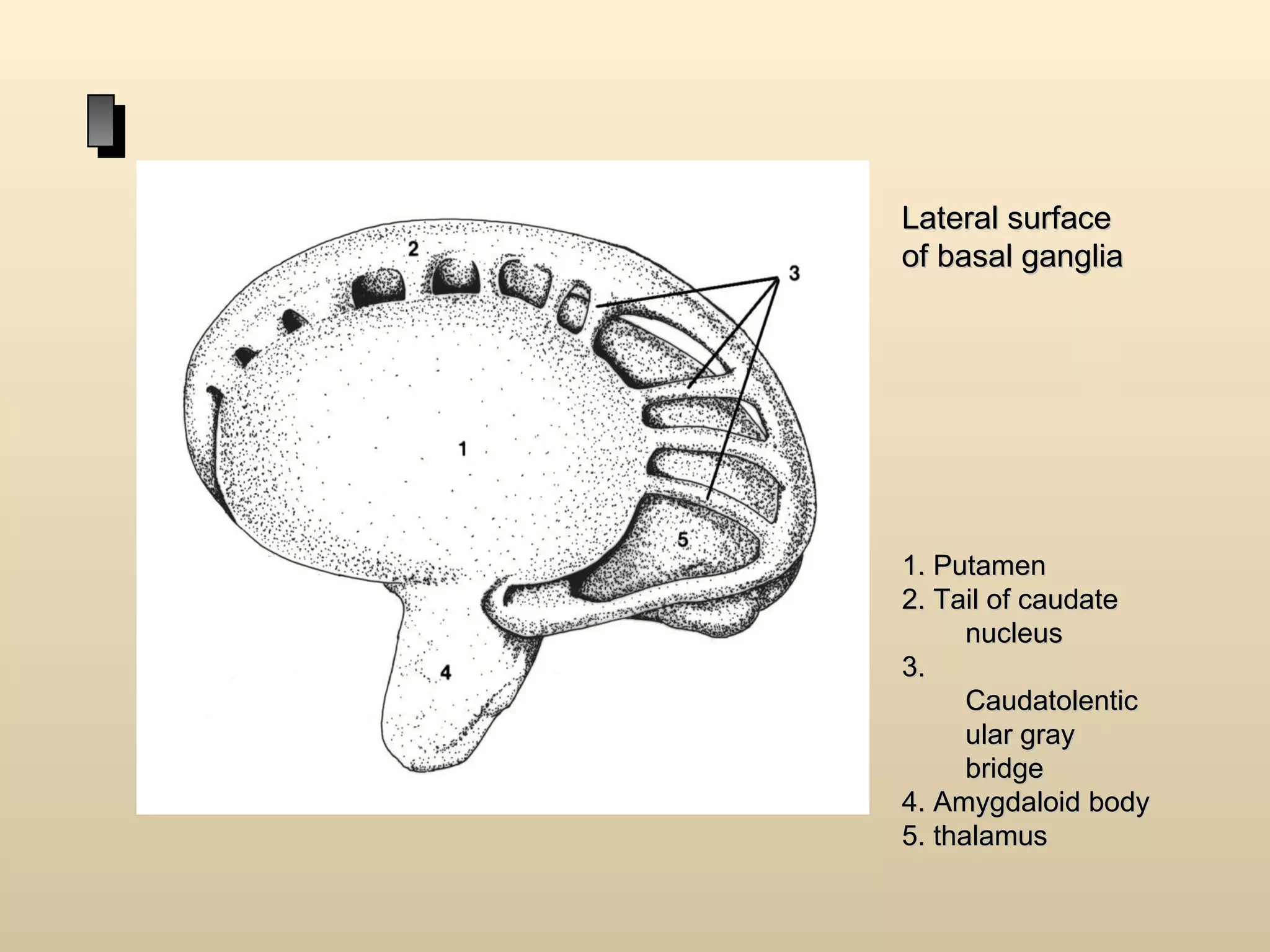
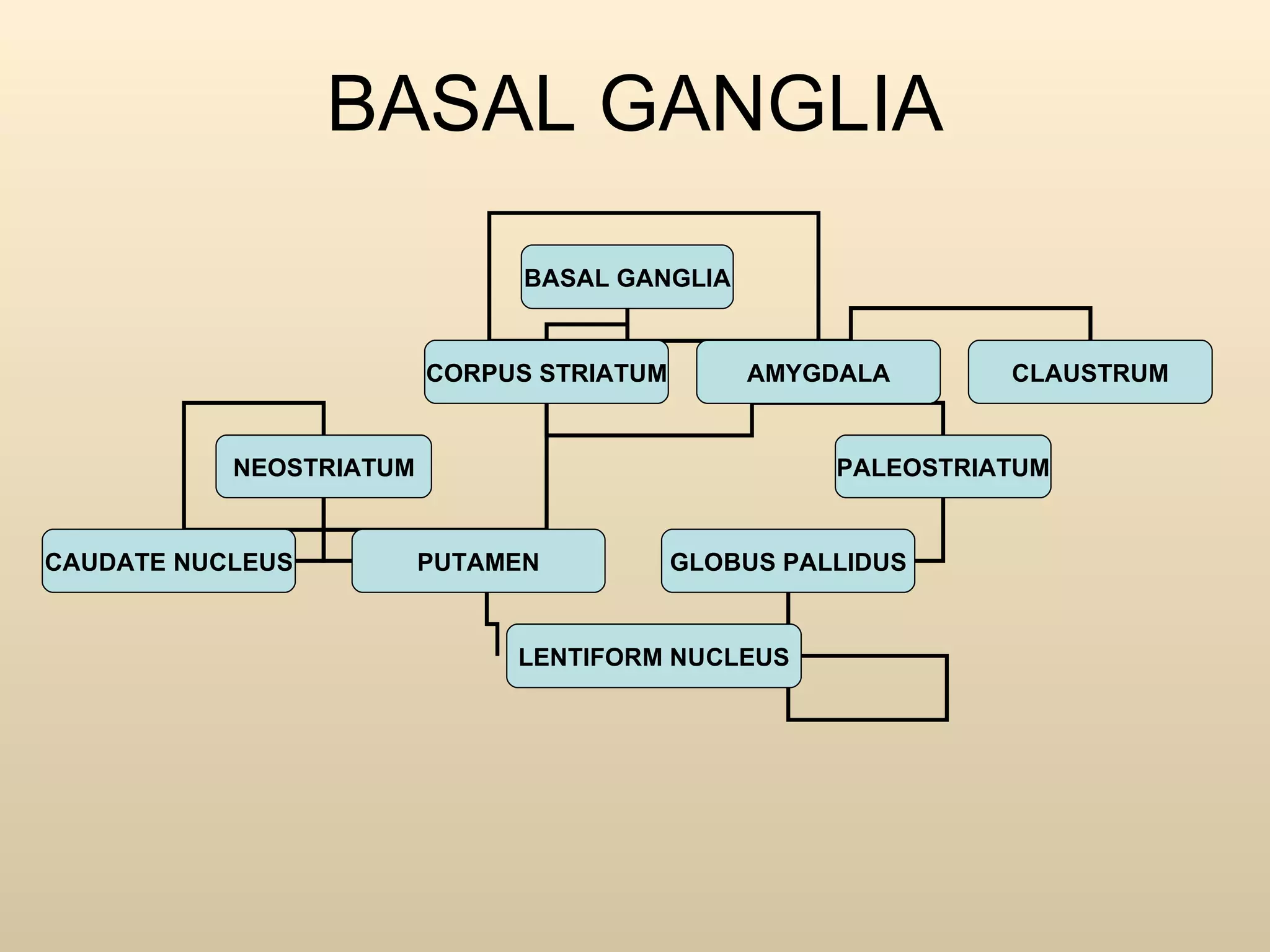
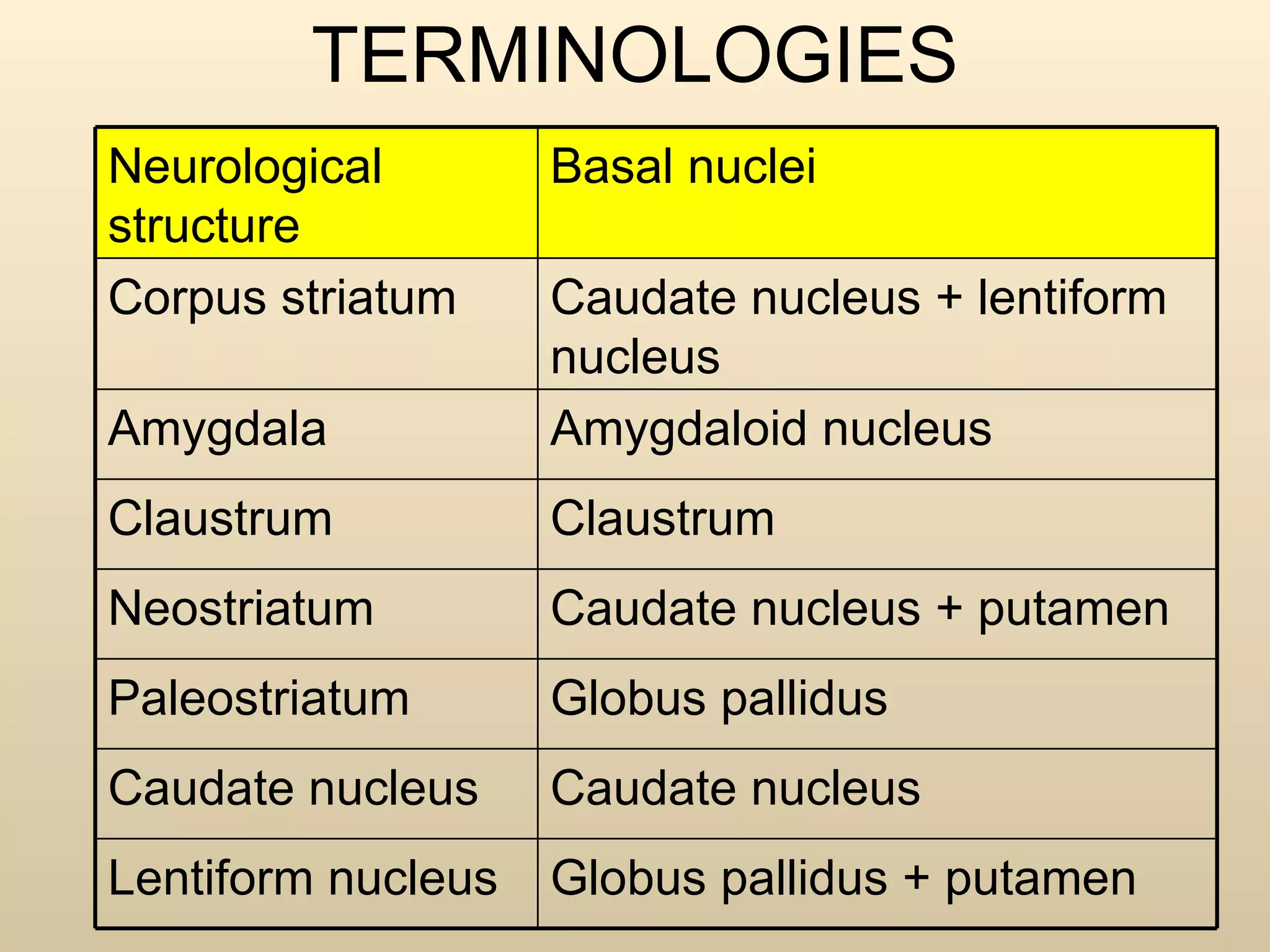
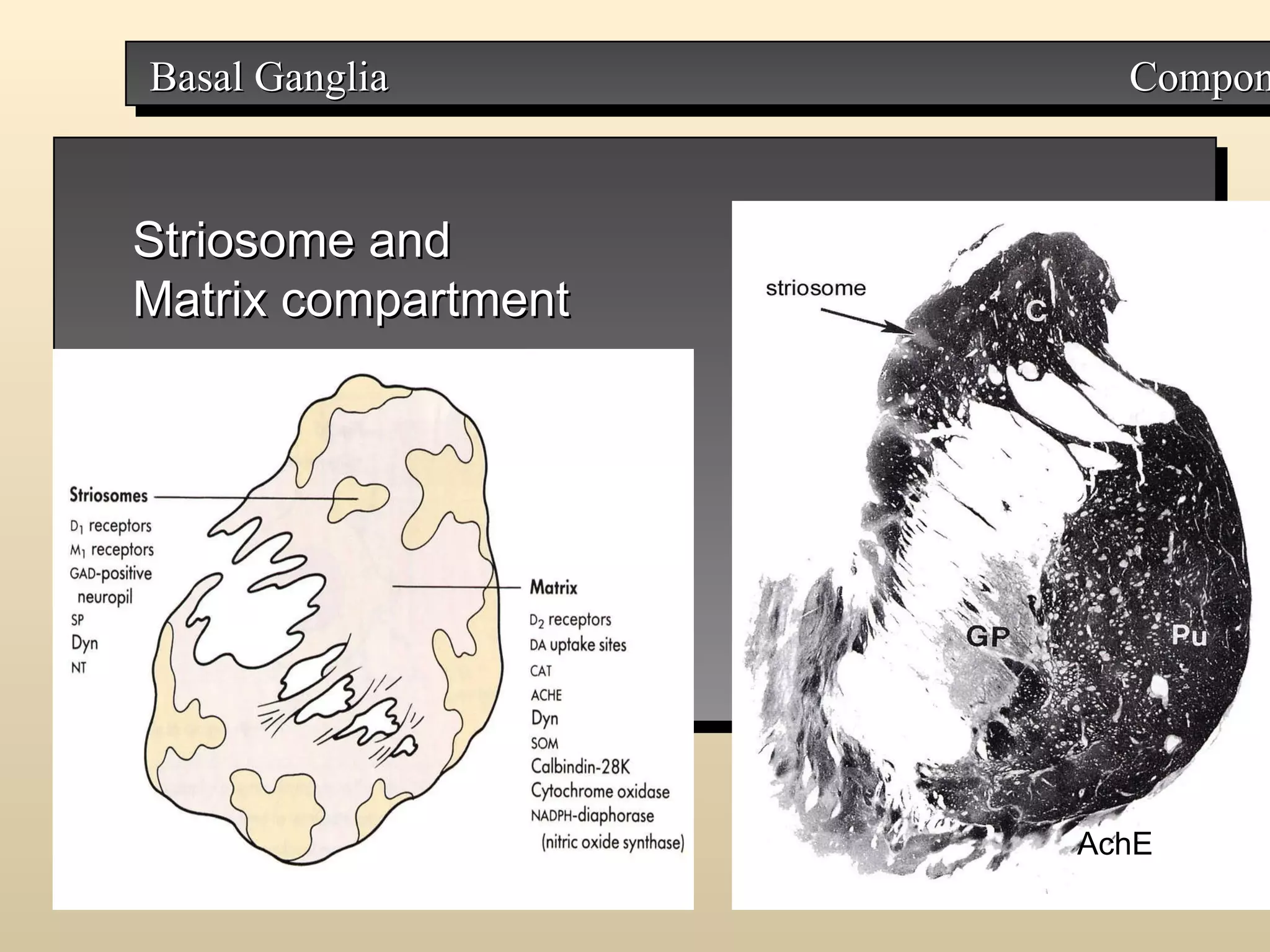
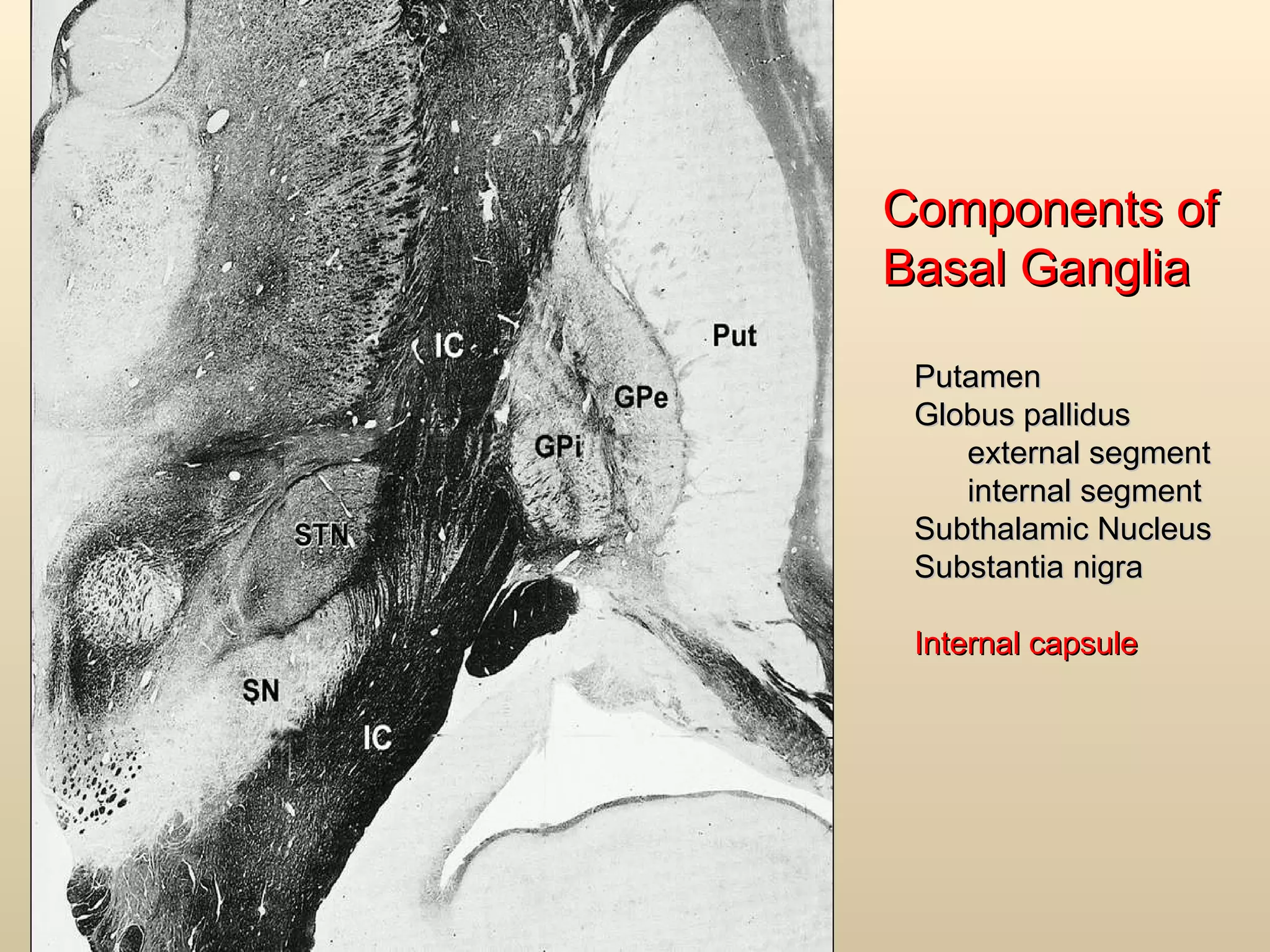
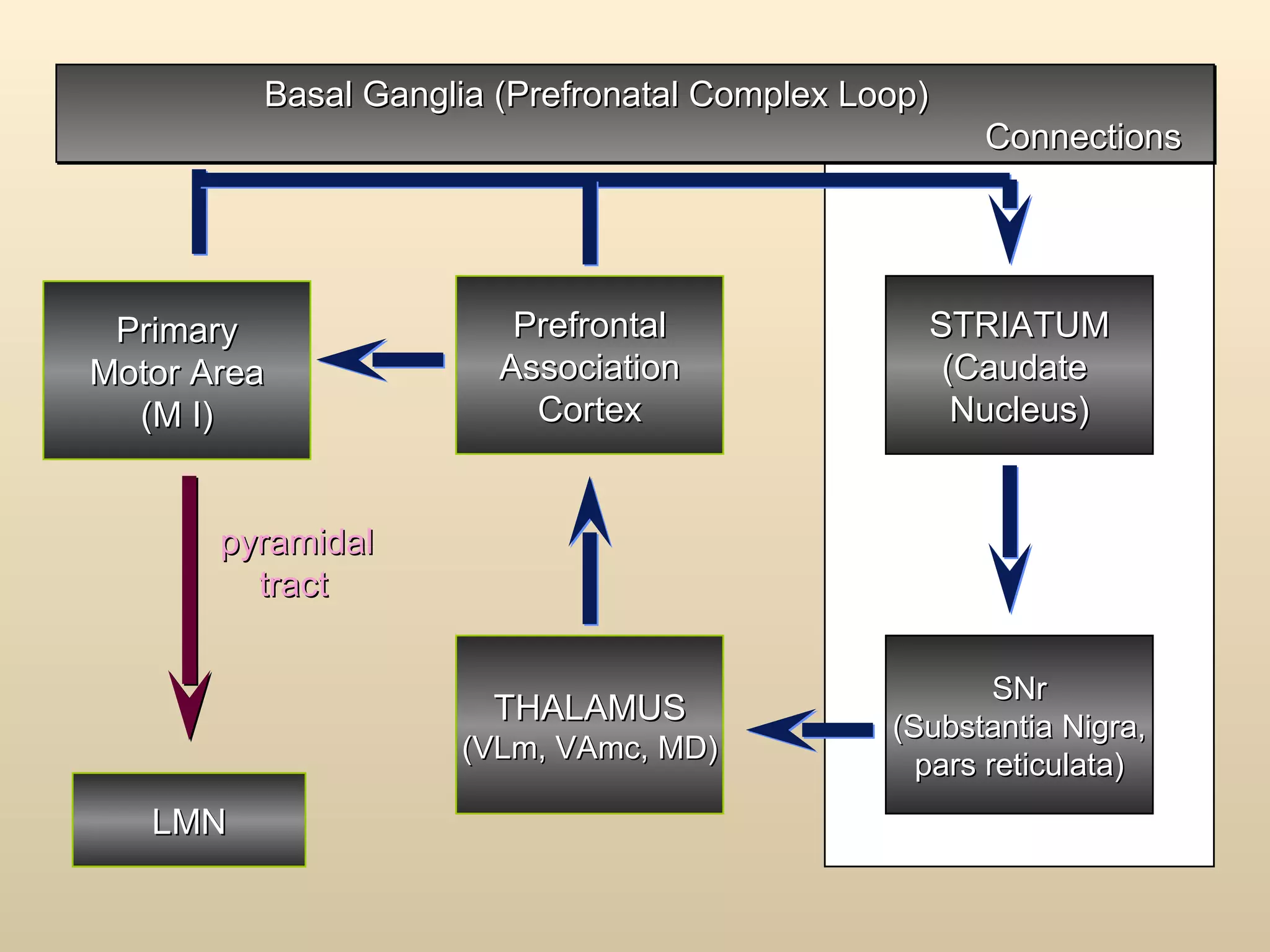
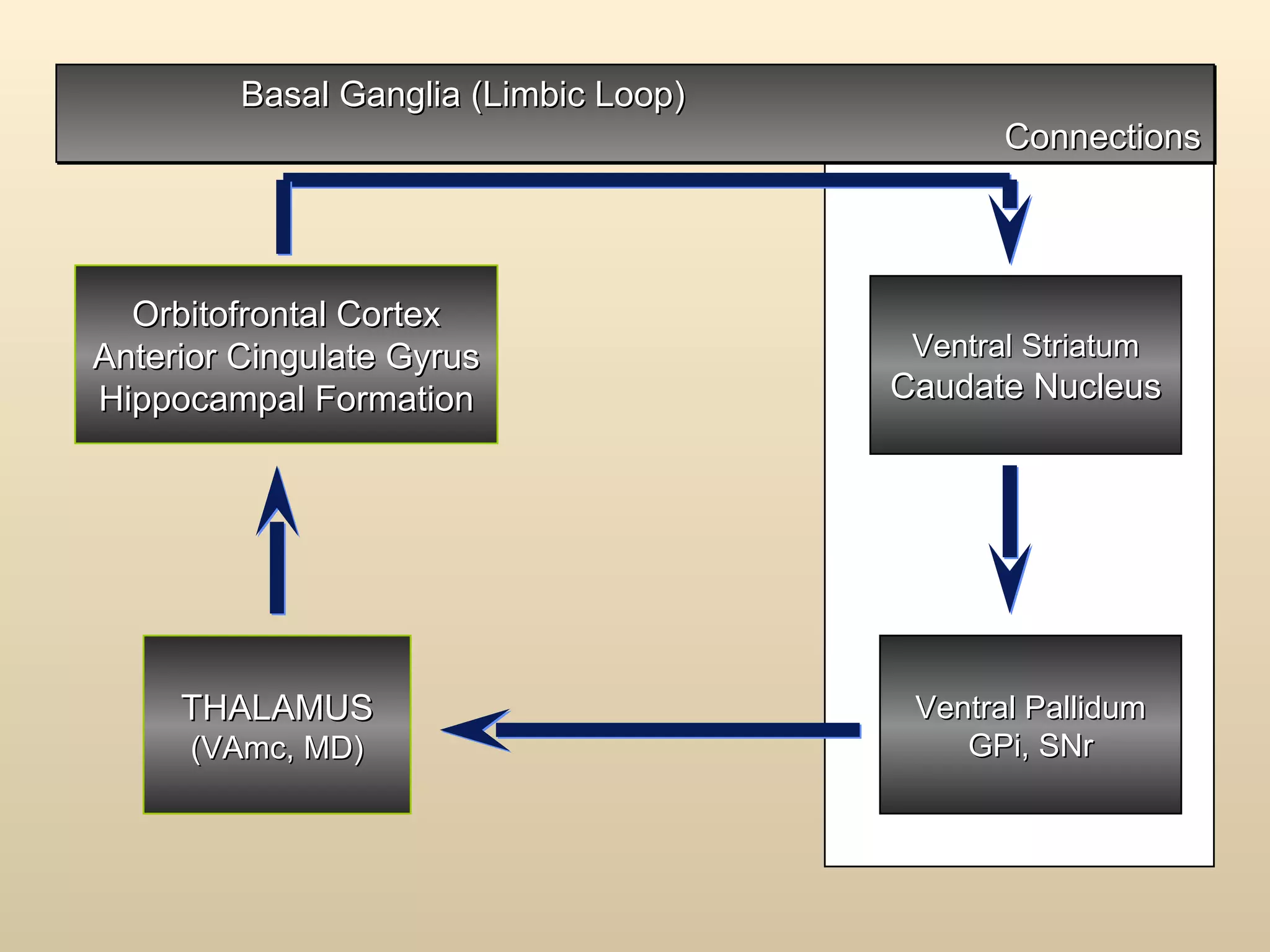
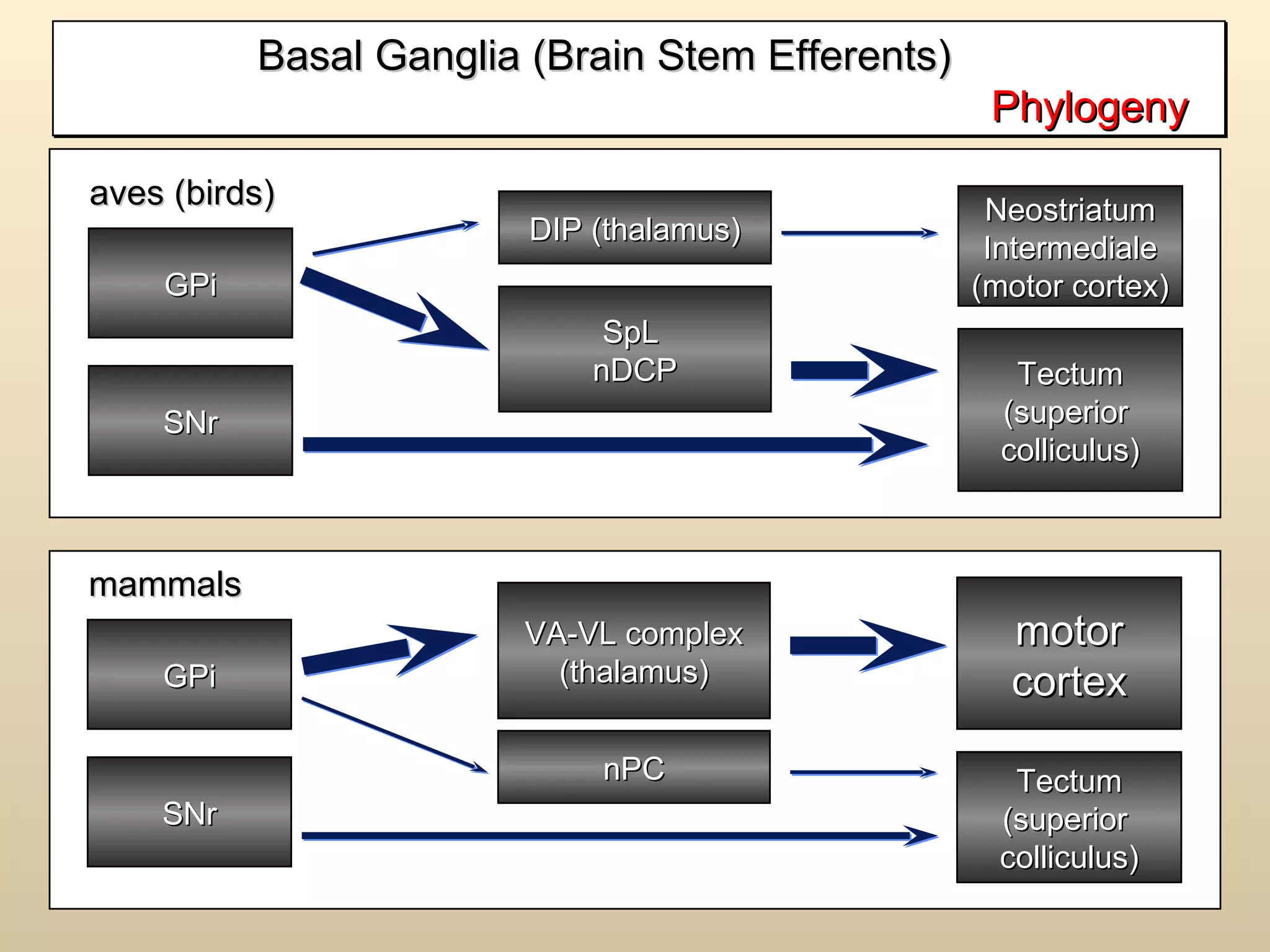
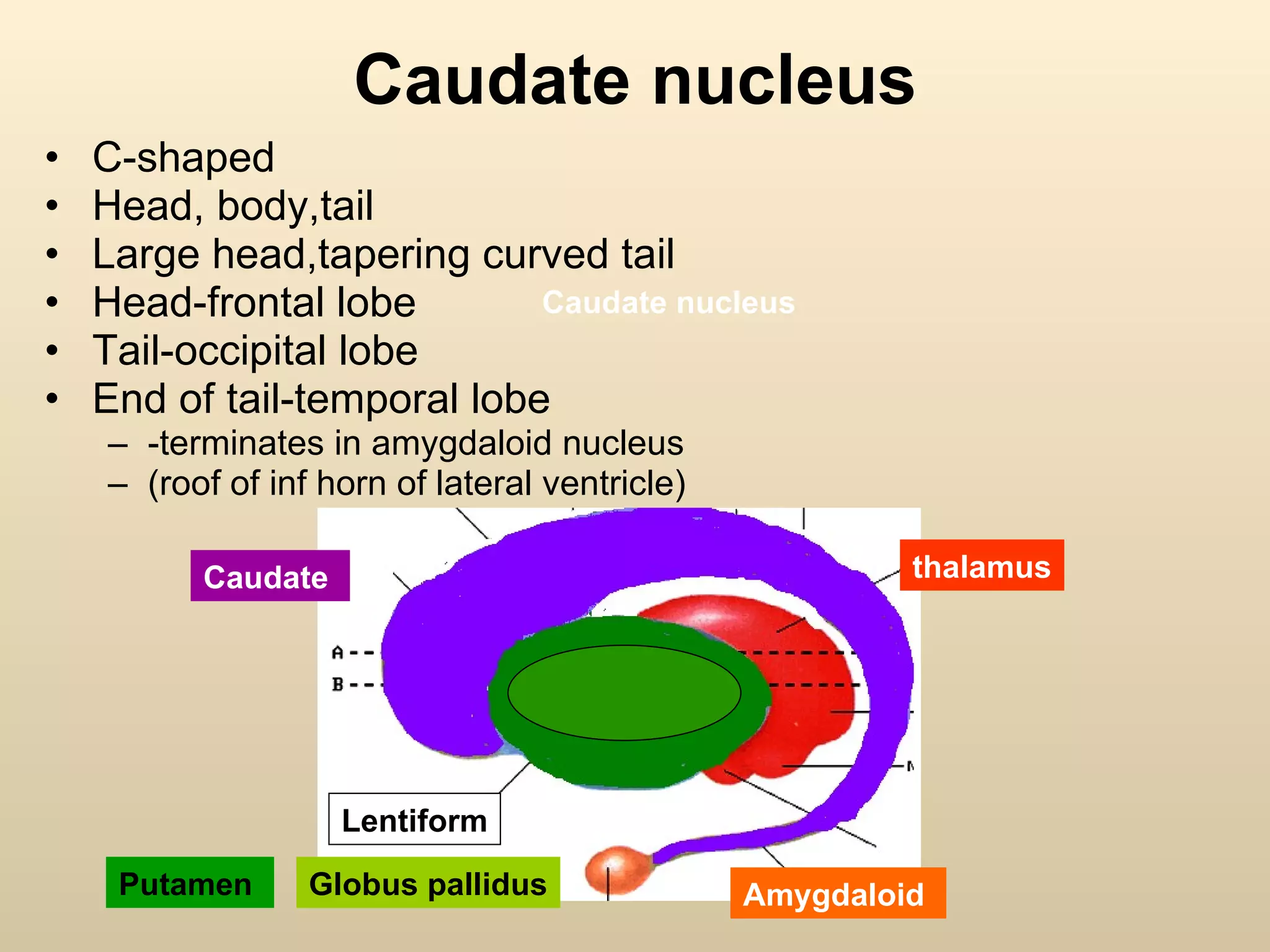
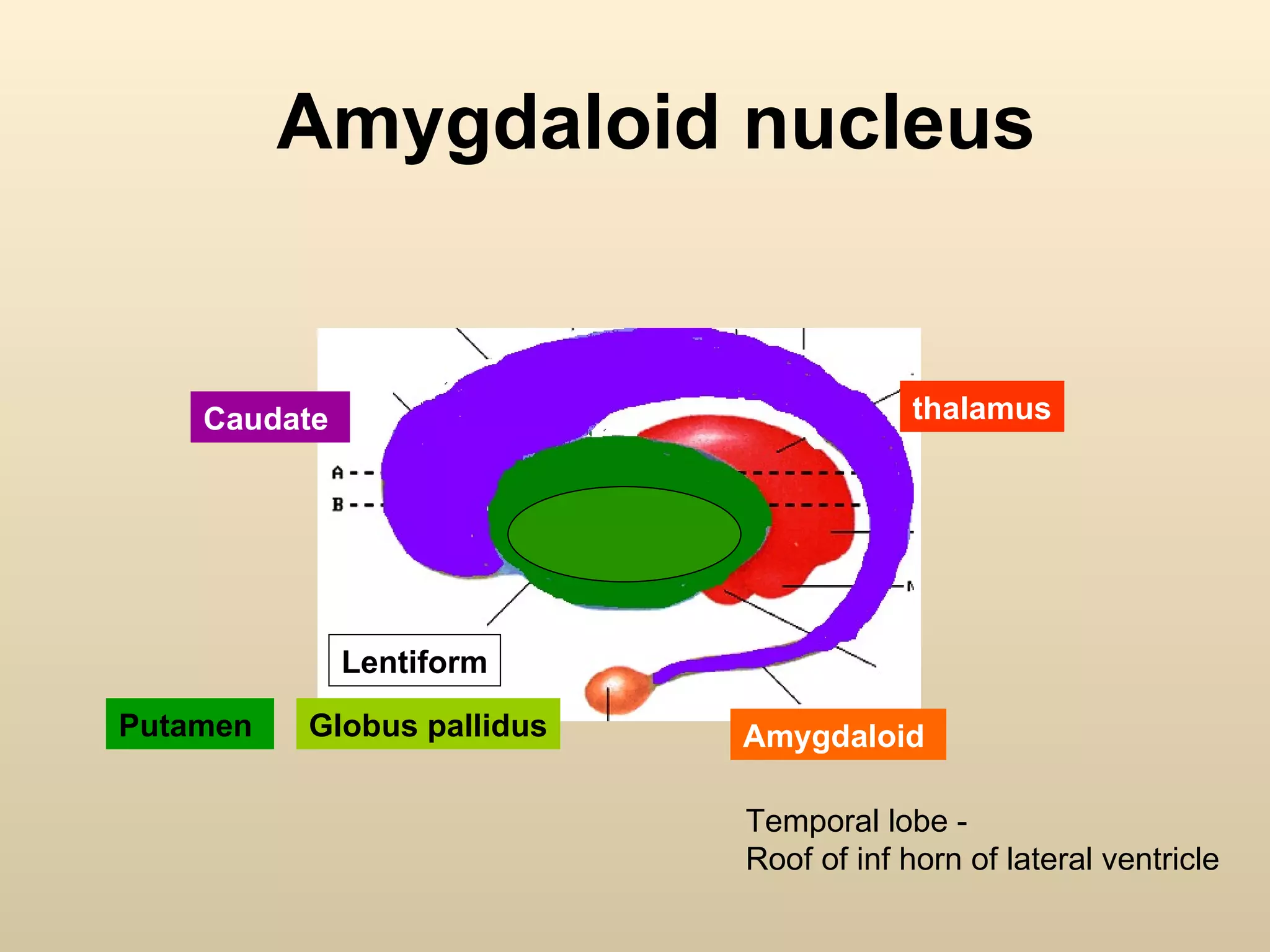
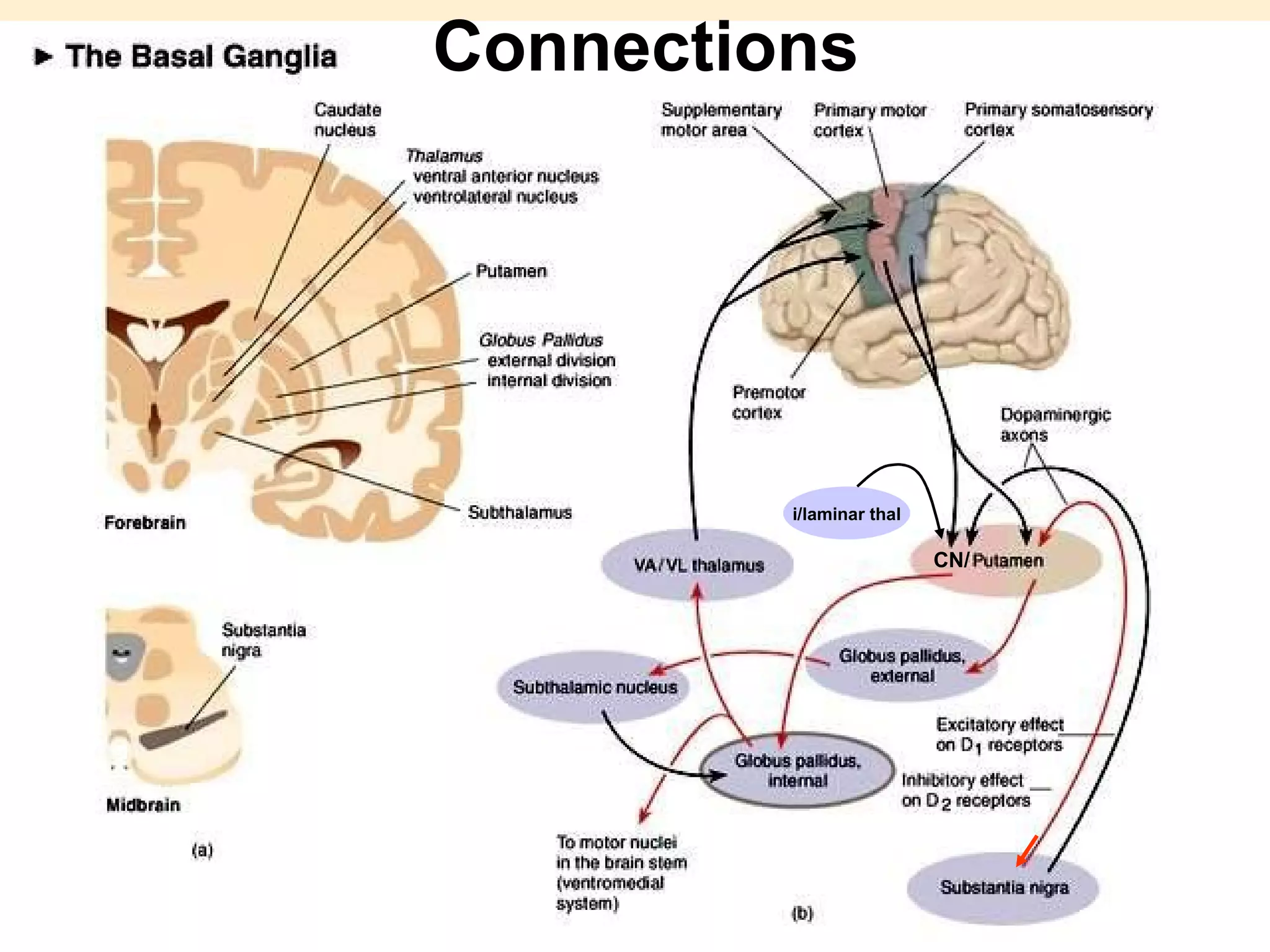
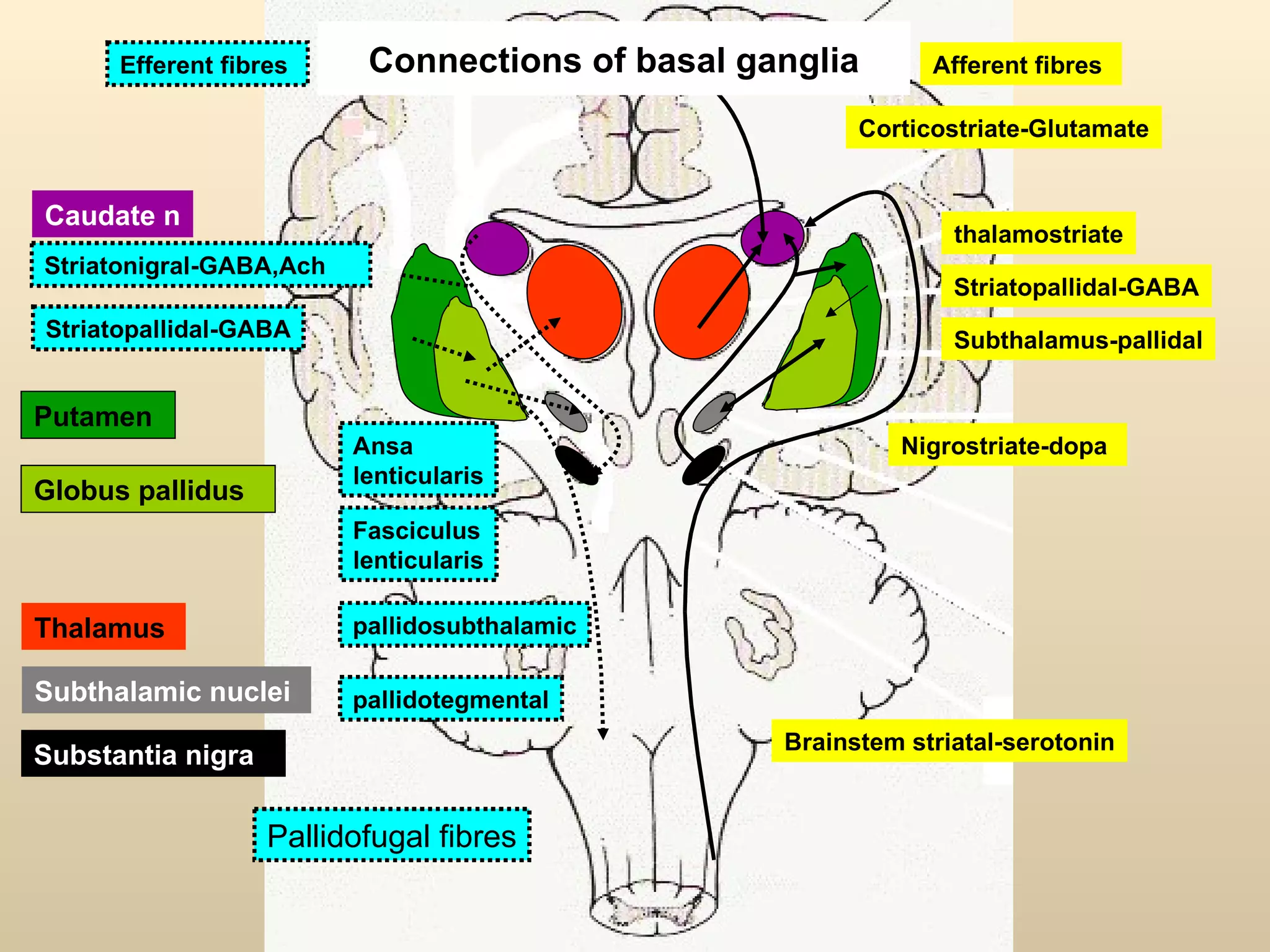
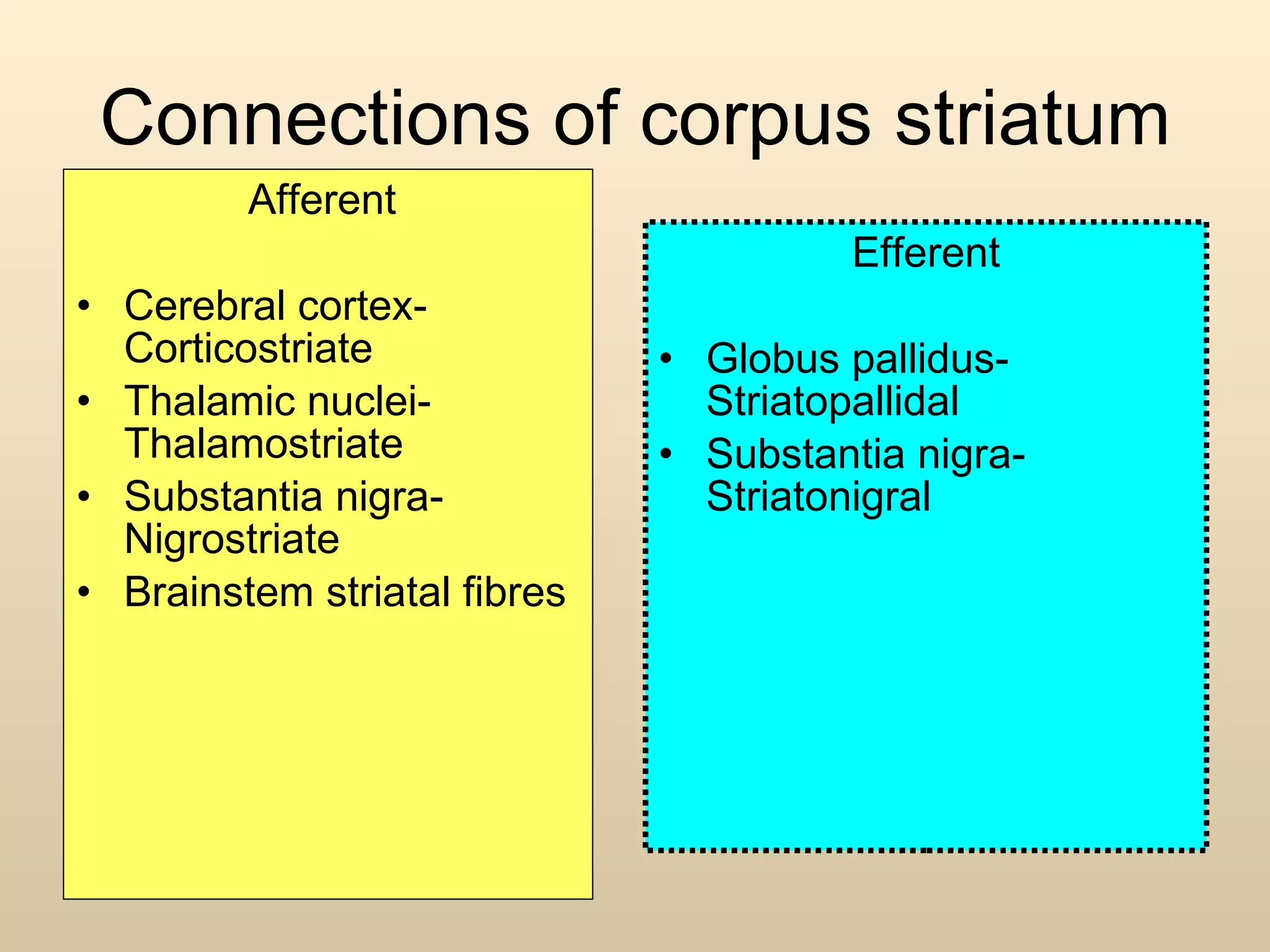
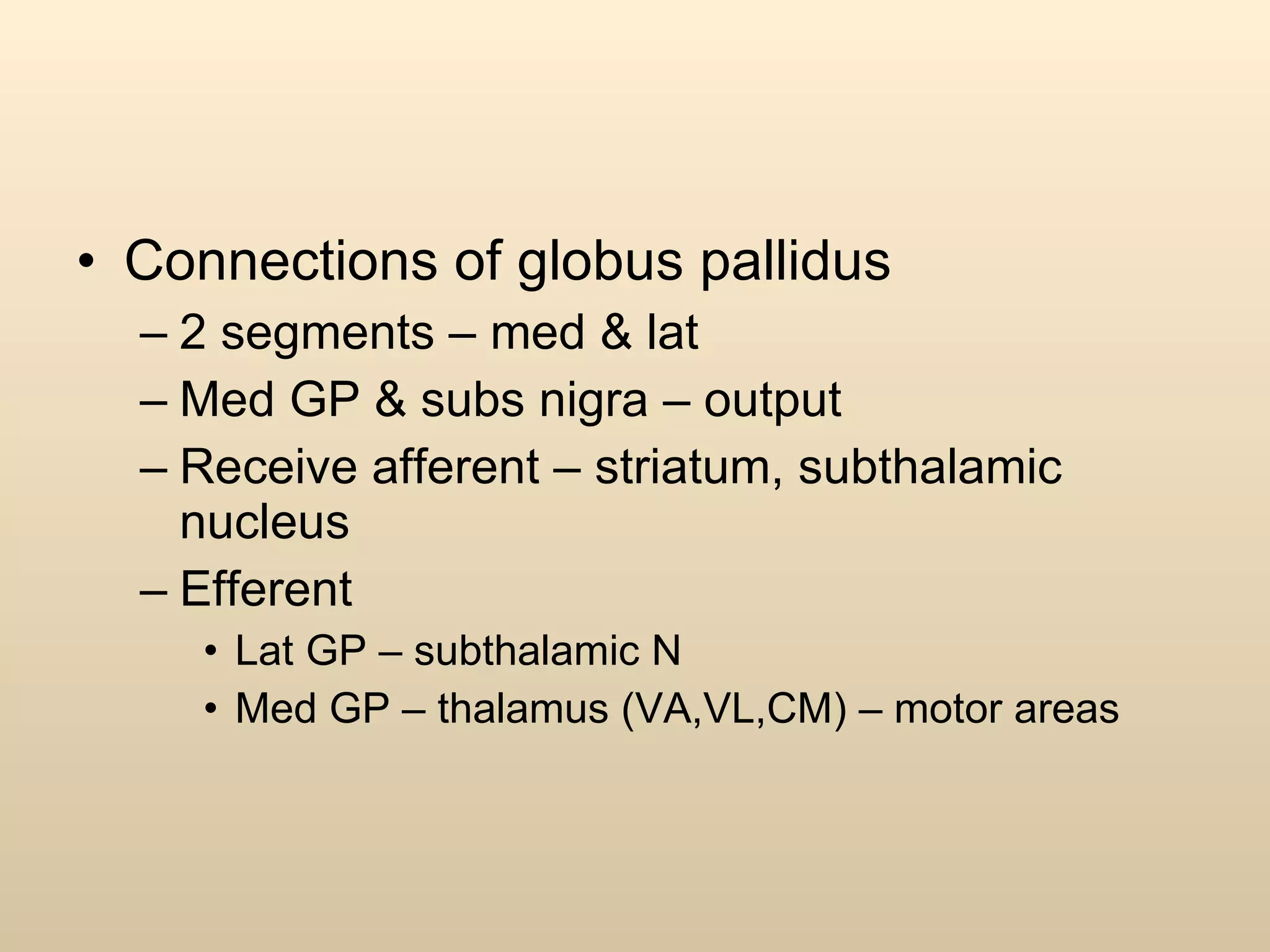
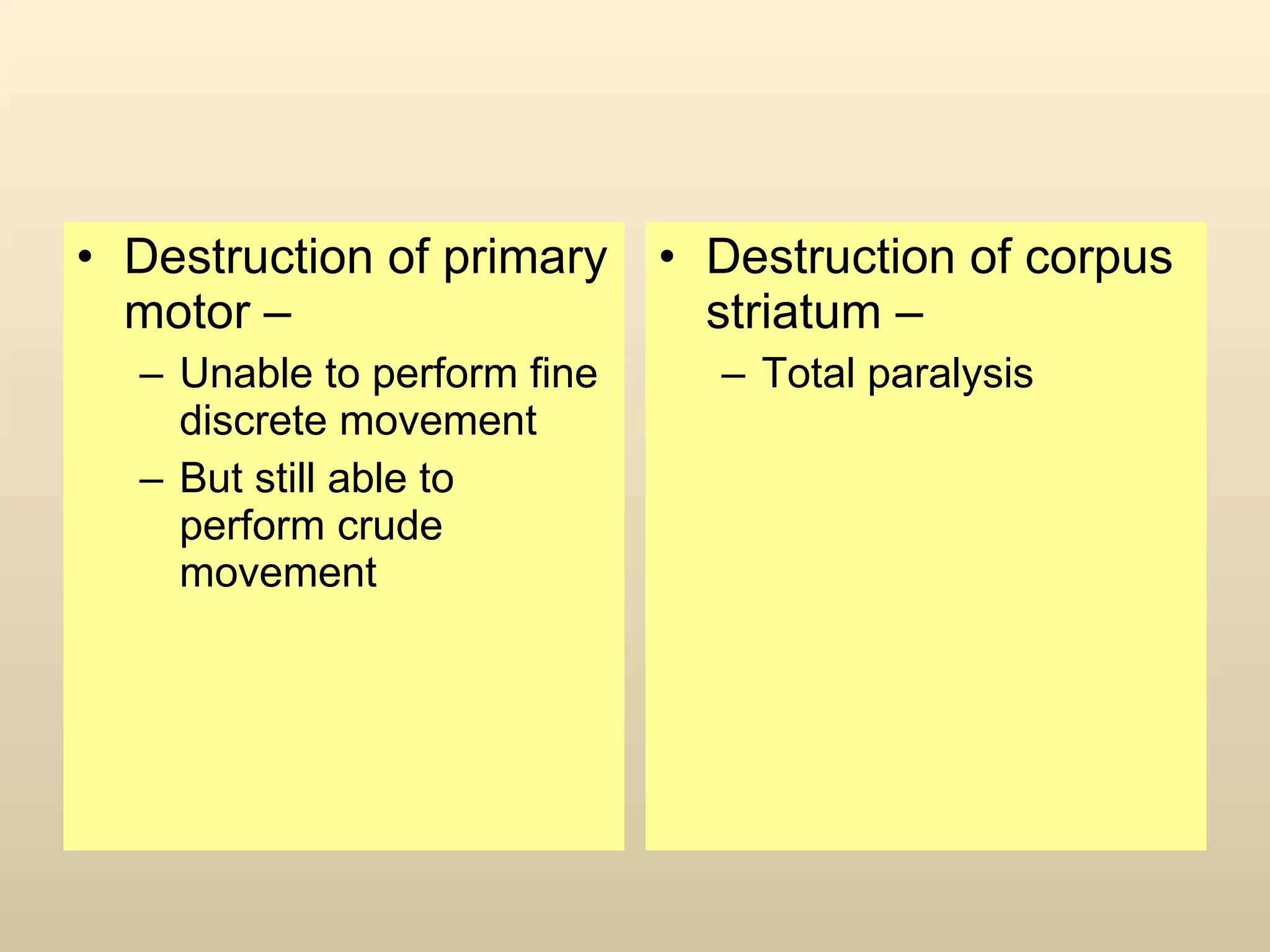
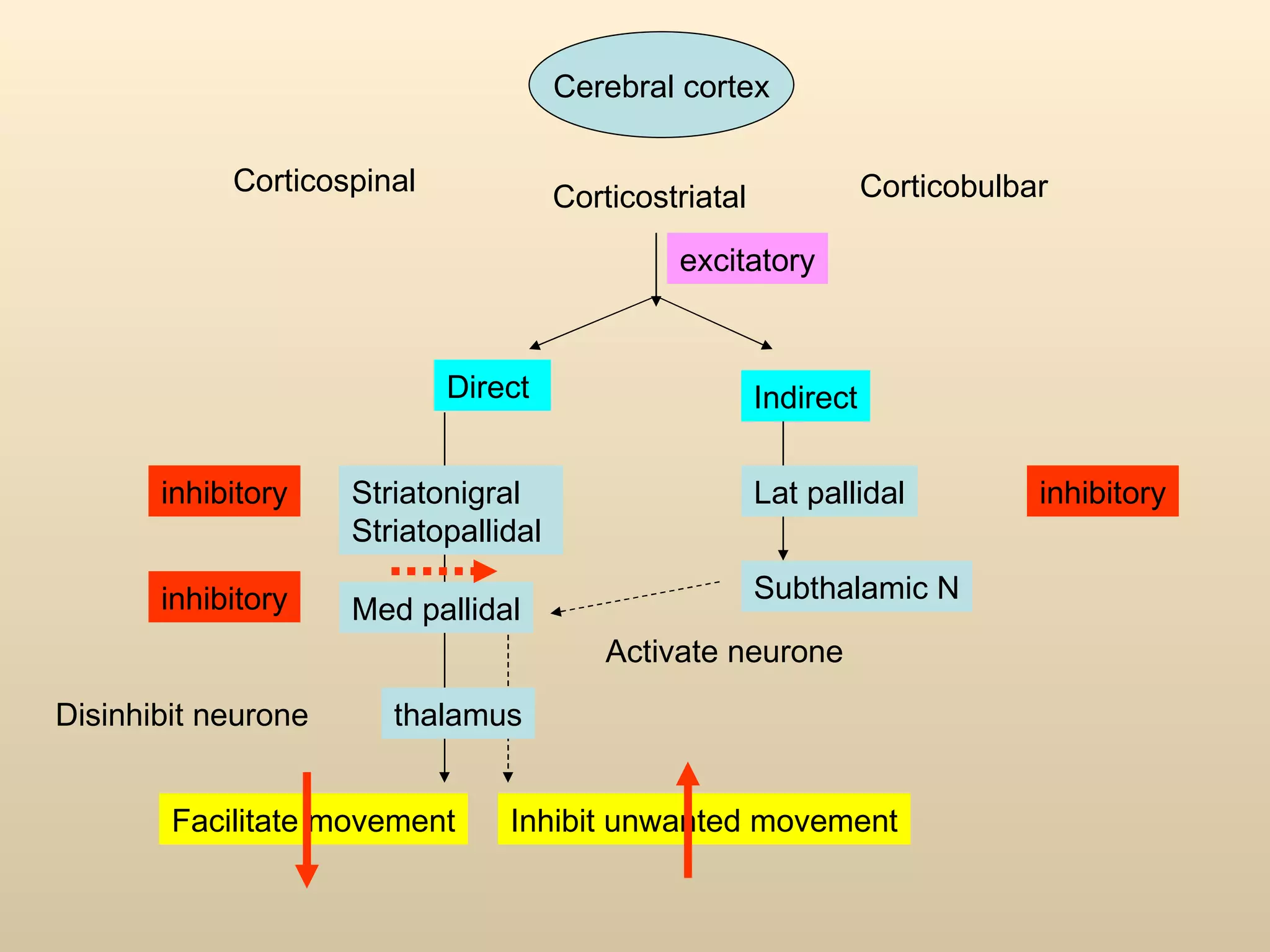
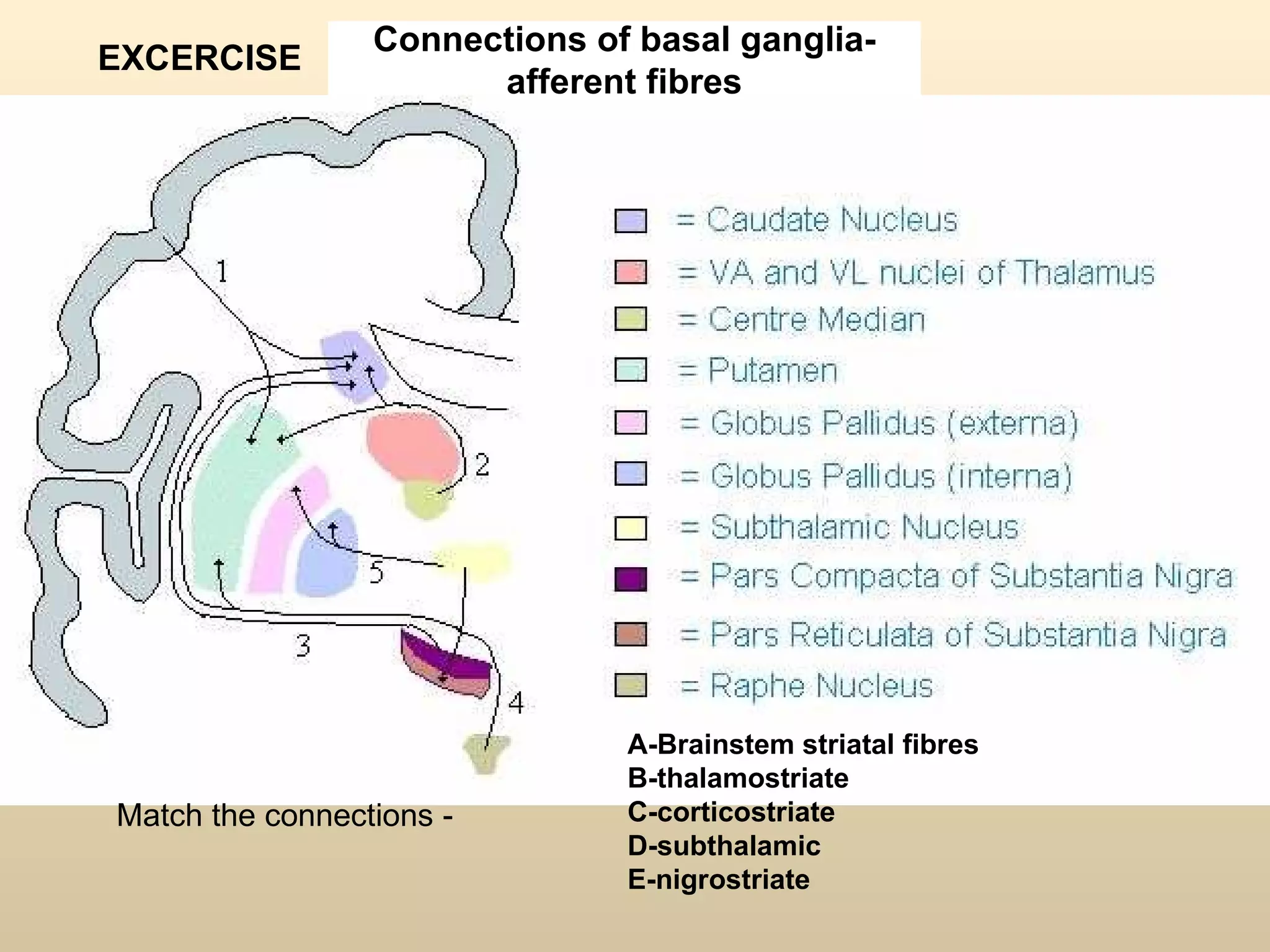
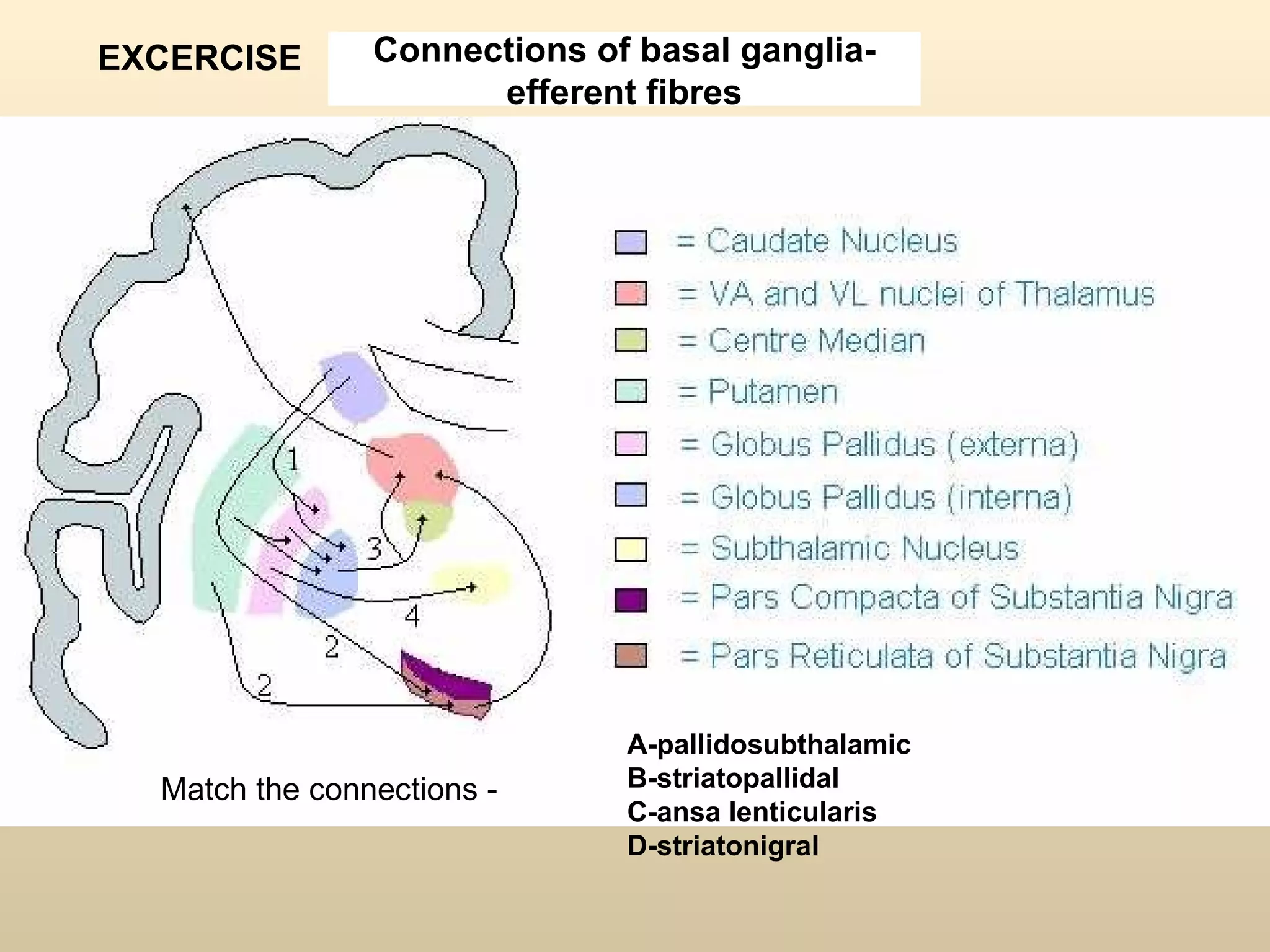
The document discusses the basal ganglia, which are a group of subcortical gray matter structures in the cerebrum that include the corpus striatum, amygdala, and claustrum. It describes the main components and connections of the basal ganglia, including the striatum, globus pallidus, substantia nigra, and subthalamic nucleus. The basal ganglia are involved in coordinating movement through connections with the cerebral cortex, thalamus, and brainstem. Disorders like Parkinson's disease can result from basal ganglia dysfunction and cause issues like tremors, rigidity, and bradykinesia.