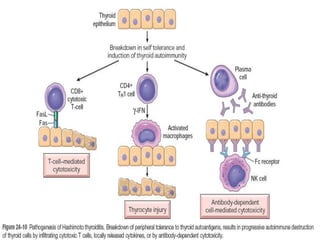
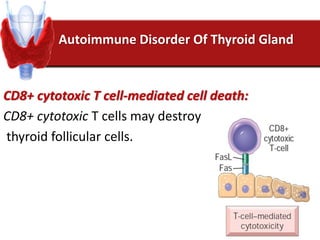
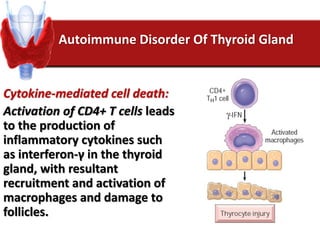
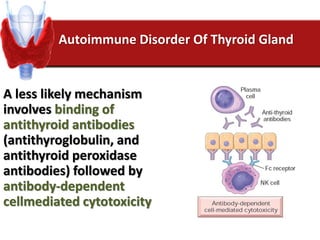
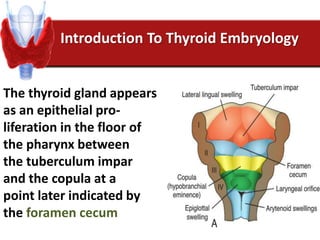
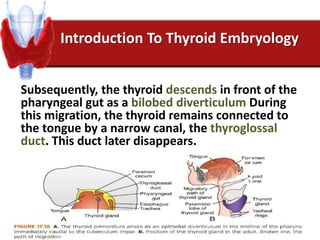
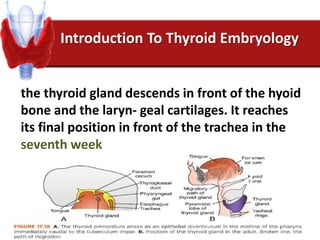
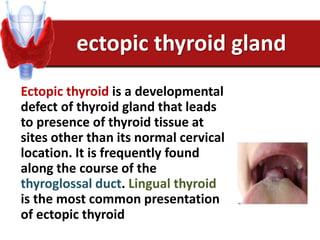
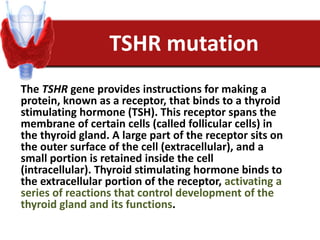
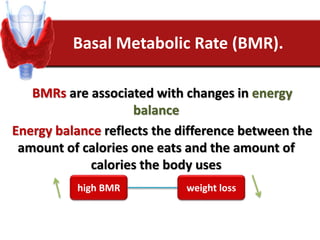
Hashimoto's thyroiditis is an autoimmune disease that results in the destruction of the thyroid gland and gradual hypothyroidism. It is the most common cause of hypothyroidism in iodine-sufficient areas and typically affects those aged 45-65, predominately women. The thyroid gland may be destroyed through CD8+ cytotoxic T cell killing or cytokine-mediated cell death. Congenital hypothyroidism can be caused by an ectopic thyroid gland, defects in thyroid hormone synthesis (dyshormonogenesis), or mutations in the TSH receptor. Hypothyroidism causes dry, thickened skin and obesity due to a lowered metabolic rate and basal metabolic rate.