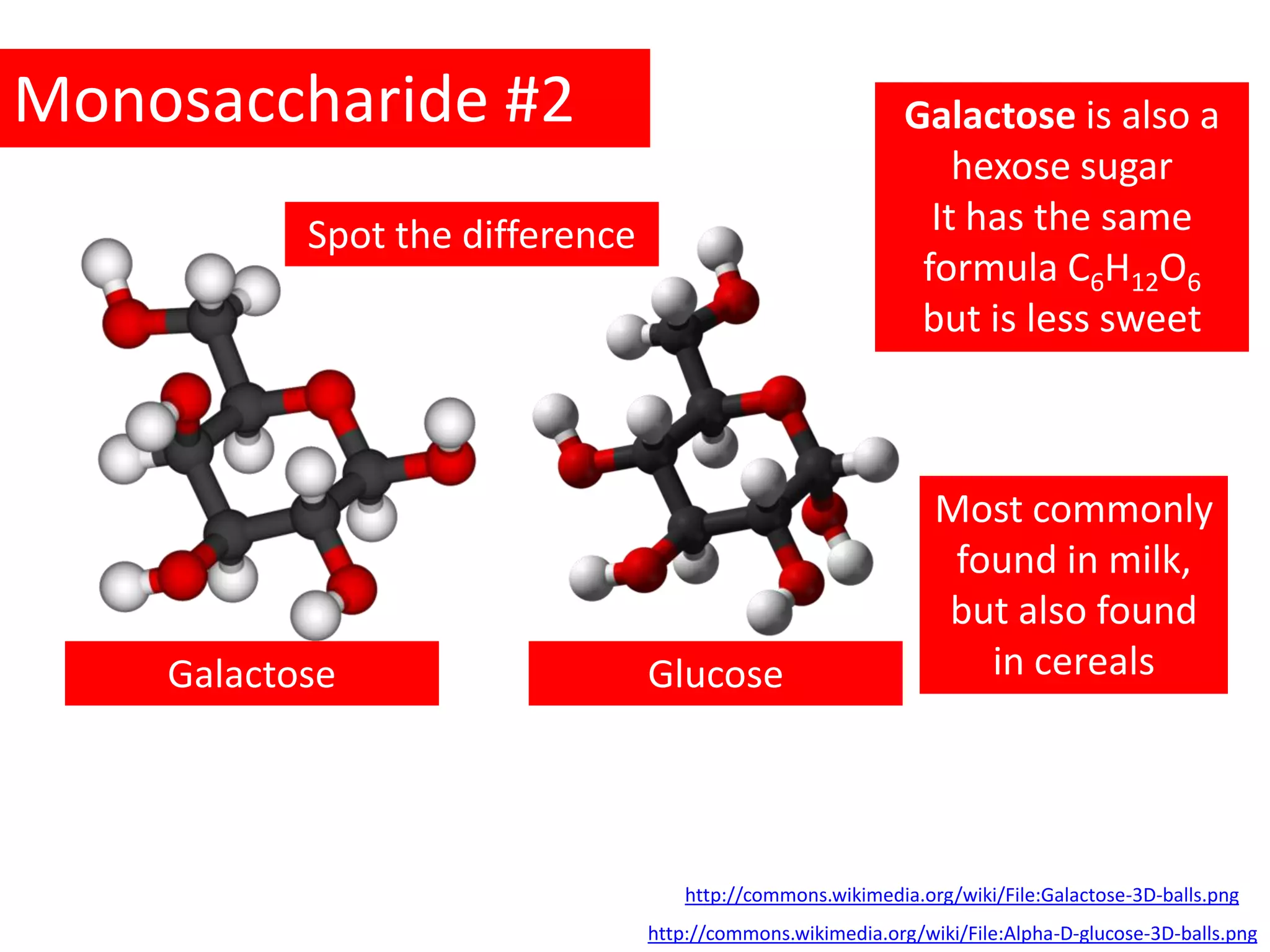
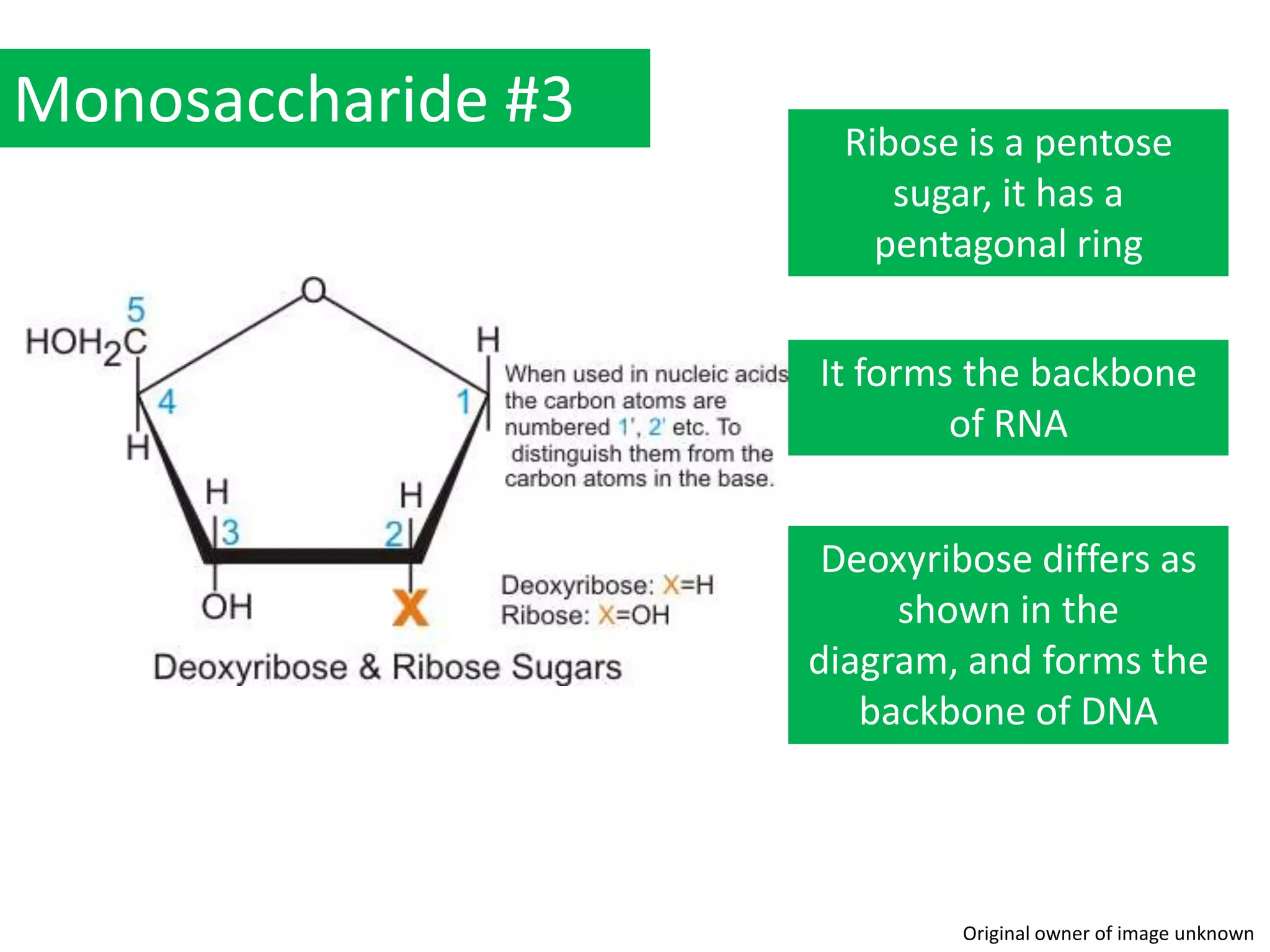
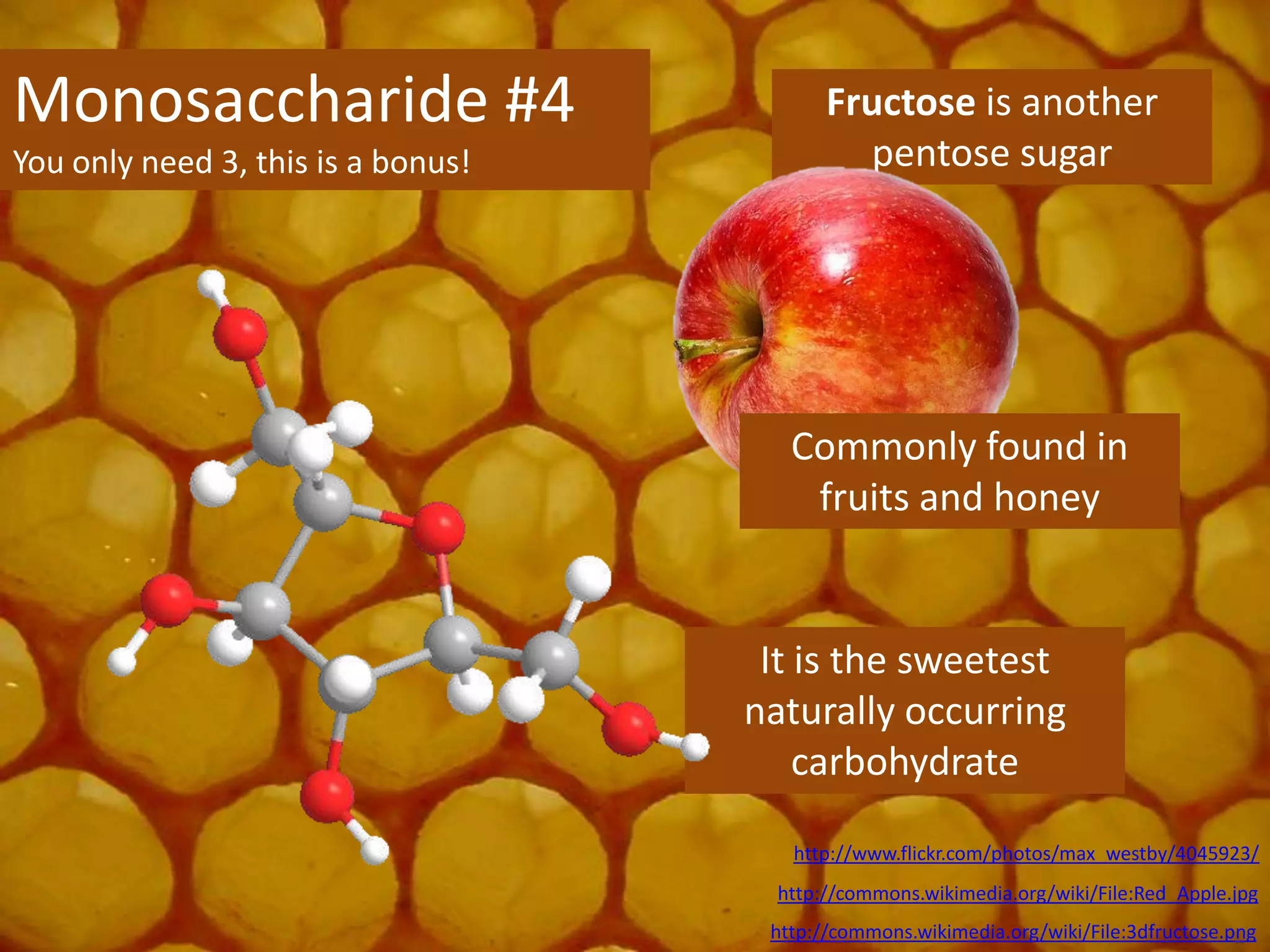
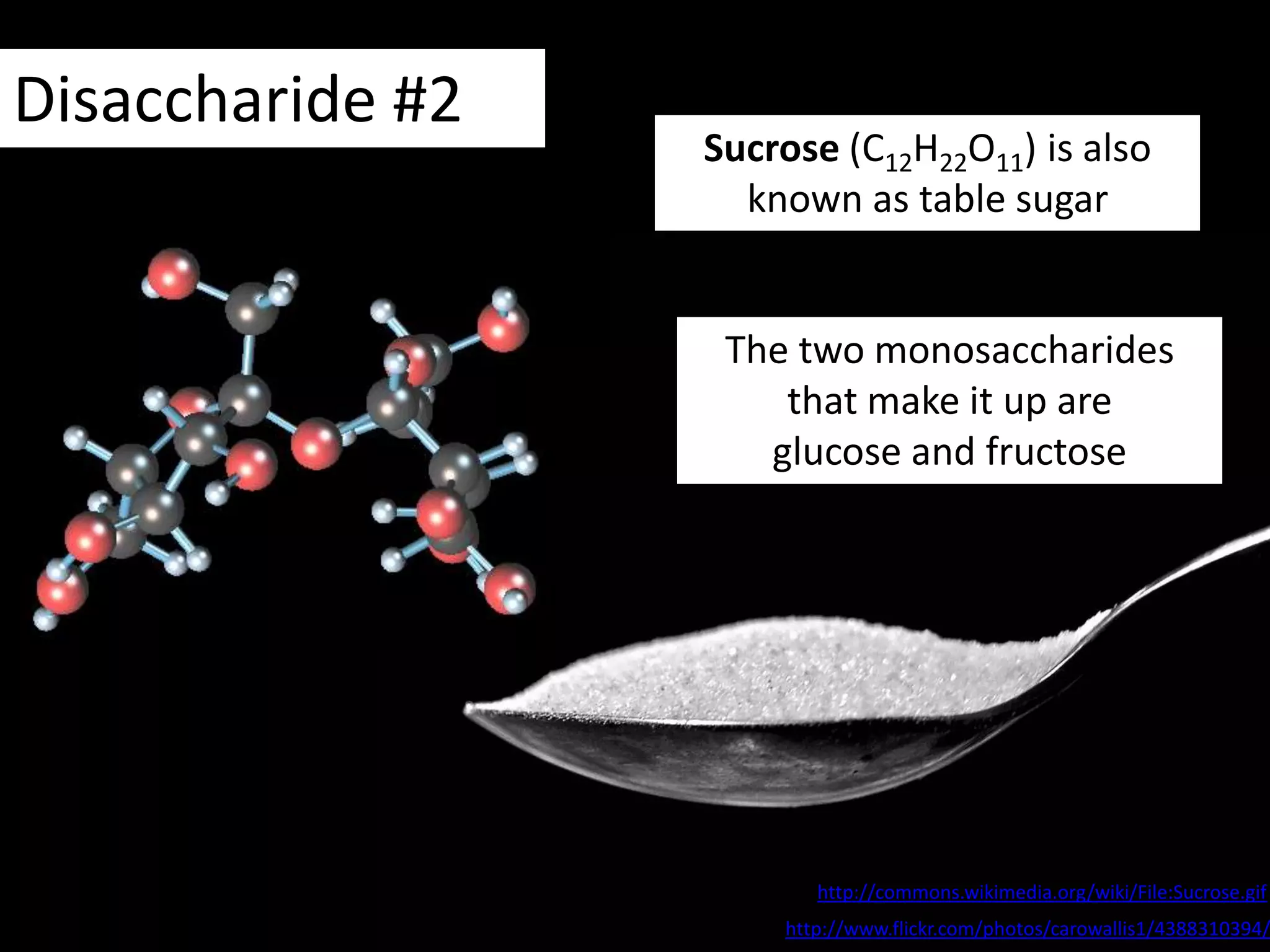
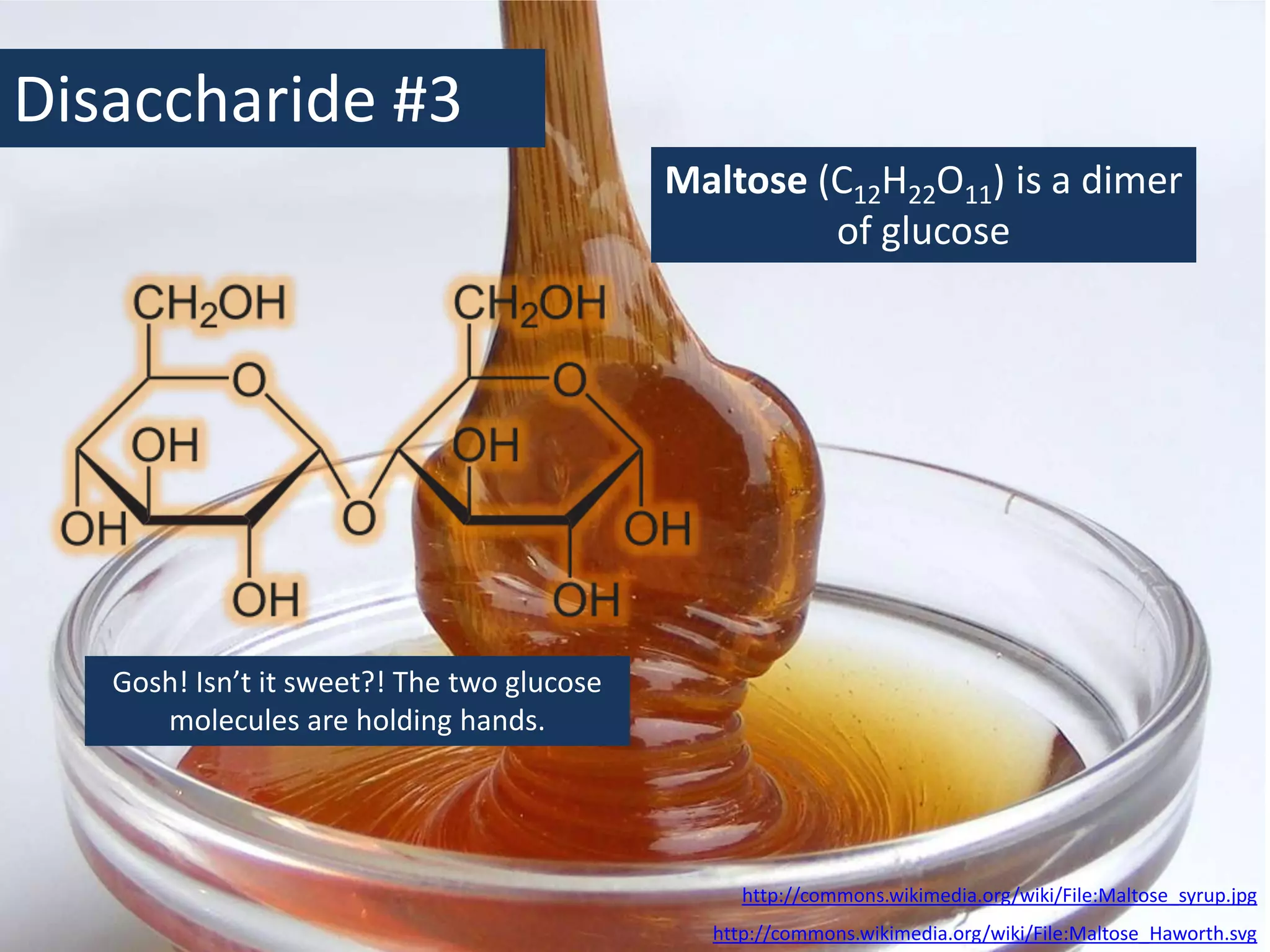
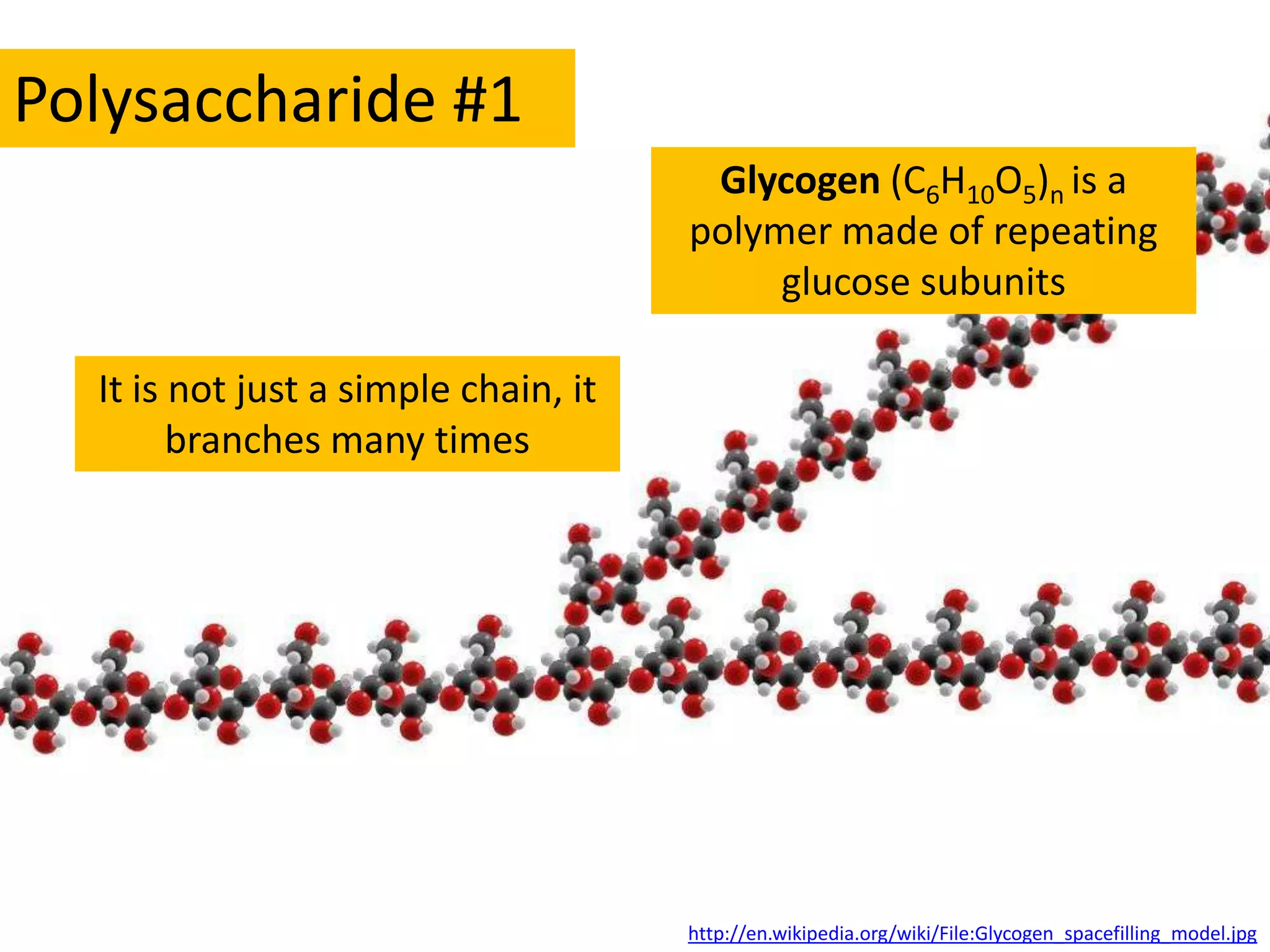
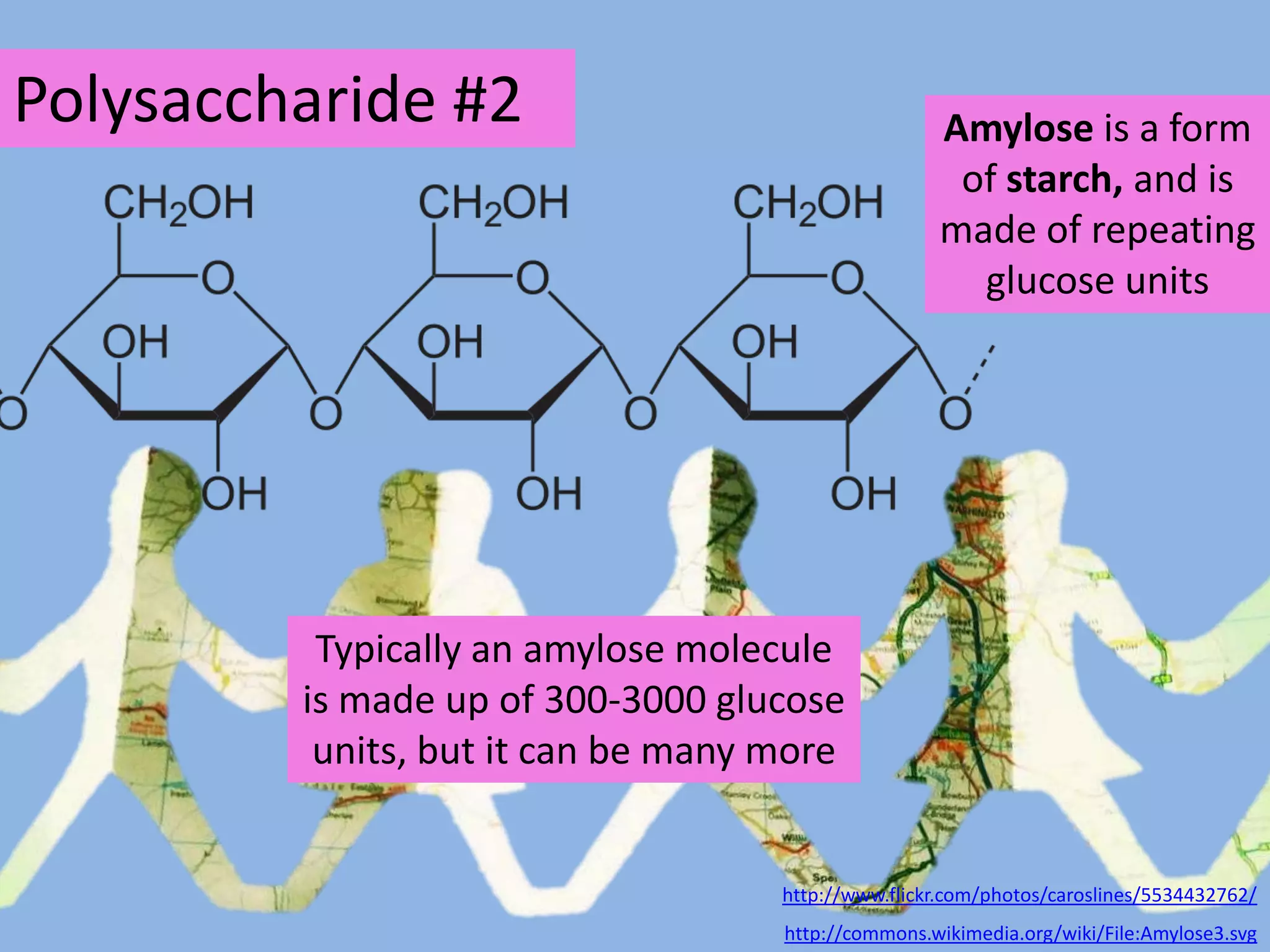
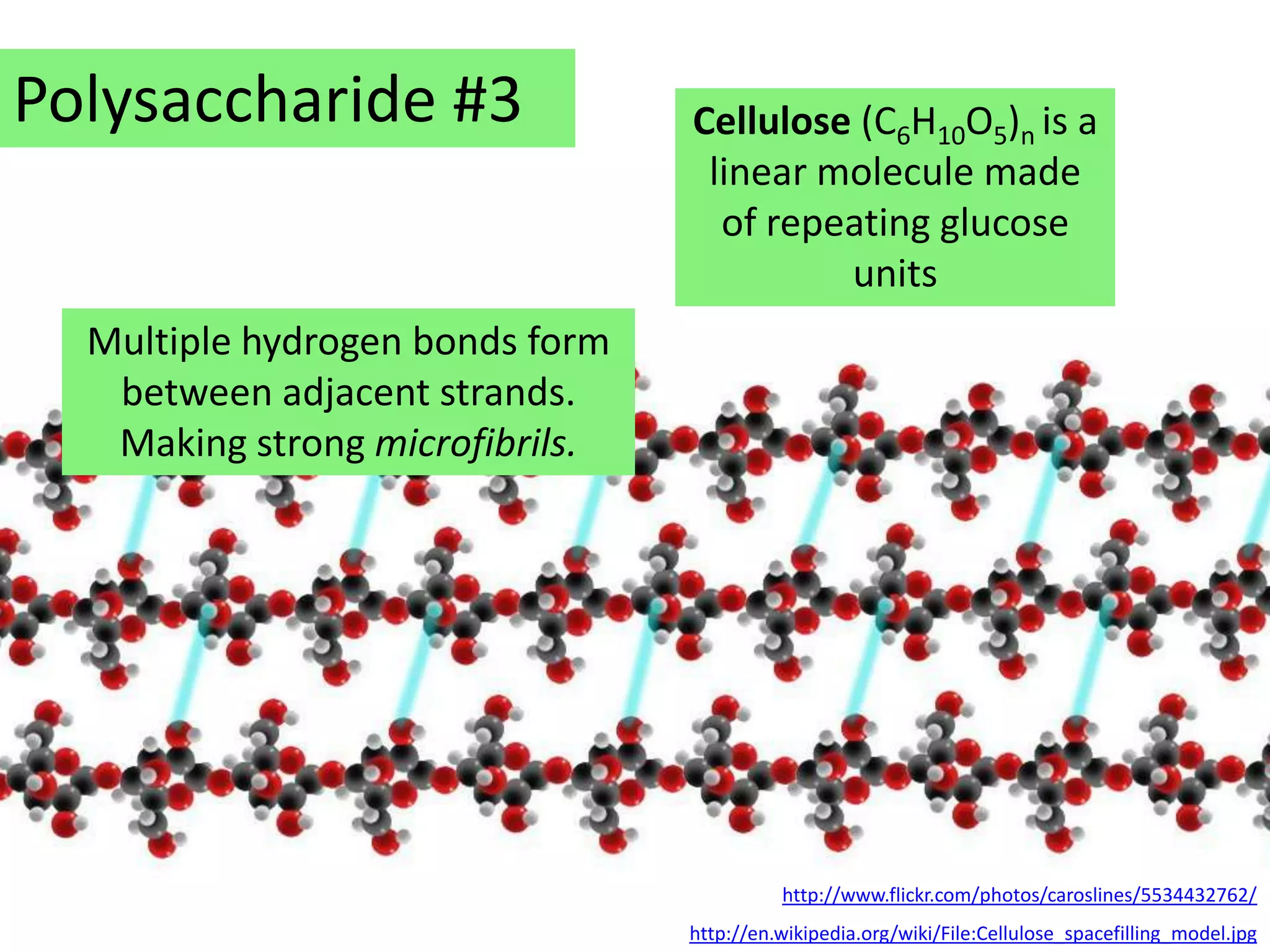
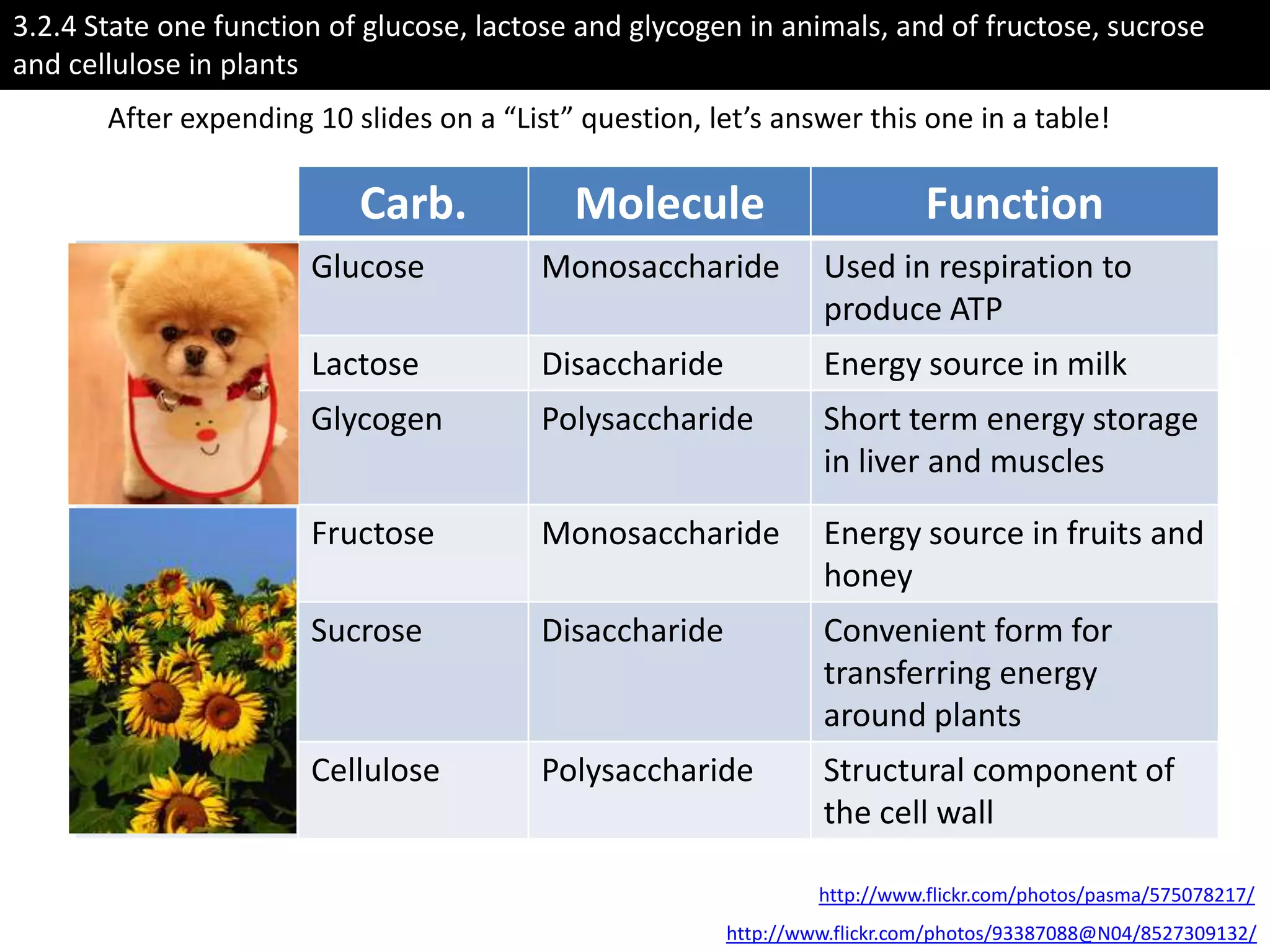
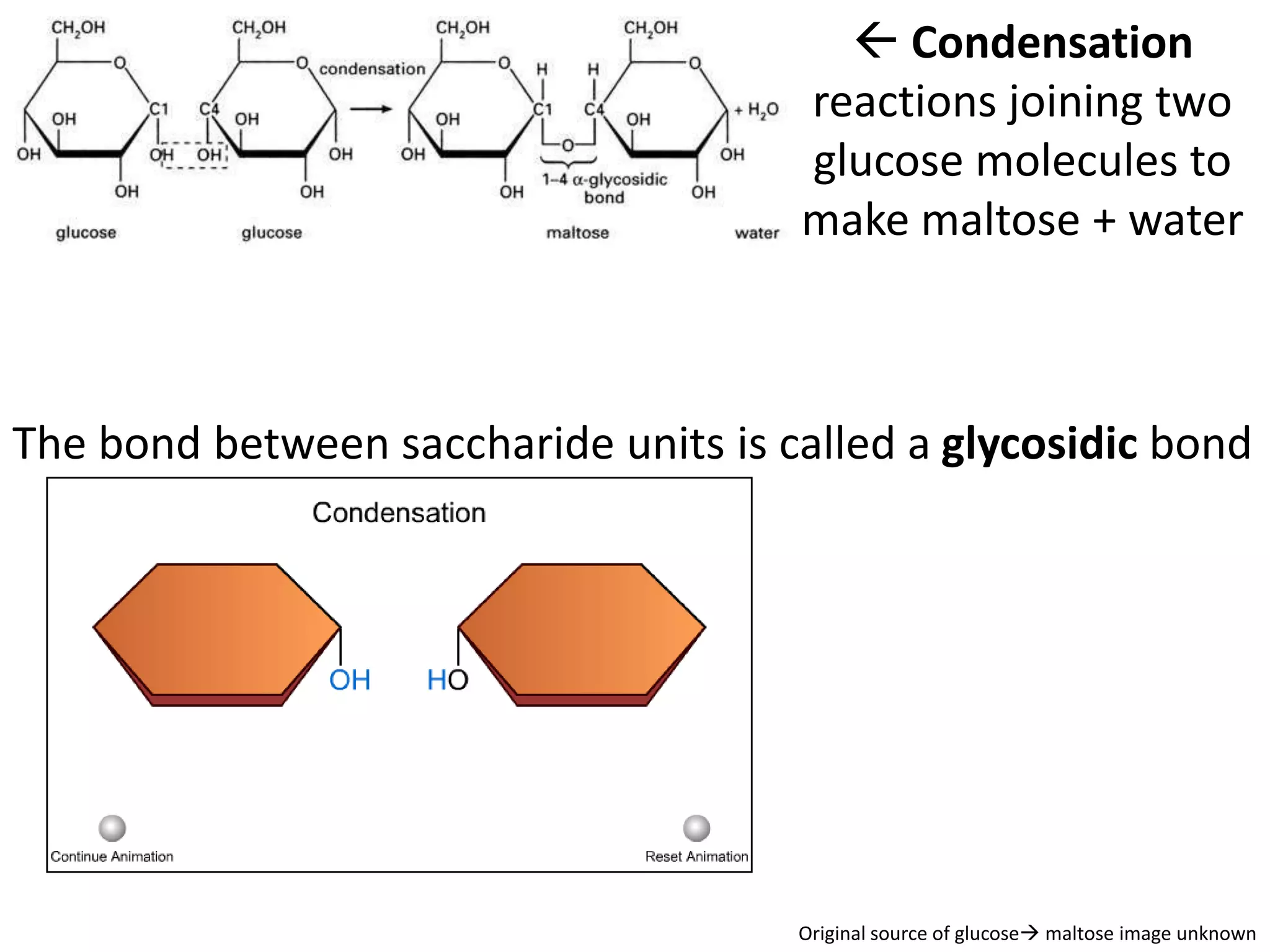
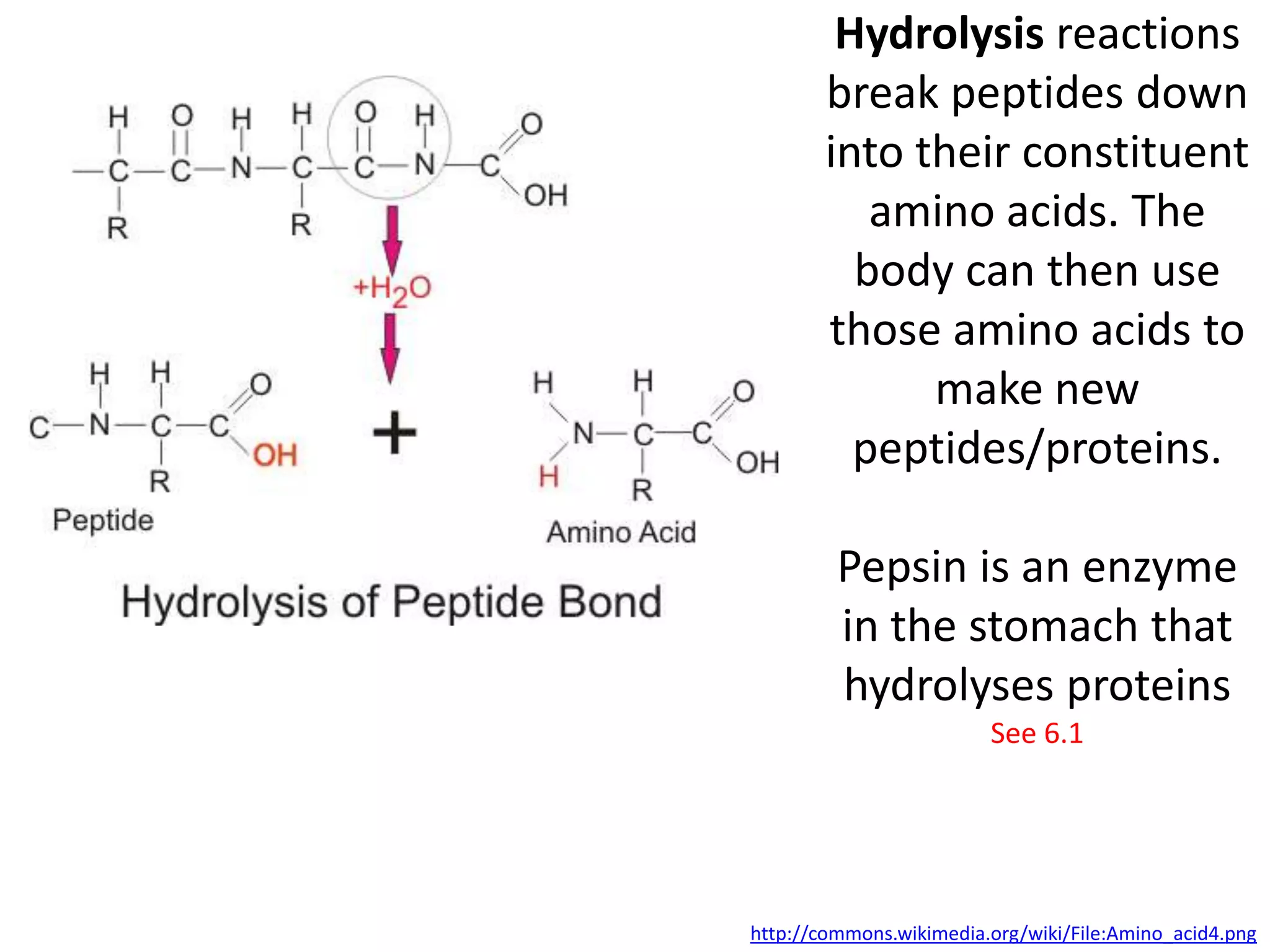
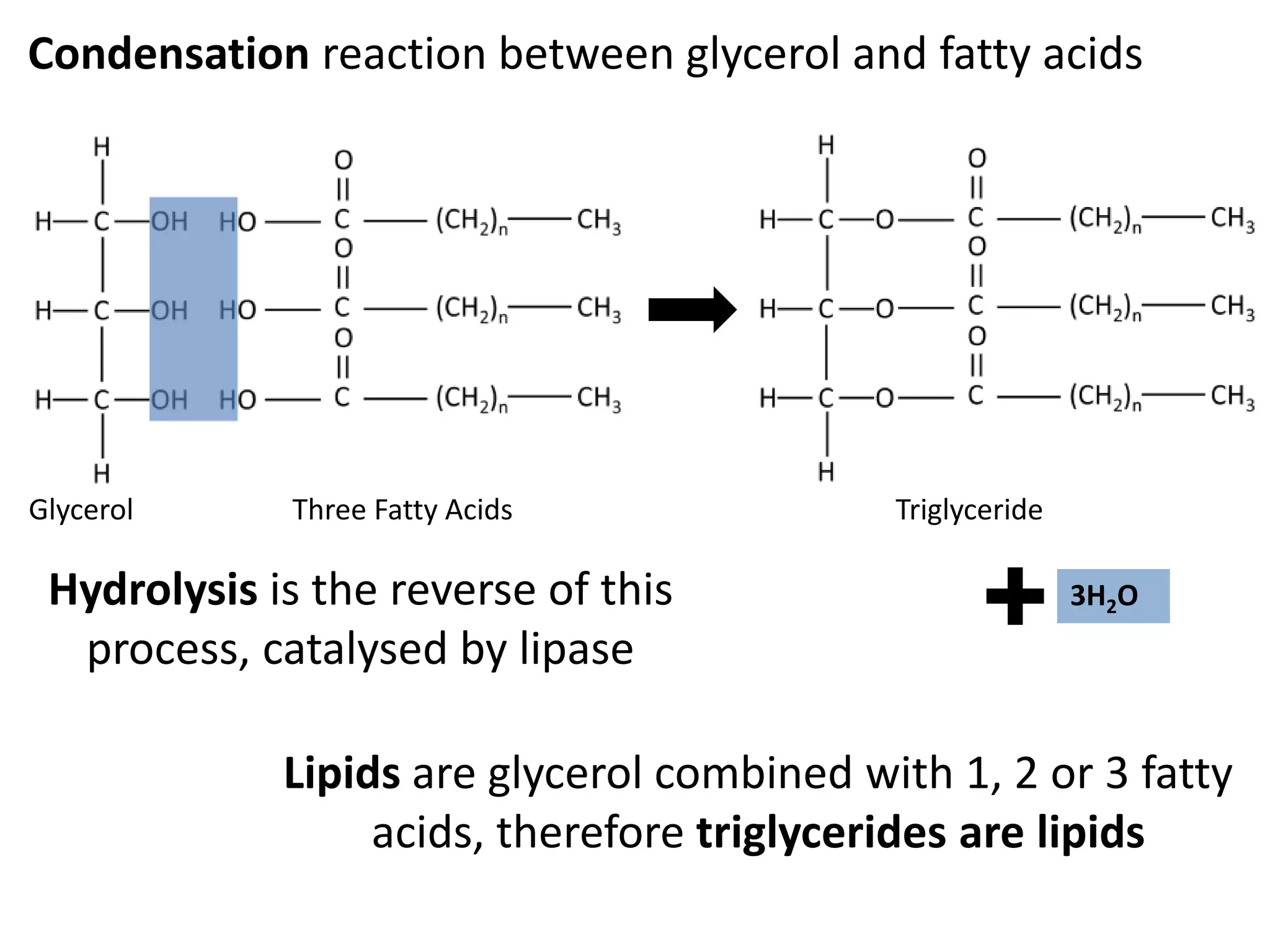
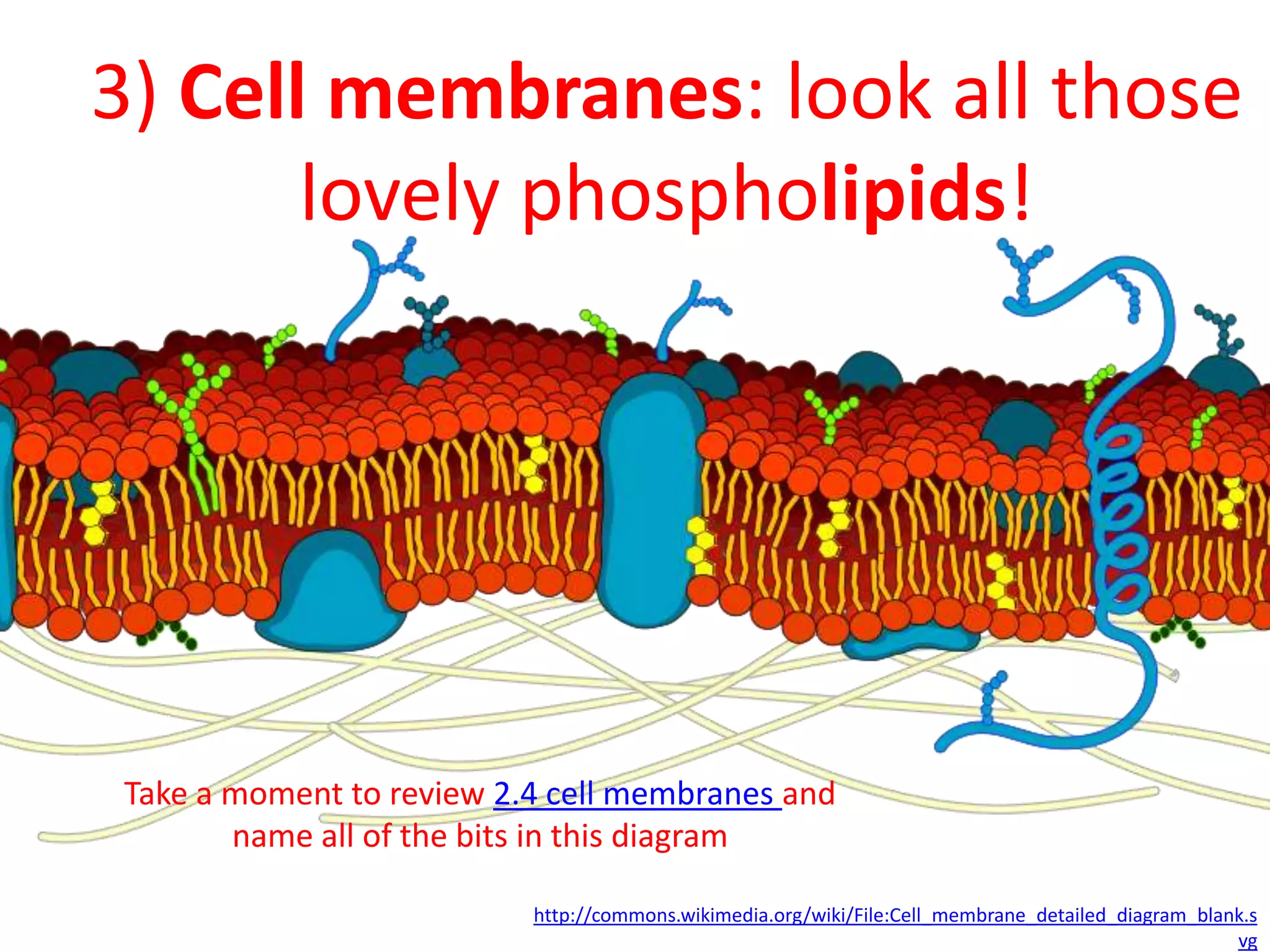
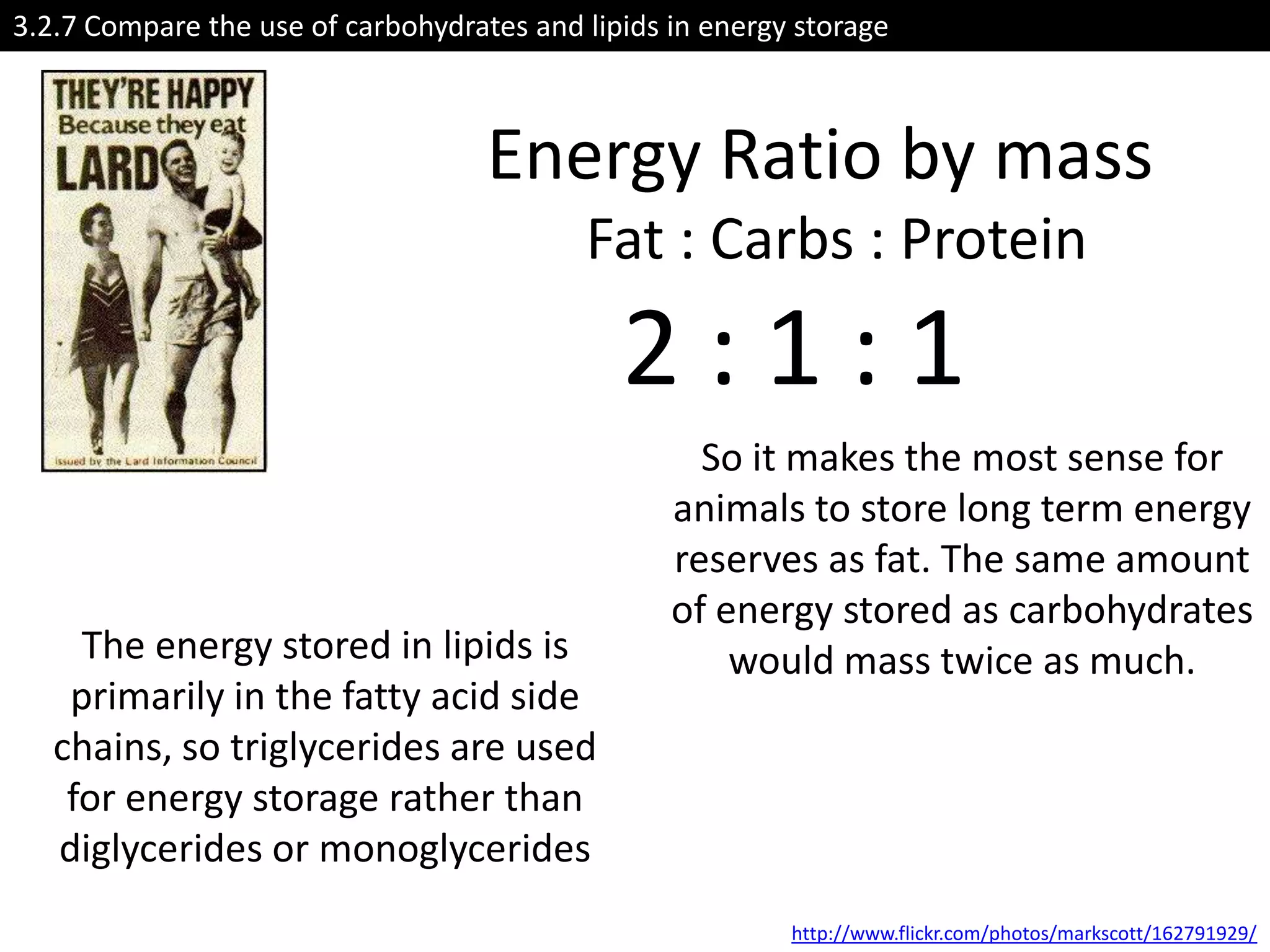
This document provides information about carbohydrates, lipids, and proteins. It defines organic and inorganic compounds, identifies the structures of amino acids, glucose, ribose, and fatty acids. Examples are given of monosaccharides like glucose and galactose, disaccharides like lactose and sucrose, and polysaccharides like glycogen and cellulose. The functions of glucose, lactose and glycogen in animals, and fructose, sucrose and cellulose in plants are stated.