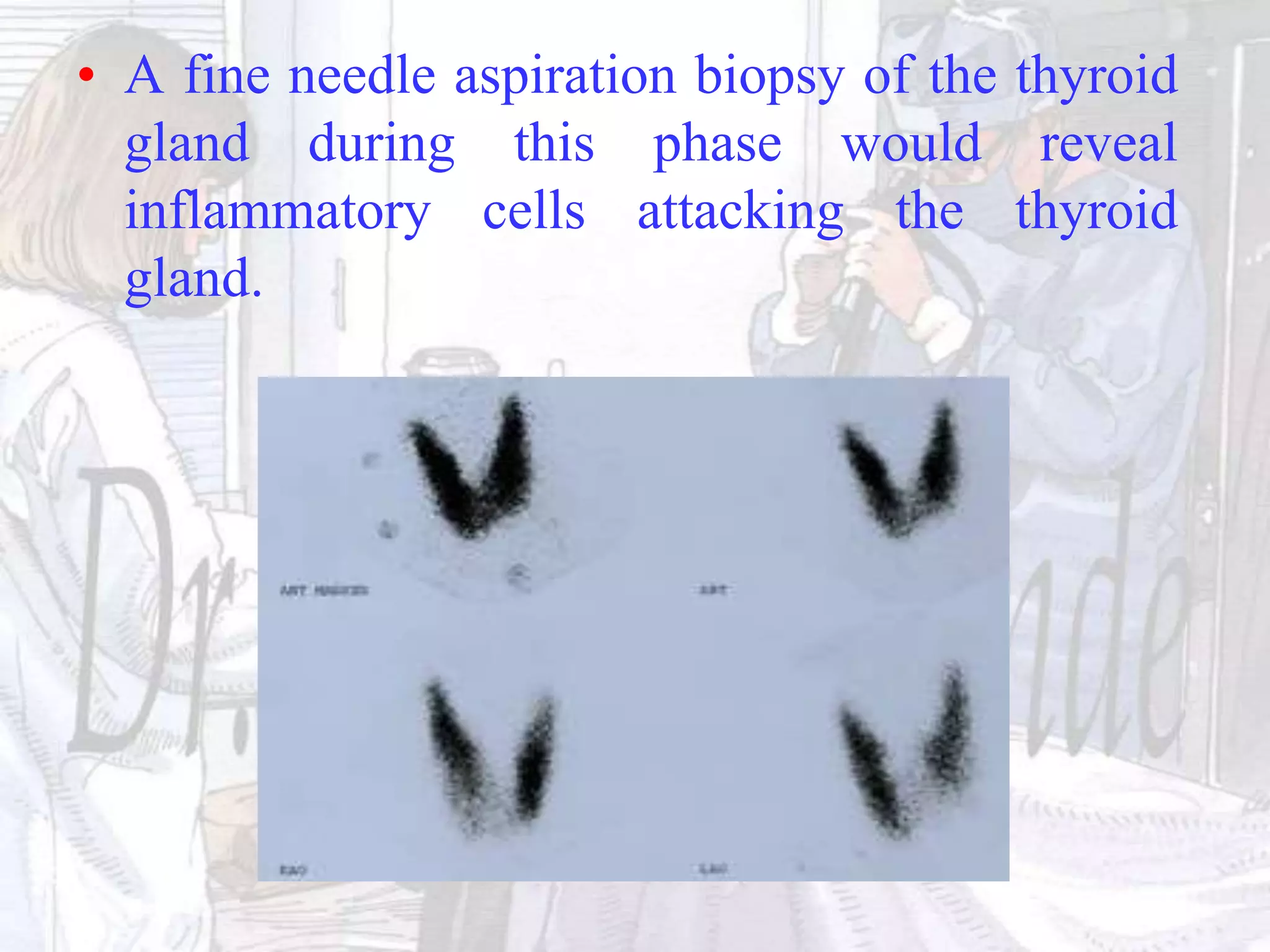
Thyroiditis is inflammation of the thyroid gland that can cause abnormal thyroid hormone levels. There are several types of thyroiditis including Hashimoto's (the most common autoimmune form), subacute, post-partum, silent, and forms induced by drugs, radiation, or infection. Symptoms vary depending on thyroid hormone levels and include fatigue, weight changes, nervousness, and neck tenderness. Treatment involves medications, steroids, thyroid hormone replacement, or surgery in rare cases. Complications can include hypothyroidism or airway obstruction.