This document discusses hypothyroidism, including three patient cases. It covers the epidemiology, causes, clinical presentation, diagnosis, and treatment of hypothyroidism. The key points are:
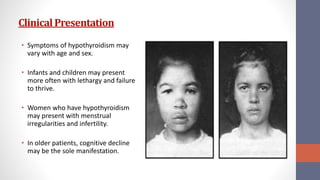
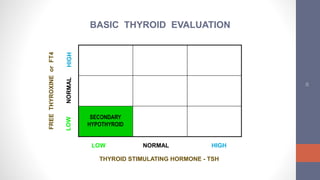
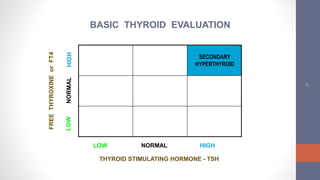
1) Hypothyroidism can be primary (thyroid gland failure) or secondary (insufficient TSH stimulation). The most common cause is autoimmune thyroid disease. Clinical symptoms vary but include fatigue, weight gain, and depression.
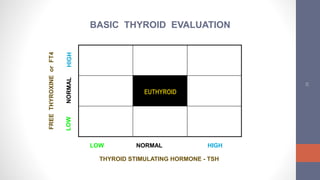
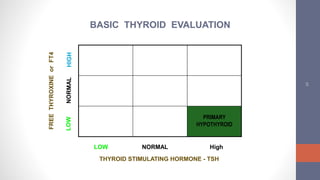
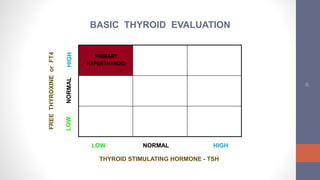
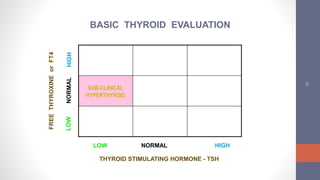
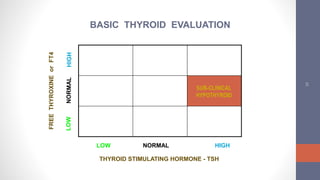
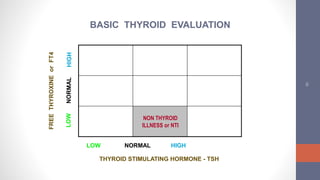
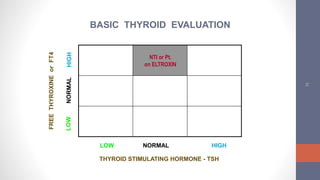
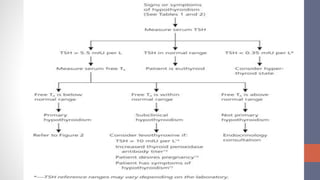
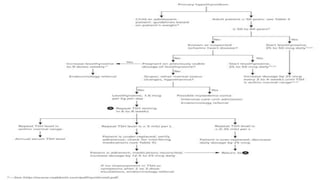
2) Diagnosis is made through lab tests - an elevated TSH with low free T4 indicates primary hypothyroidism. Subclinical hypothyroidism has an elevated TSH but normal free T4.
3) Treatment is lifelong levothyroxine