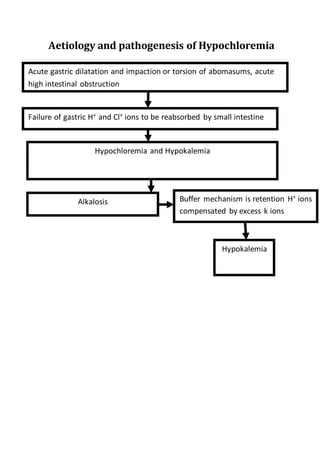
Hypochloremia occurs when there is an increase in electrolyte loss from the intestinal tract due to conditions like intestinal obstruction, dilation, or torsion of the abomasums. Normally, the stomach secretes hydrochloric acid in exchange for sodium bicarbonate, and the hydrogen, chloride, and potassium ions are absorbed by the small intestine. However, when there is a failure of the abomasums to empty or an obstruction of the small intestine, large amounts of chloride, hydrogen, and potassium ions become trapped, leading to hypochloremia, hypokalemic alkalosis, and other clinical symptoms like anorexia, weight loss, and lethargy. The main causes of