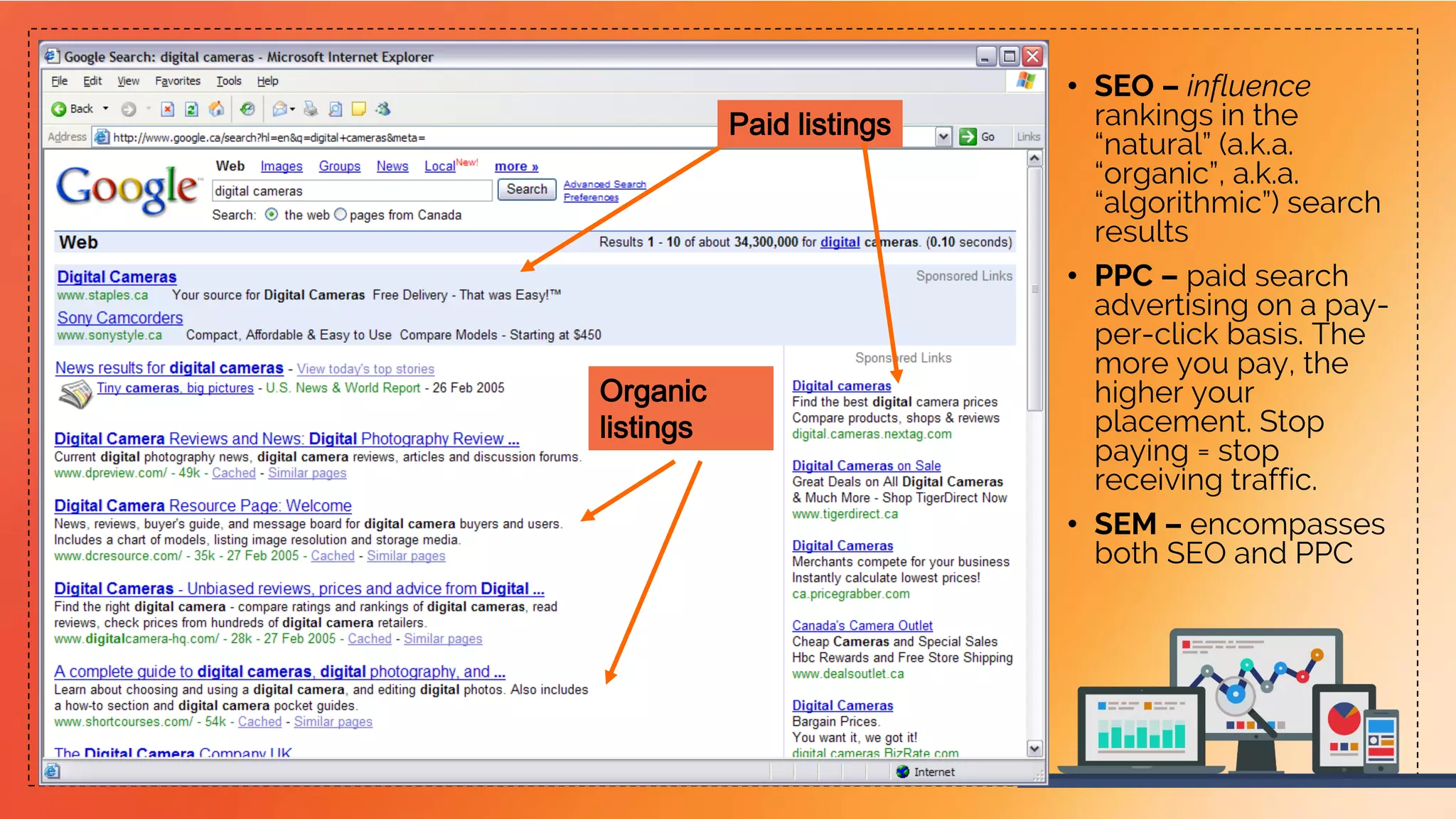
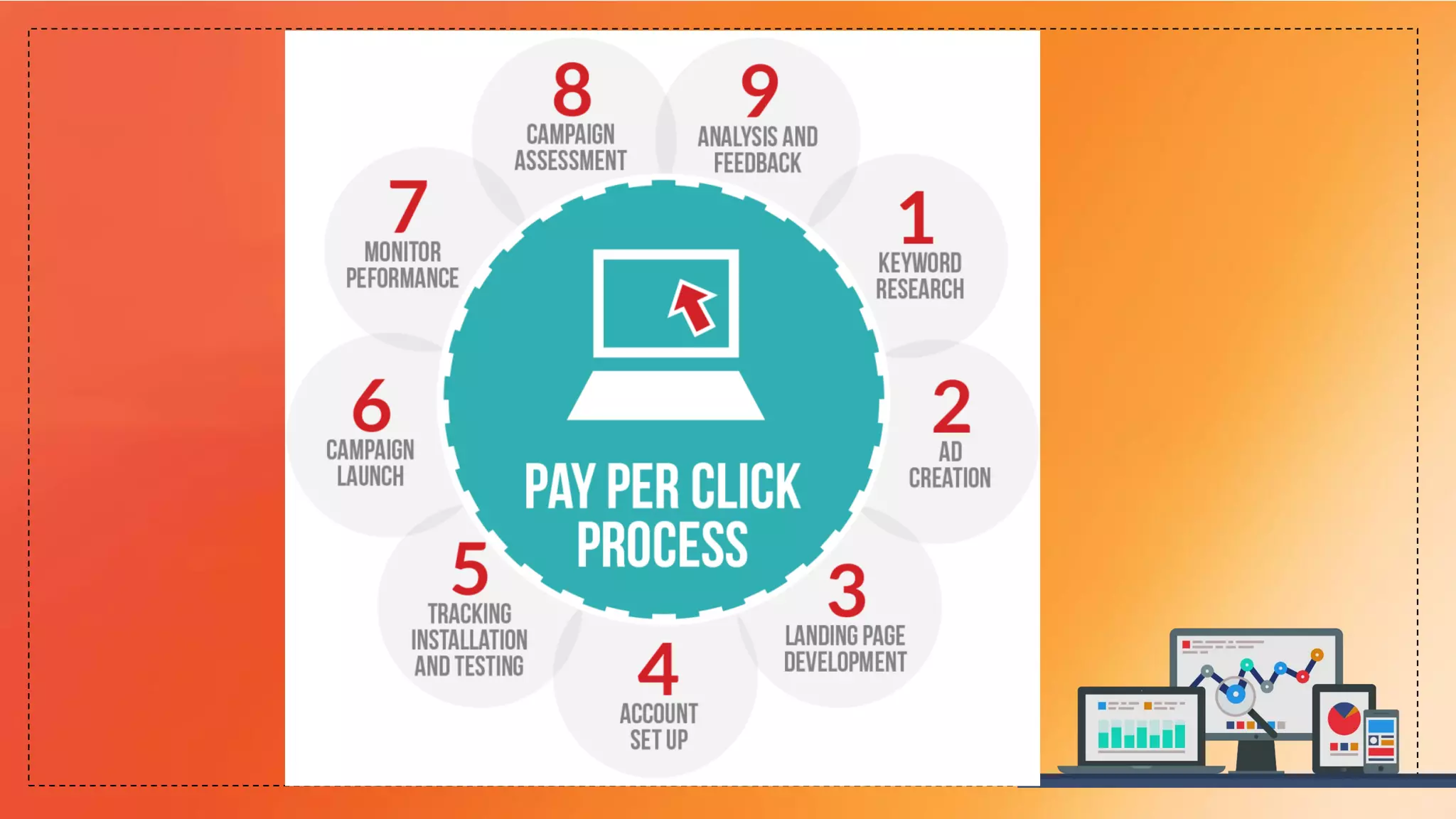
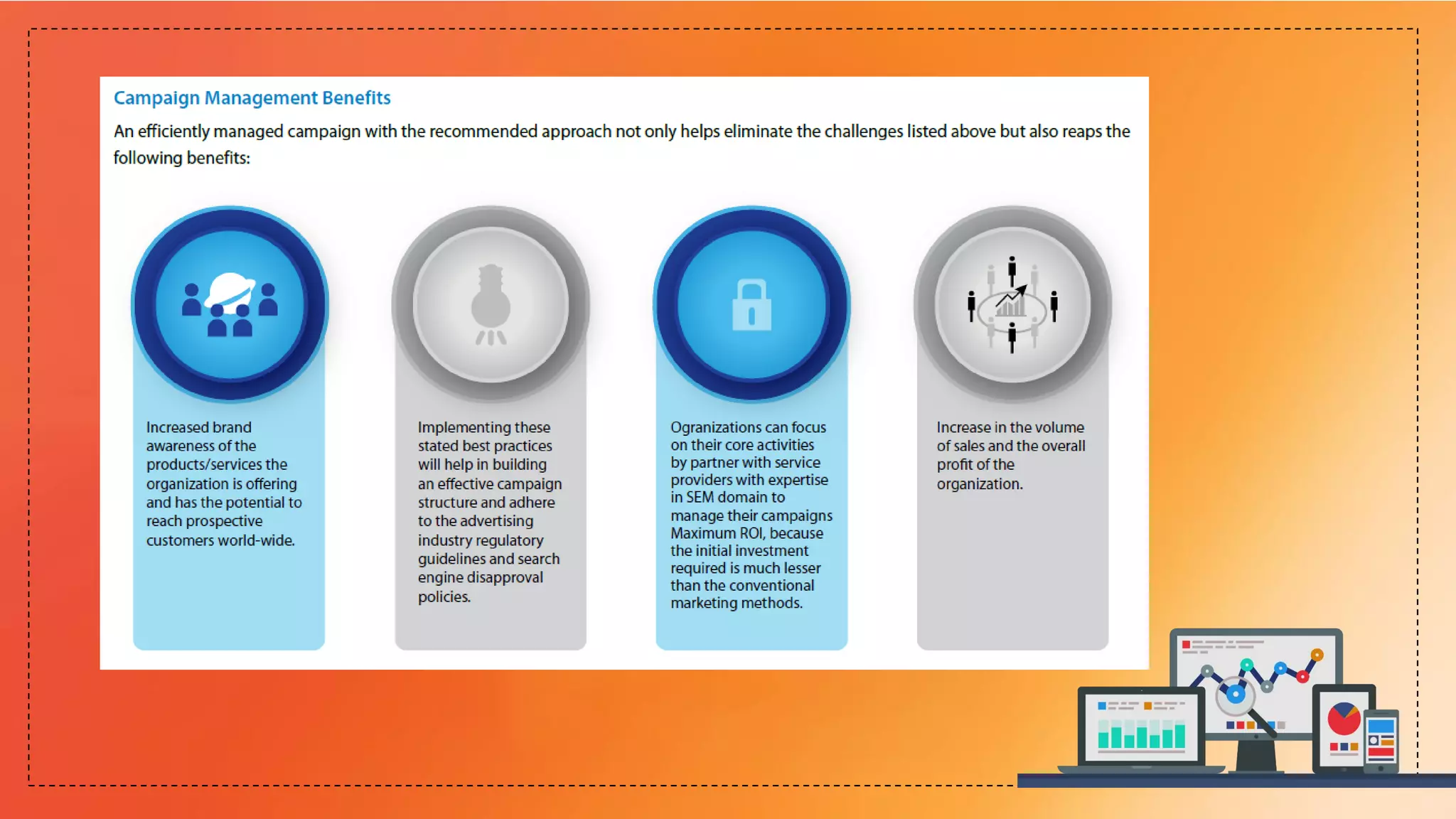
This document provides an overview of search engines, including their functions, components, and marketing implications. It highlights the importance of search engine optimization (SEO) and search engine marketing (SEM) for driving online traffic and sales, detailing techniques for improving rankings and visibility. Additionally, it addresses ethical considerations in SEO practices and the role of web analytics in measuring campaign effectiveness.