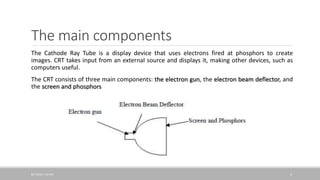
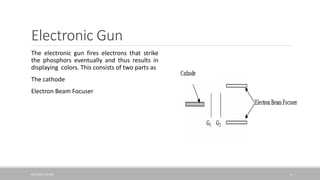
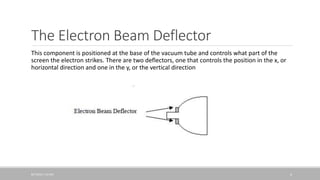
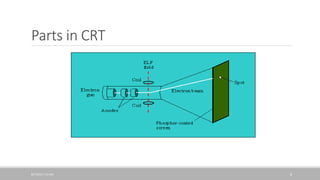
The document discusses how a cathode ray tube (CRT) works. A CRT contains three main components: an electron gun that fires electrons, an electron beam deflector that controls where the electron beam strikes the screen, and a screen coated with phosphors. When electrons from the gun strike the phosphors, they cause the phosphors to glow, creating pixels that form an image. The document explains each component in detail and how they work together to display an image on the CRT screen.