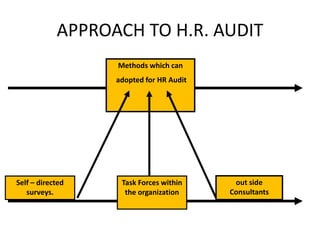
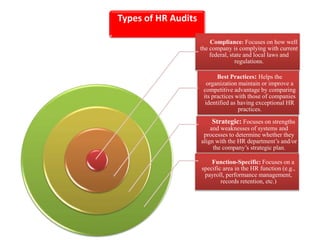
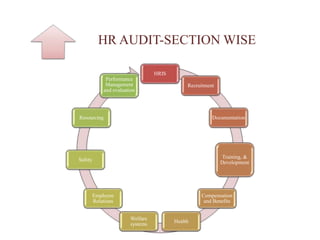
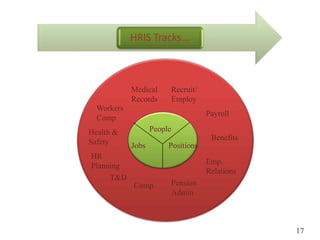
The document discusses human resource (HR) audits, which comprehensively evaluate an organization's HR strategies, systems, practices, structures, and culture to determine how well they support business goals. An HR audit assesses the effectiveness of the HR function in areas like staffing, compensation, performance management, and employee development. It identifies compliance issues, improvement opportunities, and how HR contributes to the organization. The benefits of HR audits include streamlined processes, compliance monitoring, and improved HR professionalism.