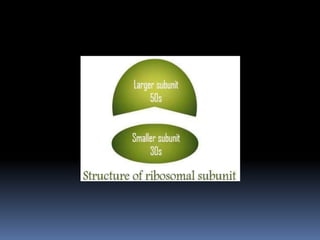
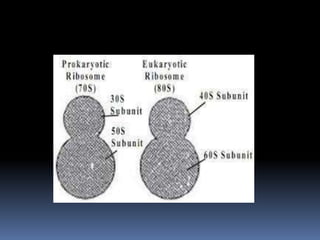
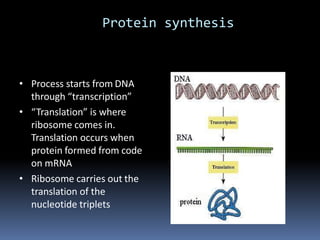
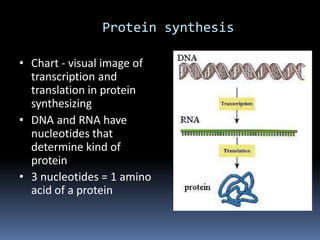
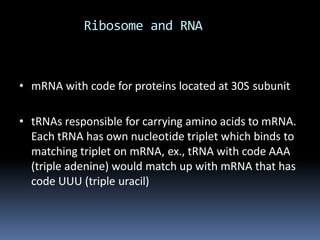
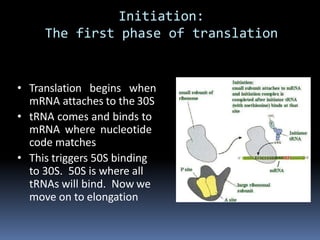
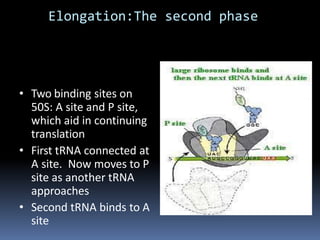
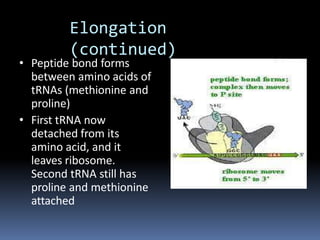
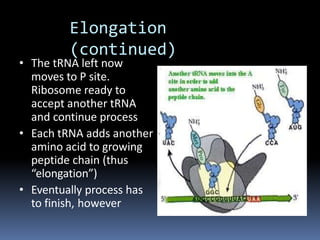
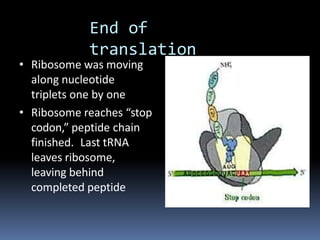
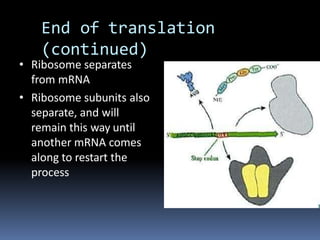
Ribosomes are large complex molecules found in all living cells that are the site of biological protein synthesis. They consist of two subunits that come together during protein translation. Ribosomes along with transfer RNA (tRNA) help translate protein-coding genes in messenger RNA (mRNA) into proteins. The process of protein synthesis begins with transcription of DNA to mRNA, which is then translated into proteins with the help of ribosomes and tRNA. Translation occurs as the ribosome moves along the mRNA, facilitating the binding of tRNA to the mRNA and the formation of peptide bonds between amino acids, eventually resulting in a completed protein chain.