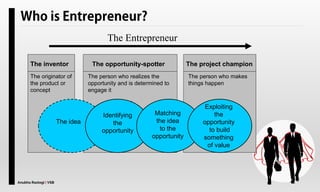
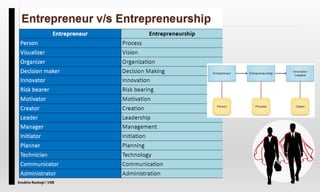
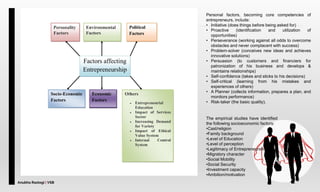
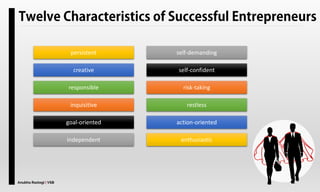
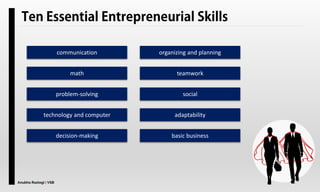
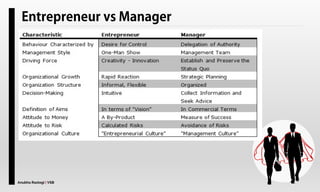
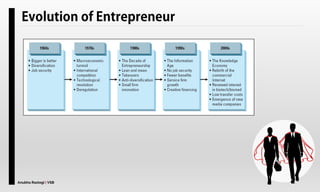
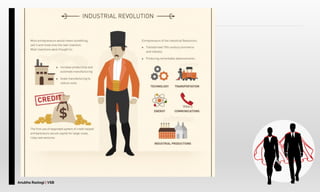
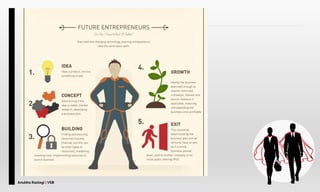
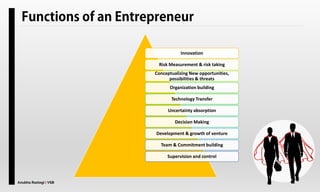
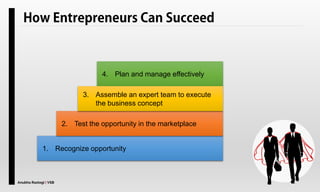
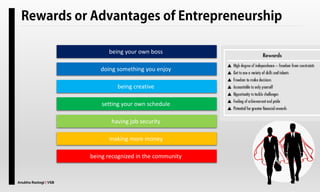
The document explores the concept of entrepreneurship, highlighting its definition, the process of opportunity identification, and the role of entrepreneurs in creating value and wealth. It also addresses common myths about entrepreneurship, outlines the personal and socioeconomic factors that contribute to entrepreneurial success, and categorizes different types of entrepreneurs based on various criteria. Additionally, it discusses the benefits and risks associated with being an entrepreneur.