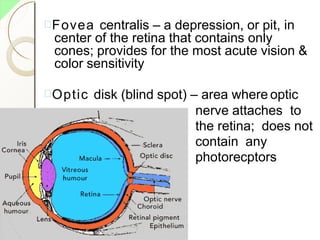
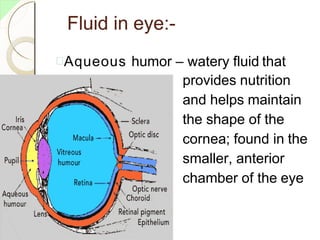
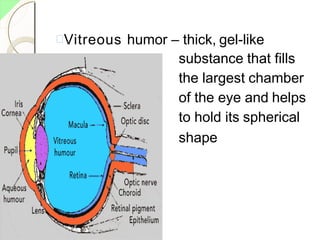
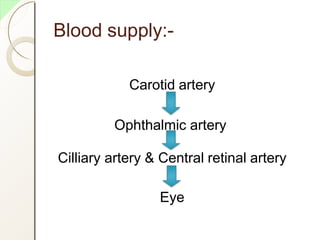
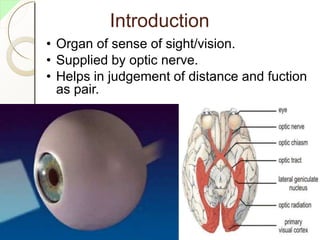
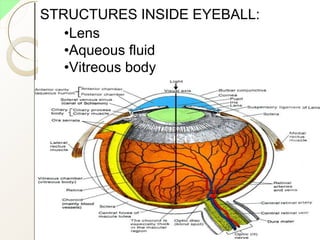
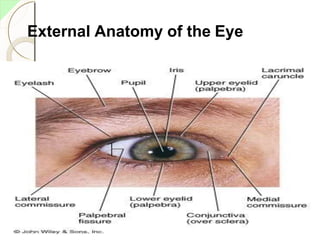
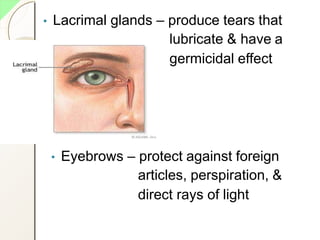
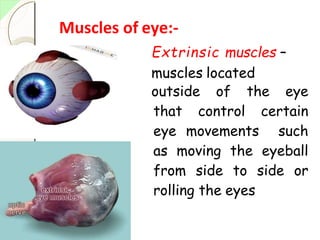
The eye has three layers - an outer fibrous layer, middle vascular layer, and inner nervous tissue layer. It contains structures like the lens, aqueous and vitreous fluids, iris, pupil, retina with rods and cones, optic nerve, and extraocular muscles. The retina contains light-sensitive photoreceptors that convert light into nerve impulses which travel via the optic nerve to the brain where vision is perceived. Accessory structures like the eyelids, eyelashes, lacrimal glands, and conjunctiva help protect and lubricate the eye.

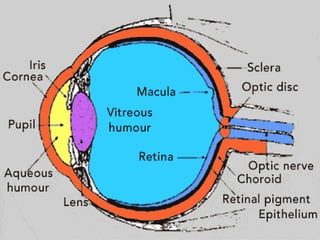
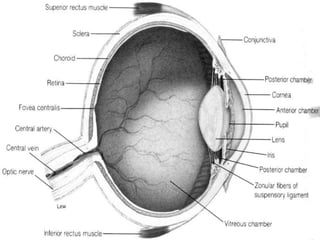
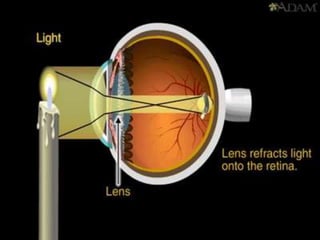
![•I t is spherical inshape
•I t is about 2.5 cm indiameter
•situated in the orbital cavity
•STRUCTURE OF THE EYE: MAIN 3 LAYERS
1. Outer fibrous layer [sclera, cornea]
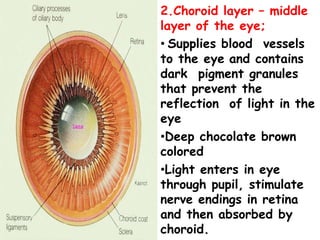
2. Middle vascular layer [choroid, ciliary
body, irish]
3. Inner nervous tissue layer [retina]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/eyeanatomybypari-200211101306/85/Eye-Anatomy-Physiology-5-320.jpg)


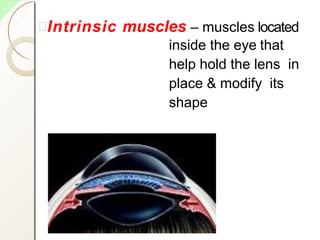



![• IRISH SUPPLY:
sympathetic and parasympathetic nerve
parasympathetic Stimulates constriction
of pupil and Sympathetic nerve cause
dilatation of pupil.
Irish and its pigmented cells decide the
colour of eye. [blue eye:few pigmentcell]
PUPIL – rounded opening of the iris
through which light passes
LENS – High elastic circular biconvex
body.
Lying on behind the pupil.
Lens bend light rays reflected by
objects in front of eye.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/eyeanatomybypari-200211101306/85/Eye-Anatomy-Physiology-17-320.jpg)