This document provides an overview of topics related to human evolution, including:
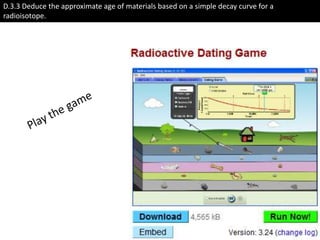
- Methods for radioactive dating of rocks and fossils using carbon-14 and potassium-40 isotopes.
- Key anatomical features that define humans as primates, such as grasping limbs and binocular vision.
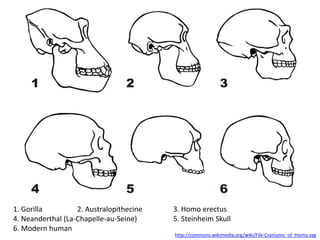
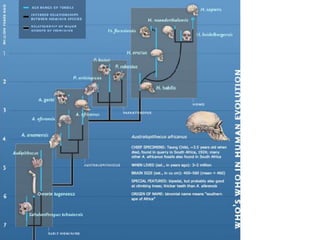
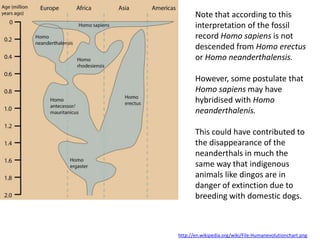
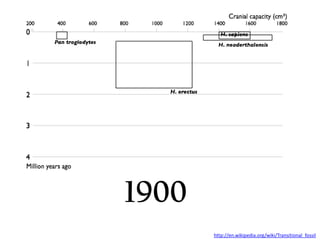
- Major trends seen in hominid fossils like Ardipithecus, Australopithecus, and Homo species showing brain size increase and facial shortening over time.
- Potential for multiple hominid species to coexist and uncertainties due to an incomplete fossil record.
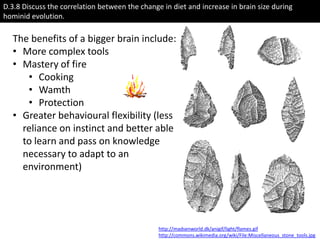
- Relationship between increased brain size and diet change in hominids, correlated with meat consumption.
- Distinction between genetic evolution through natural selection