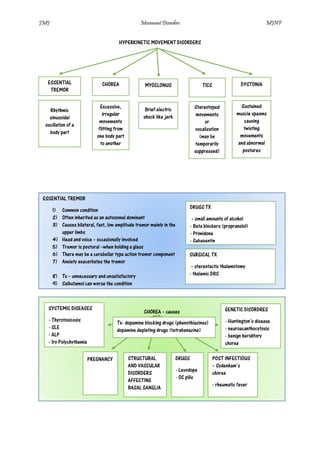
Essential tremor is a common condition characterized by bilateral, fast, low amplitude tremors mainly in the upper limbs that are often inherited and worsened by anxiety. It causes postural tremors when holding objects. Huntington's disease is a cause of chorea that presents in middle life with initial subtle movements and later psychiatric and cognitive symptoms due to a CAG trinucleotide repeat expansion. Tourette's syndrome is the most common cause of tics, characterized by multiple motor and at least one vocal tic starting in childhood and persisting over a year, affecting boys more than girls and associated with behavioral problems and disorders like ADHD and OCD.