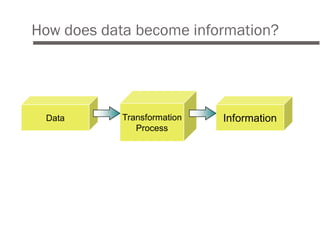
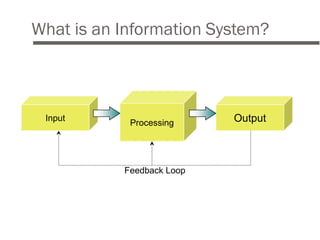
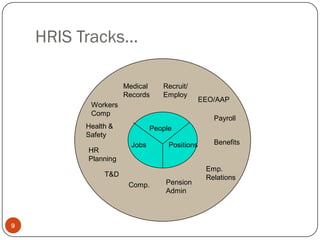
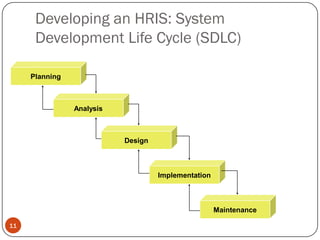
An HRIS is a system used to collect, store, and analyze an organization's human resources data. It consolidates employee information across departments into a single system to support HR decision making. Key functions of an HRIS include record keeping of employee data, payroll processing, benefits administration, and reporting. When implemented effectively, an HRIS can streamline workflows, increase efficiency, reduce costs, and provide strategic value by better managing an organization's most important asset - its people. However, HRIS initiatives can fail if goals are unclear, the wrong system is selected, or there is lack of buy-in or compatibility with other systems.













![Saving time [efficiency]
Easy data maintenance
Administrative processes automated
Employee „self-service‟
Adequate information base that leads to timely and just
decision making
Responding faster to employee inquiries to enhance
efficiency and productivity
18](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hris-090910132026-phpapp02/85/Hris-18-320.jpg)




