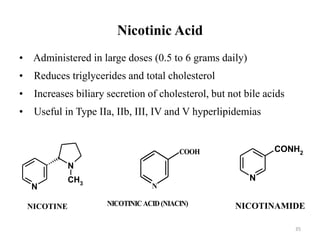
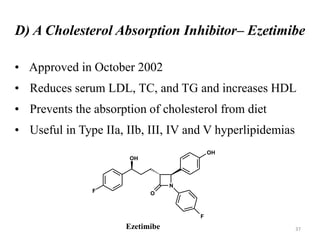
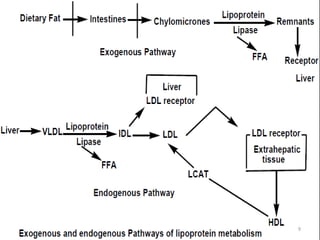
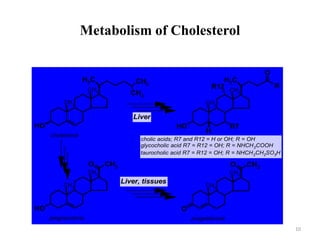
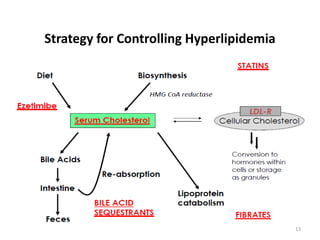
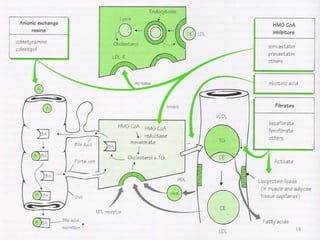
Hyperlipidemia, or high lipid levels, is a common disorder that increases the risk of heart disease. It results from abnormalities in lipid metabolism or transport. The main causes are lifestyle factors like obesity and lack of exercise, as well as medical conditions like diabetes. Drugs used to treat hyperlipidemia work by inhibiting cholesterol biosynthesis, sequestering bile acids to reduce cholesterol absorption, altering cholesterol metabolism, or inhibiting absorption of dietary cholesterol. Statins are the most commonly used class that lower LDL cholesterol by inhibiting HMG-CoA reductase. Other drug classes include bile acid sequestrants, fibrates, and niacin. Combination therapies may be used for more severe or treatment-resistant cases of





![Hyperlipoprot
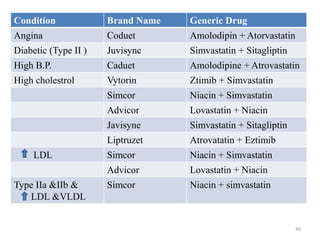
einemia
Synonyms Increased
lipoprotein
Treatment
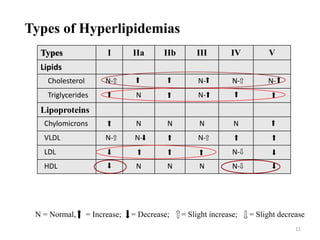
Type I (rare) ''Buerger-Gruetz syndrome'', ''Primary
hyperlipoproteinaemia'', or ''Familial
hyperchylomicronemia''
Chylomicrons Diet control
Type IIa ''Polygenic hypercholesterolaemia'' or
''Familial hypercholesterolemia
LDL Bile acid
sequestrants,
statins, niacin
Type IIb ''Combined hyperlipidemia'' LDL and VLDL Statins,
niacin, fibrate
Type III (rare) ''Familial dysbetalipoproteinemia'' IDL Fibrates,
statins
Type IV ''Familial hyperlipidemia'' VLDL Fibrate,
niacin],
statins
Type V (rare) ''Endogenous hypertriglyceridemia VLDL and
Chylomicrons
Niacin, fibrate
Types , Synonyms & their treatment
12](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/komal-161005141337/85/Hyperlipidemia-and-its-treatment-12-320.jpg)


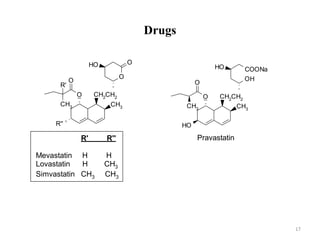
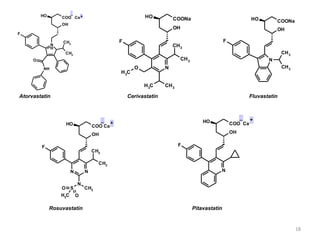

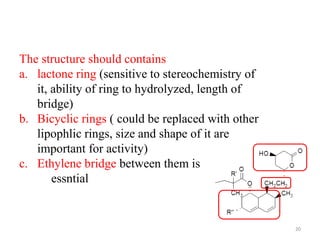







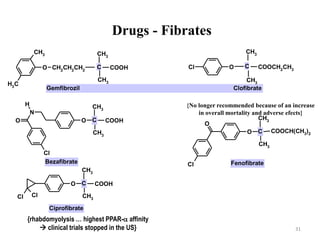
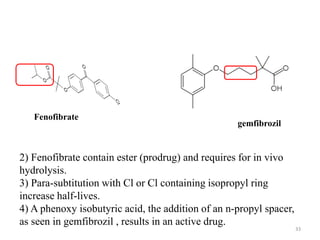
![SAR of Fabric acid derivatives
[aromatic ring]-O-[spacer group]-C(CH3)2-CO-OH
1) They are classified as analogues of isobutyric
acid derivatives (essential for activity)
Fabric acid
32](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/komal-161005141337/85/Hyperlipidemia-and-its-treatment-32-320.jpg)