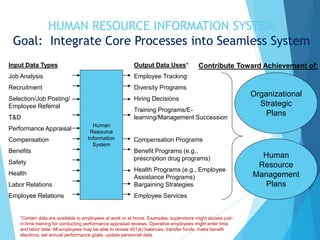
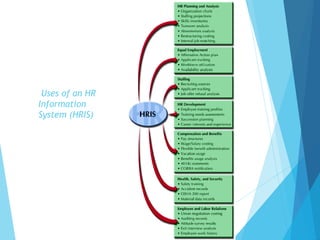
The document discusses the significance of Human Resource Information Systems (HRIS) in enhancing HR management functions by integrating data, automating processes, and improving decision-making efficiency. It highlights the benefits of HRIS, covers design and implementation issues, and outlines how HR accounting can measure and communicate the value of human resources. Additionally, it emphasizes the importance of HR audits and benchmarking in assessing HR effectiveness and ensuring organizational compliance.