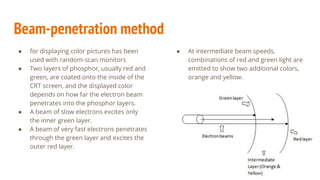
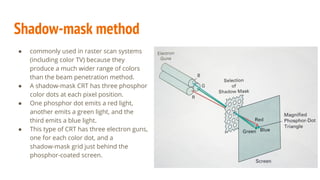
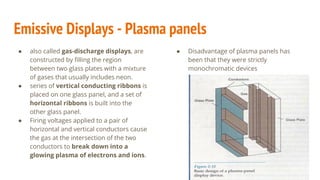
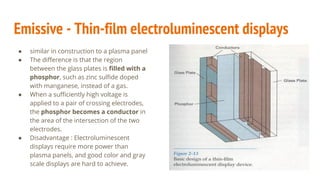
The document compares color CRT monitors and flat-panel displays, detailing how CRTs produce color through techniques like beam-penetration and shadow-mask methods, using phosphors and electron beams. It also discusses flat-panel displays, dividing them into emissive (such as plasma panels and LEDs) and non-emissive (like LCDs) types, highlighting their construction and operation. Overall, flat-panel displays offer advantages such as reduced volume and power requirements compared to CRTs.