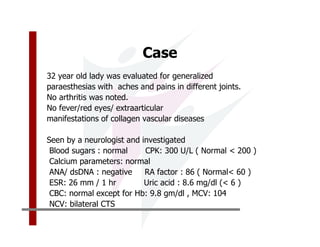
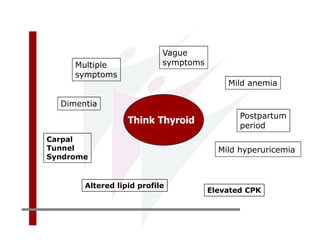
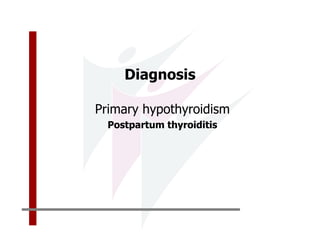
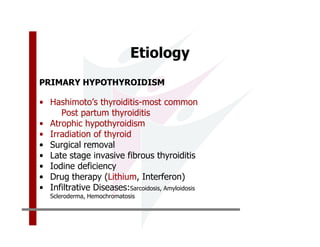
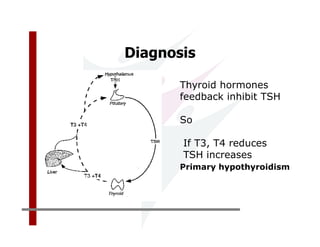
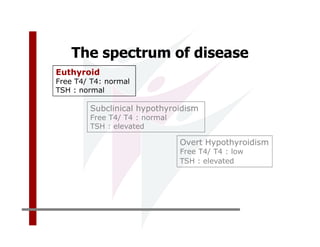
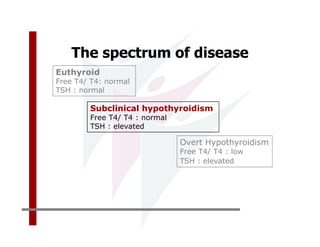
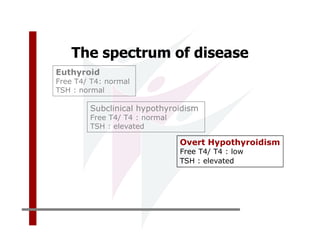
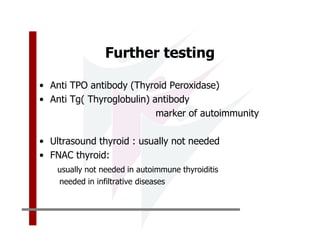
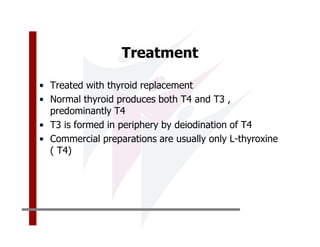
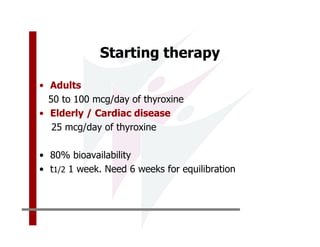
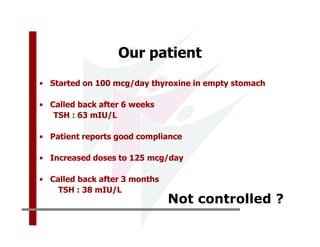
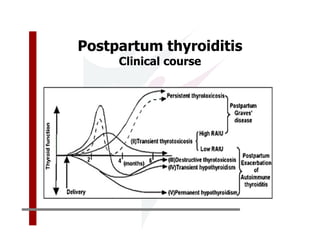
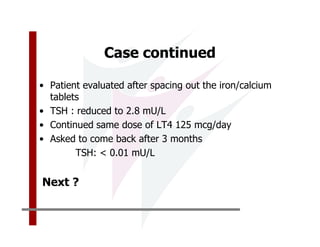
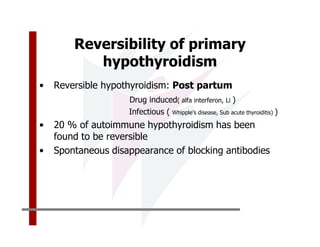
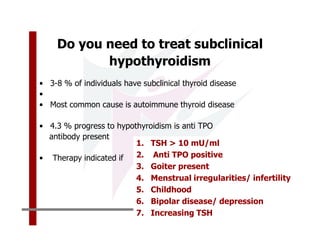
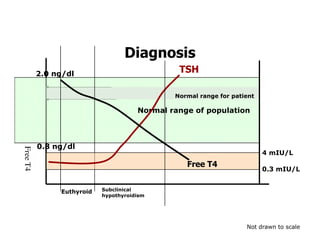
This document discusses the diagnosis and management of primary hypothyroidism in a 32-year-old woman. She was found to have a very high TSH level of over 100 IU/ml and a low free T4, consistent with overt primary hypothyroidism. Further testing found she had a family history of hypothyroidism and goiter. She was diagnosed with postpartum thyroiditis, a common cause of transient hypothyroidism after delivery. Treatment involves thyroid hormone replacement with levothyroxine titrated based on follow-up TSH levels, with the goal of achieving a normal TSH level.