Embed presentation
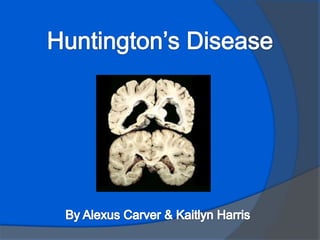

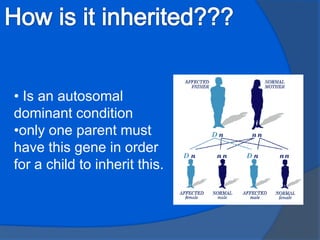



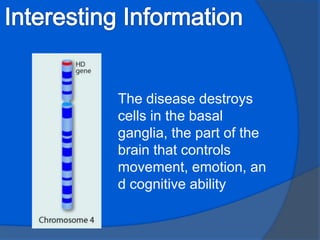


Huntington's disease is a genetic disorder that causes certain nerve cells in the brain to break down over time. It is inherited in an autosomal dominant pattern, meaning only one parent needs to carry the gene for a child to be at risk. Common symptoms include behavioral changes, abnormal movements, dementia, and difficulty swallowing and speaking. While there is no cure, lifestyle interventions including diet, supplements, exercise and social support can help manage symptoms and potentially delay onset. The disease is caused by destruction of cells in the basal ganglia and approximately 1 in 33,333 people in the US are affected.









