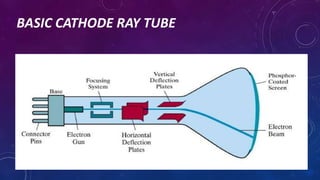
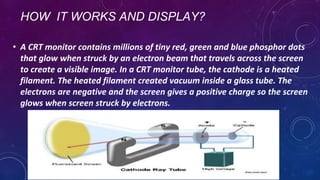
The document discusses the cathode ray tube (CRT) technology used in early computer monitors and televisions. It describes how a CRT works by using an electron gun to shoot a beam of electrons that excite phosphors on the screen, producing an image. The document outlines the history of the CRT from its discovery in the 1860s to its use in early TVs and monitors. It also discusses the advantages of CRTs like good color accuracy but notes disadvantages like health risks from radiation and large size.